-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 15
Module Commands
Functionatiy of Wiregost is mostly expressed and used through modules, that are very much like Metasploit modules.
They are of different categories (payload, post, auxiliary).
To use a module (here a payload):

You can then list the information and options of the module:
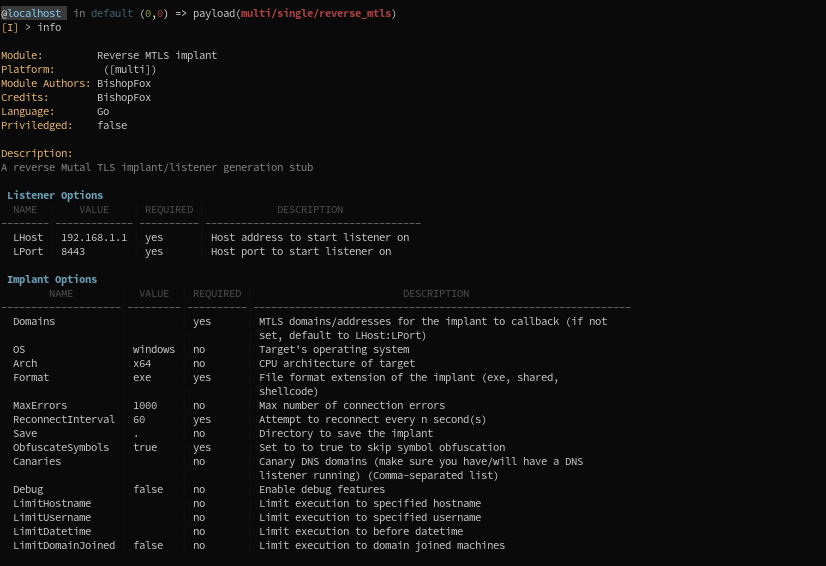
You can also simply type options to just show options.
In the present case, the module used is a payload module: to have more complete documentation, go check Payload Modules. Options, in this case are separated in two categories: Listener and Implant.
We set here the Listener host:
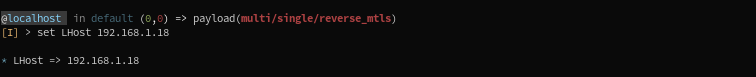
And we set here the Domain (host:port, or host:url) for the MTLS implant. It will callback to this address when spawned on the target.

Each time an option is set, its current value is both:
- Changed in the module object that is kept by the client
- Sent to the C2 Server, that will change its own version of the module object.
In addition to all main shell commands (all the ones evoqued in the previous pages), module-specific commands are available.
Some are common to all module types, like run and set. The run command will always start the main functionality of the module.
For payload modules, for instance, it will compile the implant payload, while for post modules it will run the module on the implant's
target.
Some will vary depending on the module type:
- For payload module:
-
to_listener: (equivalent ofto_handlerin Metasploit) will spawn a listener -
to_profile: Generate an implant profile based on current implant options -
parse_profile: Parse a profile in the current module
-

All options for a module are completed. However, there are several things to note:
- Because some payload modules have multiple protocols, options need to have a different name, so that completed options
may slightly differ from their displayed names. Don't panic, however, because they are always sorted in the same order than their
display order. So, in the example above, the
DomainsMTLSis displayed as Domains, and its completion index is [2], which is the same than the display index. - A more thorough illustration of this can be found at Multi-Protocol Payloads.