-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 107
5.2. Harbor Boost
Handle:
boost
URL: http://localhost:34131/

boost is an optimising LLM proxy. It can be used to create various workflows that'll run between your LLM backend and the client. This can include, reasoning, prompt re-writing, or any other transformation that can help the downstream model to perform better.
Features that make Harbor's boost special:
- 🥇 First-class support for streaming completions
- 🗣️
boostmodules can provide intermediate output, like status messages or internal monologue - 🎭
boostcan serve as a plain LLM proxy (multiple downstream APIs behind a single endpoint) - ✍️
boostis scriptable, you can write your own modules

The main focus, of course are the workflows that can help improve the LLM output in specific scenarios. Here are some examples of what's possible with boost:
- Add R1-like reasoning to any LLM
- When "random" is mentioned in the message,
klmbrwill rewrite 35% of message characters to increase the entropy and produce more diverse completion - Launch self-reflection reasoning chain when the message ends with a question mark
- Expand the conversation context with the "inner monologue" of the model, where it can iterate over your question a few times before giving the final answer
- Apply a specific LLM personality if the message contains a specific keyword
- Add external memory to your interactions with a specific model
- Make your LLM pass a skill check before replying to you
Boost is scriptable, you can provision your own modules with the workflows suitable for your needs. See Custom Modules section for more information.
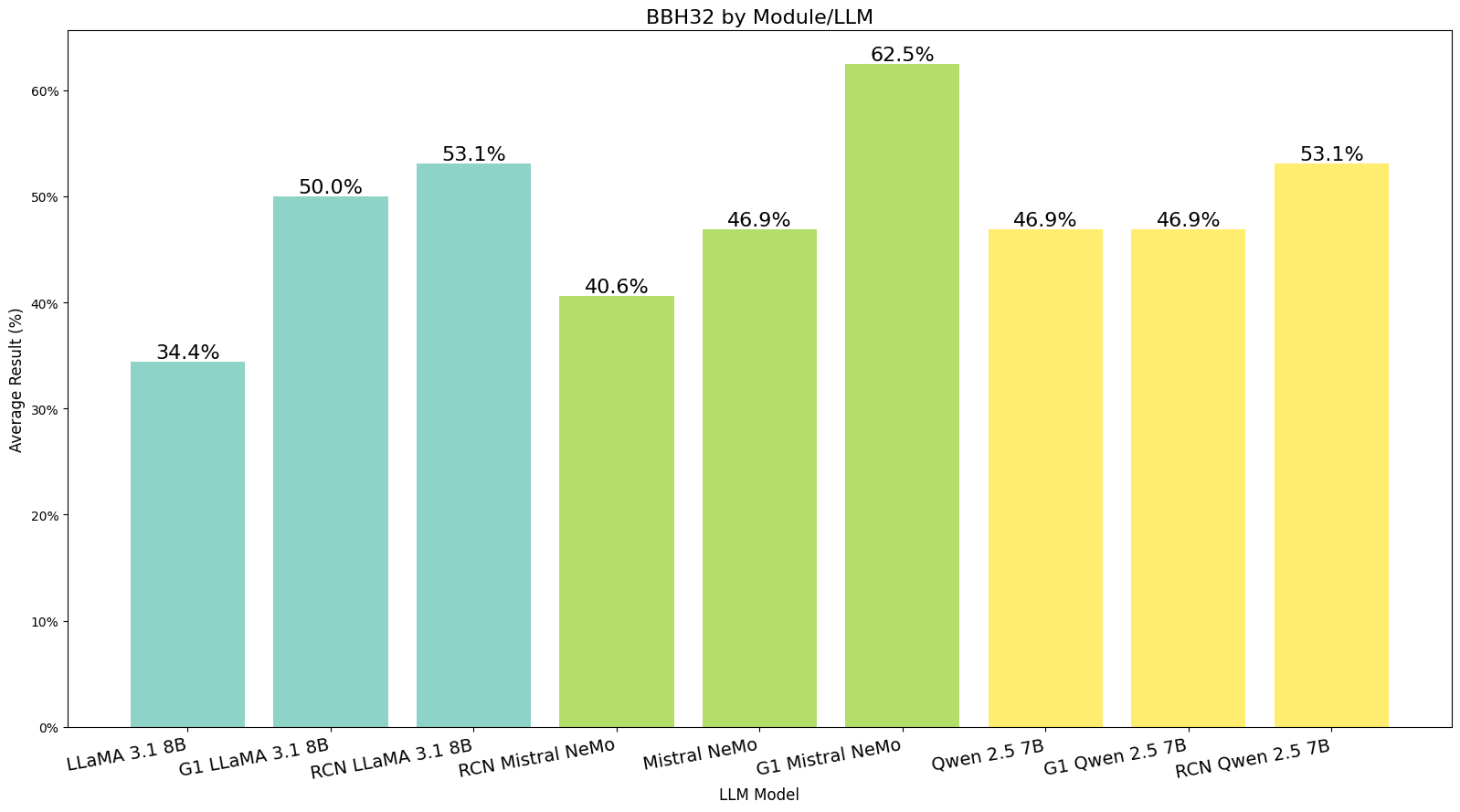
g1 and rcn optimizer modules compared to original LLMs. BBH256 task, run with Harbor Bench
boost operates at the OpenAI-compatible API level, so can be used with any LLM backend that accepts OpenAI API requests. You can also plug boost into the UIs that are compatible with OpenAI API.
Important
You don't have to use Harbor to run boost. See the Standalone Usage section for more information.
- Starting
- Standalone Usage
- Configuration
-
Modules
klmbr- boost llm creativityrcn- recursive certainty validationg1- o1-like reasoning chainsmcts- Monte Carlo Tree Searcheli5- Explain Like I'm 5supersummer- Super Summarizationr0- R1-like reasoning chainsmarkov- token completion graphdnd- skill check- Custom Modules (not configurable, mostly examples, but can still be enabled)
- discussurl - parse mentioned URLs and add them to the context
- meow - the model ignores all previous instructions and just meows
- unstable - a random personality is generated for every response, model is asked to follow it
- API
- Custom Modules
# [Optional] pre-build the image
harbor build boost
# Start the service
harbor up boostboost is automatically connected to the LLM backends integrated with Harbor. It has its own API which will serve "boosted" models.
# Get the URL for the boost service
harbor url boost
# Open default boost enpdoint in the browser
harbor open boostWhen running with Harbor's Open WebUI, "boosted" models will be available there automatically.
Configuration is done via the Harbor CLI, harbor config or the .env file. All three ways are interchangeable, you can read more about them in the User Guide.
# Enable/Disable a module
harbor boost modules add <module>
harbor boost modules rm <module>
# Set a parameter
harbor boost <module> <parameter>
harbor boost <module> <parameter> <value>
# See boost/module help entries
# for more info
harbor boost --help
harbor boost klmbr --help
harbor boost rcn --help
harbor boost g1 --helpYou can adjust certain aspects of the boost service that are shared between all the modules. This includes the API behavior and specifics of the module execution. Please find supported configuration options below.
# Adjust the port that Boost will linked to on the host
harbor config set boost.host.port 34131
# Additional OpenAI-compatible APIs to boost
harbor boost urls add http://localhost:11434/v1
harbor boost urls rm http://localhost:11434/v1
harbor boost urls rm 0 # by index
harobr boost urls ls
# Keys for the OpenAI-compatible APIs to boost. Semicolon-separated list.
# ⚠️ These are index-matched with the URLs. Even if the API doesn't require a key,
# you still need to provide a placeholder for it.
harbor boost keys add sk-ollama
harbor boost keys rm sk-ollama
harbor boost keys rm 0 # by index
harbor boost keys lsBelow are additional configuration options that do not have an alias in the Harbor CLI (so you need to use harbor config directly). For example harbor config set boost.intermediate_output true.
boost.api.key
By default, boost will accept and serve any request, but you can configure one or more API keys to restrict access to the service.
# Configure the API key
harbor config set boost.api.key sk-boost
# Send the API key in the header
# Authorization: sk-boost
# You can specify multiple keys as well
# note "keys" instead of "key", and semicolon-separated list
harbor config set boost.api.keys sk-user1;sk-user2;sk-user3boost.intermediate_output
When set to true, the boost output the intermediate steps of the module, not only the final result, providing more dynamic feedback to the user.
Intermediate output includes status messages, internal monologue, and other non-final completions. Note that it doesn't mean "all output" from the module, as the module source can still decide to not emit specific things at all, or inverse - emit them even if this setting is off.
Example of the intermediate output from the g1 module - underlying reasoning steps:

boost.status.style
A module can call llm.emit_status during its processing, which will be streamed as a "status" or "progress" message to the user. This setting controls the format of this message, which will be dependent on what's supported by the frontend where boost response is displayed.
Options:
md:codeblock "\n```boost\n{status}\n```\n",
md:h1 "\n\n# {status}\n\n",
md:h2 "\n\n## {status}\n\n",
md:h3 "\n\n### {status}\n\n",
plain "\n\n{status}\n\n",
none ""The default is md:codeblock and looks like this in the WebUI:
boost.base_models
Depending on the configuration of your setup, your LLM backend might or might not be connected to the UI directly. If not (or using boost as a standalone service), you can toggle this option on for the boost to serve them as is.
# Now "unboosted" models will also be available
# via the boost API
harbor config boost.base_models trueboost.model_filter
When specified, boost will only serve models matching the filter. The filter is a key/value expression that'll be matched against the model metadata. See examples below:
# Only boost models with the "llama" in the name
harbor config set boost.model_filter id.contains=llama
# Only boost models matching the regex
harbor config set boost.model_filter id.regex=.+q8_0$
# Boost by regex matching multiple IDs
harbor config set boost.model_filter "id.regex=.*(llama3.1:8b|llama3.2:3b|qwen2.5:7b)"
# Only boost a model with the exact ID
harbor config set boost.model_filter id=llama3.1:8bThis filter runs after the boosted models (per module) are added, so you can filter them out as well.
Modules configuration
You can configure modules using either harbor boost modules alias or by editing the HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES variable in the .env file.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add <module>
# Disable the module
harbor boost modules rm <module>
# List enabled modules
harbor boost modules lsNote that new Harbor releases might introduce new modules, so the default value of this setting could change in the future. Check out Harbor Profiles for a way to save and restore your configuration.
Host Port
You can adjust the port that boost will be linked to on the host. The default is 34131.
# Set the port
harbor config set boost.host.port 8042
# Restart for changes to take effect
harbor restart boostboost is built from modules implementing specific optimisation workflows. Those aren't limited to the reasoning or prompt re-writing, but can include any transformation that can help the downstream model to perform better.
Modules can be enabled/disabled and configured via the Harbor CLI or the .env file manually. You'll need
to restart the boost service for the changes to take effect.
# Enable/Disable a module
harbor boost modules add <module>
harbor boost modules rm <module>Tip
You can use Harbor profiles to quickly rollback to the default configuration.
# Save current changes, if needed
harbor profile save <name>
# Rollback to the default configuration
harbor profile use defaultRCN is an original technique based on two principles: context expansion and self-validation. It works by first expanding the context of the input by asking the model to explain the meaning of the every word in the prompt. Then, a completion is generated, then model is asked to validate how sure it is that the answer is correct. After two iterations, model is asked to give a final answer.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add rcnParameters
-
strat- strategy for selection of the messages to rewrite. Default ismatch-
all- match all messages -
first- match first message regardless of the role -
last- match last message regardless of the role -
any- match one random message -
percentage- match a percentage of random messages from the conversation -
user- match all user messages -
match- use a filter to match messages
-
-
strat_params- parameters (filter) for the selection strategy. Default matches all user messages-
percentage- forpercentagestrat - the percentage of messages to match, default is50 -
index- formatchstrat - the index of the message to match -
role- formatchstrat - the role of the message to match -
substring- formatchstrat - will match messages containing the substring
-
Example
# Configure message selection
# to match last user message
harbor boost rcn strat match
harbor boost rcn strat_params set role user
harbor boost rcn strat_params set index -1Handle:
klmbr

Boosts model creativity by applying character-level random rewrites to the input. Read a full overview of the technique in the source repo.
Every LLM will respond to rewrites in a different way. Some models will generate more diverse completions, while others might start generating completely random sequences. Default parameters are tuned for Llama 3.1 8B, you might want to adjust them when running with a different model.
Parameters
-
percentage- amount of characters to rewrite in the input. Default is35 -
mods- types of rewrites to apply. Default isall, available options:-
capitalize- swaps character capitalization -
diacritic- adds a random diacritic to the character -
leetspeak- replaces characters with leetspeak equivalents -
remove_vowel- removes vowels from the input
-
-
strat- strategy for selection of the messages to rewrite. Default ismatch-
all- match all messages -
first- match first message regardless of the role -
last- match last message regardless of the role -
any- match one random message -
percentage- match a percentage of random messages from the conversation -
user- match all user messages -
match- use a filter to match messages
-
-
strat_params- parameters (filter) for the selection strategy. Default matches all user messages-
percentage- forpercentagestrat - the percentage of messages to match, default is50 -
index- formatchstrat - the index of the message to match -
role- formatchstrat - the role of the message to match -
substring- formatchstrat - will match messages containing the substring
-
Examples
# Reduce the rewrite percentage
harbor boost klmbr percentage 20
# Enable/disable rewrite modules
harbor boost klmbr mods rm all
harbor boost klmbr mods add capitalize
harbor boost klmbr mods add diacritic
harbor boost klmbr mods add leetspeak
harbor boost klmbr mods add remove_vowel
# Change the selection strategy
# 1. Match all user messages
harbor boost klmbr strat match
harbor boost klmbr strat_params role user
# 2. Match the last message (regardless of the role)
harbor boost klmbr strat match
harbor boost klmbr strat_params index -1
# 3. Match messages containing a substring
harbor boost klmbr strat match
harbor boost klmbr strat_params substring "random"Dynamic Chain-of-Thought pattern.
See original implementation for Grok. Harbor also has a dedicated ol1 service (UI only) that implements the same technique.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add g1Parameters
-
max_steps- Maximum amount of iterations for self-reflection, default is 15 -
strat- strategy for selection of the messages to rewrite. Default ismatch-
all- match all messages -
first- match first message regardless of the role -
last- match last message regardless of the role -
any- match one random message -
percentage- match a percentage of random messages from the conversation -
user- match all user messages -
match- use a filter to match messages
-
-
strat_params- parameters (filter) for the selection strategy. Default matches all user messages-
percentage- forpercentagestrat - the percentage of messages to match, default is50 -
index- formatchstrat - the index of the message to match -
role- formatchstrat - the role of the message to match -
substring- formatchstrat - will match messages containing the substring
-
This is a less-cool version of the Visual Tree Of Thoughts Open WebUI Function. Less cool because there's no way to rewrite the message content from a proxy side (yet), so all of the intermediate outputs are additive.
Nonetheless, the core of the technique is the same and is based on the Tree Of Thoughts and MCTS algorithms. An initial "idea" or answer is generated and then is improved upon for a given amount of steps.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add mctsParameters
All parameters below are prefixed with boost.mcts. in harbor config
-
strat- strategy for selection of the messages to rewrite. Default ismatch, other values:-
all- match all messages -
first- match first message regardless of the role -
last- match last message regardless of the role -
any- match one random message -
percentage- match a percentage of random messages from the conversation -
user- match all user messages -
match- use a filter to match messages
-
-
strat_params- parameters (filter) for the selection strategy. Default matches all user messages, fields:-
percentage- forpercentagestrat - the percentage of messages to match, default is50 -
index- formatchstrat - the index of the message to match -
role- formatchstrat - the role of the message to match -
substring- formatchstrat - will match messages containing the substring
-
-
max_iterations- Maximum amount of Monte Carlo iterations to run (same tree), default is2 -
max_simulations- Improvement steps per iteration, default is2 -
max_thoughts- This number + 1 will be amount of improved variants to generate per node
# Strategy to find the message to start from
harbor config set boost.mcts.strat match
# Match last user message, for example
harbor config set boost.mcts.strat_params role=user,index=-1Based on a simple idea of explaining complex things in a simple way. The module will ask the LLM to explain a question to itself first and then will use that explanation for the final answer.
Parameters
eli5 module supports selection strategy parameters identical to mcts, g1, and rcn modules, just under the boost.eli5 prefix.
# Strategy to find the message to start from
harbor config set boost.eli5.strat match
# Match last user message, for example
harbor config set boost.eli5.strat_params role=user,index=-1Based on a technique of generation of a summary of the given given content from key questions. The module will ask the LLM to provide a given amount of key questions and then will use them to guide the generation of the summary.
Parameters
supersummer module supports selection strategy parameters identical to mcts, g1, and rcn modules, just under the boost.supersummer prefix.
# Strategy to find the message to start from
harbor config set boost.supersummer.strat match
# Match last user message, for example
harbor config set boost.supersummer.strat_params role=user,index=-1In addition to that, it's possible to adjust number of questions the model will generate, as well as the desired length of the summary.
# Number of questions to generate
harbor config set boost.supersummer.questions 3
# Length of the summary, you can use any
# textual specification, like "one paragraph"
harbor config set boost.supersummer.length "few paragraphs"Here're sample questions and summary that supersummer generated from Harbor's readme:
Sample questions and summary
What is Harbor, and what are its primary functions? (This question addresses the central theme or argument of the text, which is to introduce Harbor as a containerized LLM toolkit.)
What services can be managed with Harbor, and how does it facilitate their use? (This question highlights important facts or evidence, such as the various services listed in the "Services" section, and how Harbor enables easy management and usage of these services.)
How does Harbor simplify local LLM development and experimentation? (This question reveals the author's purpose or perspective, which is to make local LLM development more convenient and streamlined by providing a unified CLI interface for managing services and configurations.)
What benefits does Harbor provide over using individual Docker Compose files or Linux administration commands? (This question explores any significant implications or conclusions of using Harbor, such as the convenience factor and workflow centralisation it offers.)
Can Harbor be used in conjunction with existing Docker setups, or is it intended to replace them entirely? (This question highlights important facts or evidence about Harbor's purpose and scope, such as its ability to co-exist with existing Docker setups and provide added value through its convenience features.)
Harbor is a containerized Long-Short-Memory (LLM) toolkit that enables effortless management of LLM backends, APIs, frontends, and services. Developed as an open-source project, Harbor consists of a Command-Line Interface (CLI) and a companion application to help manage and run AI services in a unified manner.
Harbor offers several key features:
- Managed Services: The platform allows users to easily manage various LLM-related services, such as UIs (User Interfaces), Backends, Frontends, and Satellites.
- Unified CLI Interface: Harbor provides a single command-line interface for managing multiple services, eliminating the need for manual configuration and streamlining development workflows.
- Convenience Utilities: A range of convenience tools helps users manage LLM-related tasks efficiently, such as setting up services, debugging, creating URLs, and establishing network tunnels.
- Cache Sharing and Reuse: Harbor shares and reuses host caches, significantly enhancing model performance and reducing memory consumption across supported services (e.g., Hugging Face models, Ollama).
- Config Profiles: The application allows users to manage multiple configuration profiles for different development tasks or projects.
Harbor's purpose is not only to provide a convenient platform but also to simplify local LLM development by making it easier to setup and experiment with various LLM-related services. As such, Harbor can perfectly align with existing Docker setups and offers several benefits over manual Linux administration commands, like ease of use and streamlined configurations management.
As the author implies, the main benefit of using Harbor lies in its ability to simplify local LLM development and reduce time required for experiments and prototyping steps in a unified and convenient setup.

This workflow allows you to add R1-like reasoning to any LLM (including older ones, like Llama 2, or Gemma 1). Of course, it won't show the same performance as an actually GRPO-boosted model, but it can still provide some interesting results as well as being a very flexible base to experiment with.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add r0Parameters
# Get/set the amount of thoughts to generate
harbor boost r0 thoughts 5
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add markovThere's no configuration for this module yet.
When serving the completion, LLM will first invent a skill check it must pass to address your message. Then, the workflow will roll a dice determining if the model passes the check or not and will guide the model to respond accordingly.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add dnd
Inspired by Chain of Draft paper.
# Enable the module
harbor boost modules add dotboost works as an OpenAI-compatible API proxy. It'll query configured downstream services for which models they serve and provide "boosted" wrappers in its own API.
See the http catalog entry for some sample requests.
Authorization
When configured to require an API key, you can provide the API key in the Authorization header.
<!-- All three versions are accepted -->
Authorization: sk-boost
Authorization: bearer sk-boost
Authorization: Bearer sk-boostGET /v1/models
List boosted models. boost will serve additional models as per enabled modules. For example:
POST /v1/chat/completions
Chat completions endpoint.
- Supports all parameters from the downstream API, for example
jsonformat for Ollama - Supports streaming completions
GET /events/:stream_id
Listen to a specific stream of events (associated with a single completion workflow). The stream ID is a unique identifier of the LLM instance processing the request (you may decide to advertise/pass it to the client in the workflow's code).
GET /health
Health check endpoint. Returns { status: 'ok' } if the service is running.
It's possible to create custom modules for boost, using the built-in abstractions.
You can write a module in Python, put it in a folder and it'll be served by boost in the same
way as the built-in modules.
Here's a simplest example, a module that echoes the input back to the user:
ID_PREFIX = "echo"
def apply(llm, chat):
await llm.emit_message(prompt=chat.tail.content)Read more on a dedicated Custom Modules page.
You can run boost as a standalone Docker container. See harbor-boost package in GitHub Container Registry.
# [Optional] pre-pull the image
docker pull ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestYou can take a look at a boost-starter for a minimal example repository to get started.
Configuration
boost can be configured via environment variables, here's a reference of what's currently supported, with respective defaults.
# OpenAI-compatible APIs to boost. Semicolon-separated list
# Example: "http://localhost:11434/v1;http://localhost:8014/openai"
# ⚠️ Even if the API doesn't require a key, you still need to provide
# a placeholder in "BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS" for it
HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS ""
# Keys for the OpenAI-compatible APIs to boost. Semicolon-separated list,
# must be index-matched with the URLs.
# Example: "key1;key2"
# ⚠️ You need to provide placeholder keys even if the API doesn't require them
HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS ""
# Boost modules to enable. Semicolon-separated list
# ℹ️ Boost can still run a workflow even if the module is disabled,
# it just won't be served via the /v1/models API (be invisible to the user)
# Example: "klmbr;rcn;g1"
HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES "klmbr;rcn;g1"
# Folders with boost modules to load.
# You can specify more than one, semicolon-separated list
# Built-in modules are in the "modules" of the container,
# you can turn them off by providing a custom folder only
# Example: "modules;/root/boost_modules"
HARBOR_BOOST_MODULE_FOLDERS "modules;custom_modules"
# Base models to serve via the boost API
HARBOR_BOOST_BASE_MODELS false
# Filter models that will be served by the boost API
# Runs after the boost own models are added, so you can filter them as well
# Examples: "id.contains=llama", "id.regex=.+q8_0$", "id=llama3.1:8b"
HARBOR_BOOST_MODEL_FILTER ""
# API key for the boost service
# If set, the key must be provided in the Authorization header
# Example: "sk-boost"
HARBOR_BOOST_API_KEY ""
# Allows specifying multiple keys instead of a single one
# Example: "sk-user1;sk-user2;sk-user3"
HARBOR_BOOST_API_KEYS ""
# Enable intermediate output for the boost modules
# "Intermediate" means everything except the final result.
# For example, status messages or internal monologue
# Note that it doesn't mean "all output" from the module,
# as module source can still decide to not emit specific things at all
# or inverse - emit them even if this setting is off
HARBOR_BOOST_INTERMEDIATE_OUTPUT true
# Allows choosing how the status messages will be formatted
# when emitted by the boost modules
# See boost.status.style section for more info
HARBOR_BOOST_STATUS_STYLE md:codeblock
# Module specific configs:
# Klmbr
HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_PERCENTAGE 35
HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_MODS all
HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_STRAT_PARAMS role=user
# RCN
HARBOR_BOOST_RCN_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_RCN_STRAT_PARAMS role=user,index=-1
# G1
HARBOR_BOOST_G1_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_G1_STRAT_PARAMS role=user,index=-1
HARBOR_BOOST_G1_MAX_STEPS 15
# MCTS
HARBOR_BOOST_MCTS_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_MCTS_STRAT_PARAMS role=user,index=-1
HARBOR_BOOST_MCTS_MAX_SIMULATIONS 2
HARBOR_BOOST_MCTS_MAX_ITERATIONS 2
HARBOR_BOOST_MCTS_THOUGHTS 2
BOOST_MCTS_EXPLORATION_CONSTANT 1.414
# eli5
HARBOR_BOOST_ELI5_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_ELI5_STRAT_PARAMS role=user,index=-1
# Supersummer
HARBOR_BOOST_SUPERSUMMER_STRAT match
HARBOR_BOOST_SUPERSUMMER_STRAT_PARAMS role=user,index=-1
HARBOR_BOOST_SUPERSUMMER_NUM_QUESTIONS 5
HARBOR_BOOST_SUPERSUMMER_LENGTH one short paragraph
# R0
HARBOR_BOOST_R0_THOUGHTS 5See the main portion of the guide for detailed explanation of these variables. You can also find the most complete overview of the supported variables in the source.
Example
# Start the container
docker run \
# 172.17.0.1 is the default IP of the host, when running on Linux
# So, the example below is for local ollama
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
# Configuration for the boost modules
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=klmbr;rcn;g1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_PERCENTAGE=60" \
# [Optional] mount folder with custom modules
-v /path/to/custom_modules/folder:/app/custom_modules \
-p 8004:8000 \
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latest
# In the separate terminal (or detach the container)
curl http://localhost:8004/health
curl http://localhost:8004/v1/models
[ { // Original, unmodified model proxy "id": "llama3.1:8b", // ... }, { // LLM with klmbr technique applied "id": "klmbr-llama3.1:8b", // ... }, { // LLM with rcn technique applied "id": "rcn-llama3.1:8b", // ... } ]