-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 55
Main concepts
GeoFence is a webapp that provides an authorization engine to GeoServer.
Authorizations are expressed as a priority-based rule set, in a similar way as iptables does.
Rules can be matched against user, user group, GeoServer instance, caller's IP address, name of OGC service, name of OGC request, workspace and layername.
When a request is made to GeoServer, GeoServer sends an authorization query to GeoFence, which will reply if the requesting user can (or can't) get access to the resource, and optionally which constraints are to be applied on the resource before it is made available to the user. Examples of constraints may be an allowed polygon for a given user which will crop all of its WMS getMap requests, or hiding a certain attribute from all the features from a given layer.
In GeoFence you can create entries for these kinds of objects:
- user
- A user that can make requests to GeoServer. Note that GeoServer users are not also GeoFence users (i.e. users that can log into GeoFence GUI).
- group
- A regroupment of users. GeoServer has no concept of this kind of group. It is only used at GeoFence level to express authorization rules for a group of users at once.
- instance
- A GeoServer instance. The instance name specified here shall match the name with which a GeoServer identifies itself when asking for an authorization check. You need to define the URL and the login credentials for the GeoServer instance in order for GeoFence to be able to ask the server some information (such as the list of workspaces, the list of layers, the attributes in a layer,...) when compiling the rules.
Note that there is no explicit concept of user role here. We'll deal with only one kind of role here, apart from the normal USER role, and that's the ADMIN. An ADMIN in GeoServer has access to everything; this means that, once authenticated as ADMIN, no further authorization requests will be made by GeoServer toward GeoFence. When editing users in the GeoFence GUI, an "is admin" checkbox will make the related user a GeoServer administrator.
A rule is defined by a priority value, a filter, an action, and optional constraints.
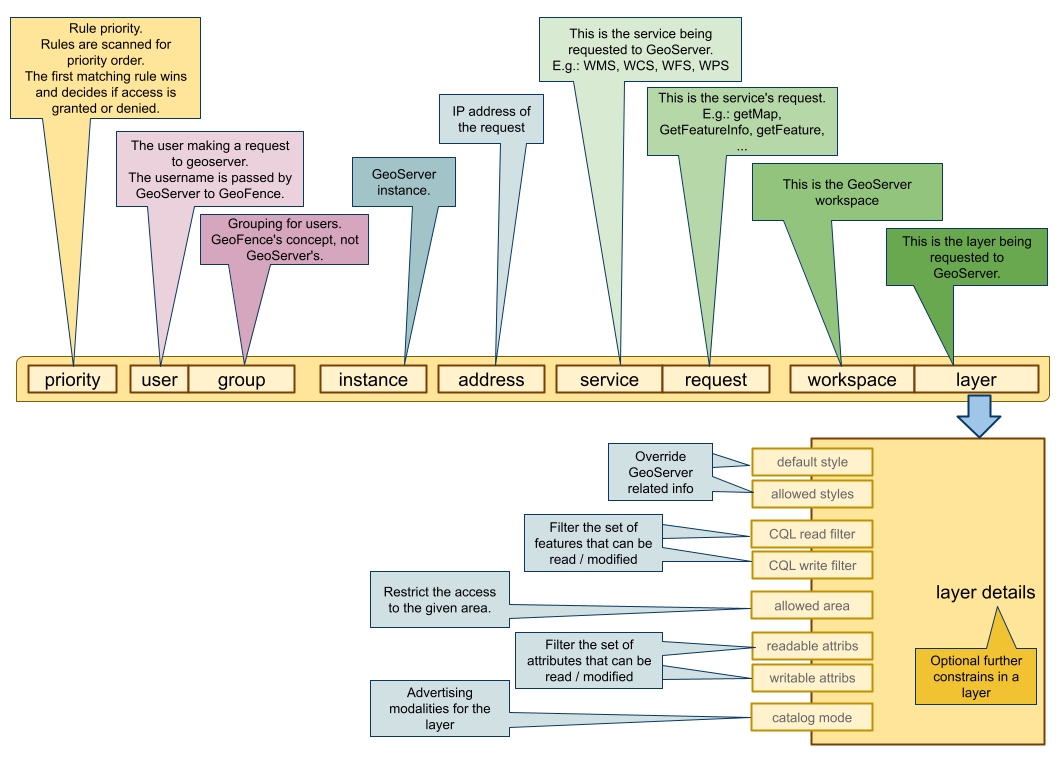
- priority
- The priority is a positive integer number. When the filter selects the matching rules, the resulting rule list is sorted by priority. The lower the priority number, the highest the priority. Usually the first matching rule is the one that "wins" and determines the final result.
When GeoServer asks for an authorization, a filter is passed within the request. The filter specifies who made the request, and what is the object of the request. Such filter will be matched against the rule fields.
Please note that any one of these fields may be not defined in a rule. In that case, the rule will match any value in the request. E.g.: a GeoServer filter with user "Tizio" will match any rule with "Tizio" set as user, and any rule with no user set (usually shown as a "*" in the GUI, meaning that any user will match that rule)
- user
- The requesting user. In the GUI, you will choose a given user from a dropdown menu.
- group
- The group the requesting user belongs to. In the GUI, you will choose a given group from a dropdown menu.
- instance
- The GeoServer instance the authorization request come from. In the GUI, you will choose a given instance from a dropdown menu.
- address
- The IP address a request is coming from. In the rule the administrator can specify an IPv4 address range in a CIDR notation (e.g. "10.10.0.0/16"). A rule will match only if the range in the rule includes the address in the filter.
- service
- The OGC service for which the authorization request is queried. From a dropdown menu you can select one from the most common ones, otherwise you can type in any other string for customized services.
- request
- The OGC request for which the authorization request is queried. From a dropdown menu you can select one from the most common ones, otherwise you can type in any other string for customized services.
- workspace
- The workspace of the requested resource. The related GeoServer instance will be queried via its REST interface to find out the list of available workspaces; The resulting workspace list will be shown in a dropdown menu.
- layer
- The requested layer. The related GeoServer instance will be queried via its REST interface to find out the list of available layers; The resulting layer list will be shown in a dropdown menu.
The Action specifies the outcome of the rule, if matched (by the filter) and selected (according to priority).
- ALLOW: merge all the LIMIT constraints and allow access to the resource.
- DENY: discard all the LIMIT constraints and deny access to the resource.
- LIMIT: add constraints to the final outcome. Constraints can be area constraints or access mode constraints.
Please check the rule matching page to understand how LIMIT constraints are merged.
Constraints on the resource can be added only in ALLOWing rules. There are different kinds of constraints, and one or more of them can be specified.
- allowed area
- an optional multipolygon constraints. It may be used wherever it applies: e.g.:
getMaprequests will be cropped, and only the graphical part internal to the multipolygon will be drawn.getFeatureswill only return features that are internal or that intersect with the restriction multipolygon. - attribute access
- only used in vector layers. For every attribute, the rule may assign the accessibility level: non accessible, read only, full read/write access.
- cql_filter_read, cql_filter_write
- these two constraints define CQL filters to limit the set of features that can be read or written.
- available_styles
- restrict the list of the available styles for the layer filtered in the current rule. It may be useful to remove the styles that use one or more inaccessible attributes.
- default_style
- override the default style for the layer filtered in the current rule.
- catalog mode
- sets the catalog mode for the layer defined in the selected rule. Note that the catalog mode behaviour could interact with the access mode, so you may have to set an
EXCLUDEvalue in thecql_filter_read.