Intraoperative margin assessment of human breast tissue in optical coherence tomography images using deep neural networks
This code is a method to implement a DNN based solution with new regularization methods for breast cancer margin assessment during lumpectomy operation. For more details, please refer to the cited paper (see Citation below).
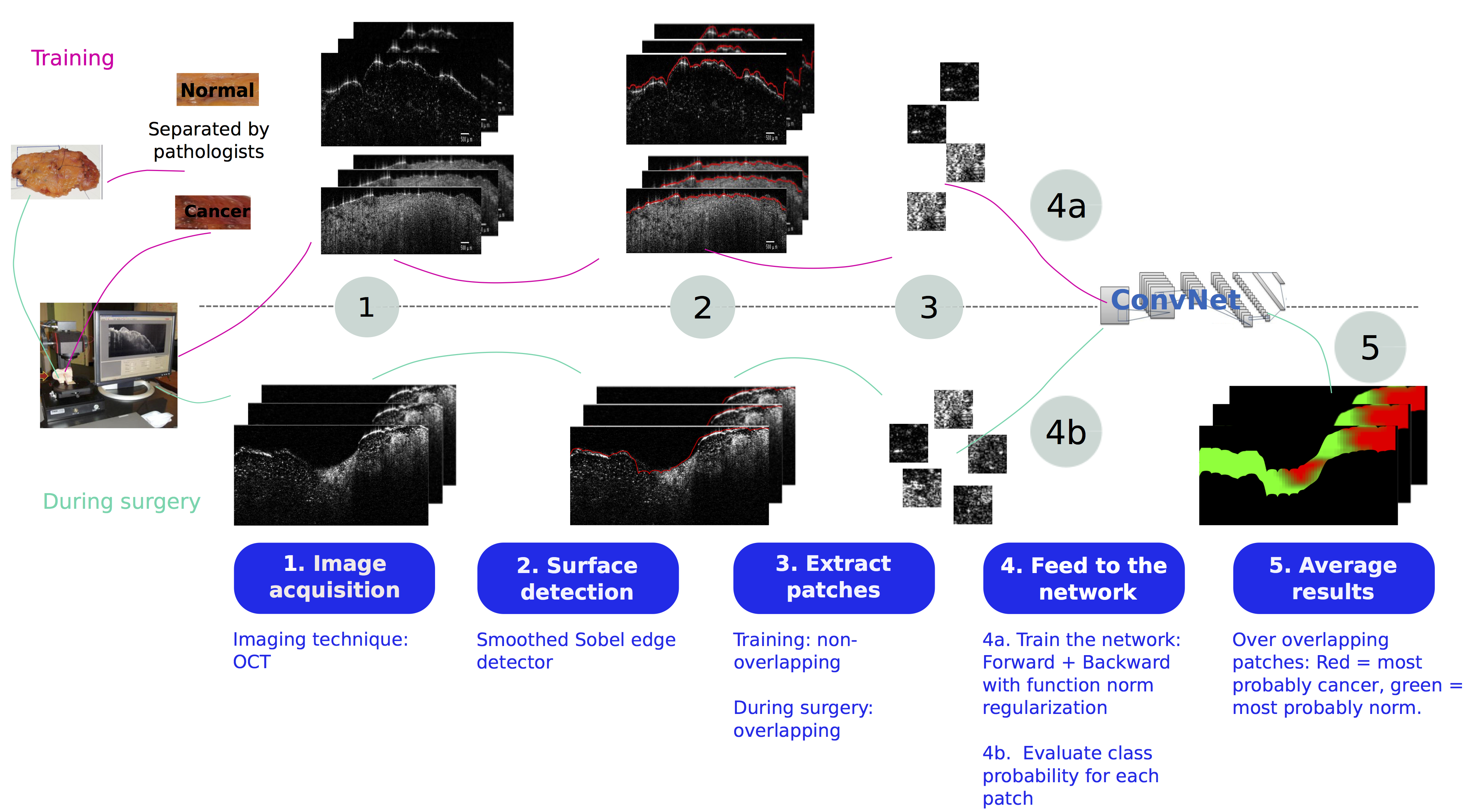
Assessing the surgical margin during breast lumpectomy operations can avoid the need for additional surgery. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that has been proven to be efficient for this purpose. However, to avoid overloading the surgeon during the operation, automatic cancer detection at the surface of the removed tissue is needed. Some methods based on the spatial statistics of the images have been developed, but the obtained results are still far from human performance. In this work, we investigate the possibility to use deep neural networks (DNNs) for real time margin assessment, demonstrating performance significantly better than the reported literature and close to the level of a human expert. Since the goal is to detect the presence of cancer, a patch-based classification method is proposed, as it is sufficient for detection, and requires training data that is easier and cheaper to collect than for other approaches such as segmentation. For that purpose, we train a DNN architecture that was proved to be efficient for small images on patches extracted from images containing only cancer or only normal tissue as determined by pathologists in a university hospital. As the number of available images in all such studies is by necessity small relative to other deep network applications such as ImageNet, a good regularization method is needed. In this work, we propose to use a recently introduced function norm regularization that attempts to directly control the function complexity, in contrast to classical approaches such as weight decay and DropOut. As neither the code nor the data of previous results are publicly available, the obtained results are compared with reported results in the literature for a conservative comparison. Moreover, our method is applied to locally collected data on several data configurations. The reported results are the average over the different trials. The experimental results show that the use of DNNs yields significantly better results than other techniques when evaluated in terms of sensitivity, specificity, F1 score, G-mean and Matthews correlation coefficient. Function norm regularization yielded higher and more robust results than competing regularization methods. We have demonstrated a system that shows high promise for (partially) automated margin assessment of human breast tissue, Equal error rate (EER) is reduced from approximately 12% (the lowest reported in the literature) to 5% – a 58% reduction. The method is computationally feasible for intraoperative application (less than 2 seconds per image) at the only cost of a longer offline training time.
- MATLAB
- MatConvNet (http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/)
- GPU: tested on a GeForce GTX 750 Ti for our experiments.
- Download/clone the current project
- Follow the steps to install MatConvNet (in the folder containnig the codes of this project)
- Copy the following files in the indicated locations: designates MatConvNet master folder:
- cnn_train_reg.m -> /examples
- vl_simplenn.m -> /matlab/simplenn
- get_sample.m ->
- get_val_f.m ->
Before running the codes, please modify the paths in each of the provided codes to match your own paths.
To run the tests, please run OCT_exp.m. This test: - operates a 5-fold cross-validation - train the selected model - test the selected model on test data base (separated into normal an cancer) This test operates the steps 1 to 4 of the graphical abstract: - Surface detection (function border_det, used in extractPatchFnc) - Patch extraction (function extractPatchFnc followed by function imdbsConstructFnc in order to generate the database in the format used by MatConvNet) - Network training (with model selection) and testing (function cnn_OCT, you can use getOptions to generate the options corresponfing to the method you want to use.)
To predict the class probabilities for a mixed tissue, please run [pred,t] = predict_im(path, ov1, ov2, ov3, T ,s) Inputs: - path = path of the OCT images - ovx designates the number of overlapping pixels(=size - ovx) in the dimension x. - T = threshold on probabilities to decide to which class a sample is assigned (if out is the network output, then out(1) >= T -> class = 1, else class =2), used value for our experiments =0.5. - s = the size of the extracted patches Outputs: - pred = a matrix of predicted classes - t = elapsed time.
- Amal Rannen Triki, Matthew B. Blaschko, Yoon Mo Jung, Seungri Song, Hyun Ju Han, Seung Il Kim and Chulmin Joo
** For questions about the code, please contact Amal Rannen Triki ([email protected])
Our paper is still under review. However, you can cite our arXiv article in the meantime:
@article{rannentriki2017intraoperative,
title={Intraoperative margin assessment of human breast tissue in optical coherence tomography images using deep neural networks},
author={Rannen~Triki, Amal and Blaschko, Matthew B and Jung, Yoon Mo and Song, Seungri and Han, Hyun Ju and Kim, Seung Il and Joo, Chulmin},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10827},
year={2017}
}This software package is freely available for research purposes. Please check the LICENSE file for details.
- This code is mainly based on MatConvNet
- The images used for our experiments are real patient images, and thus, for ethic issues, they are not provided with this project. We however provide our trained models (See Models: under this directory x-y designates the models obtained in our experiments when we train on sample x and test on sample y. Refer to the paper for more details about these data splits).