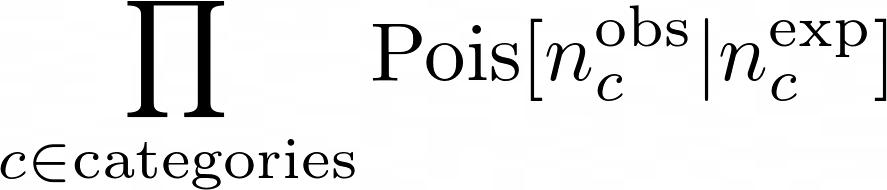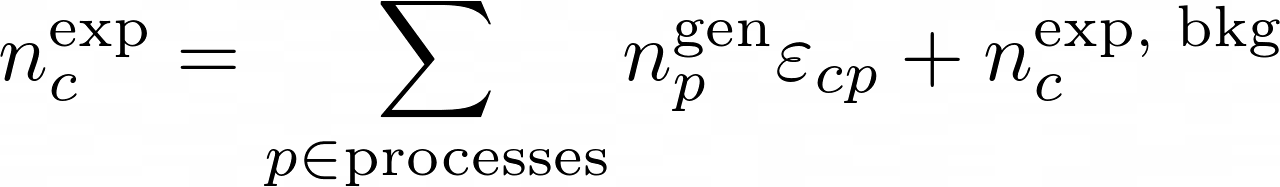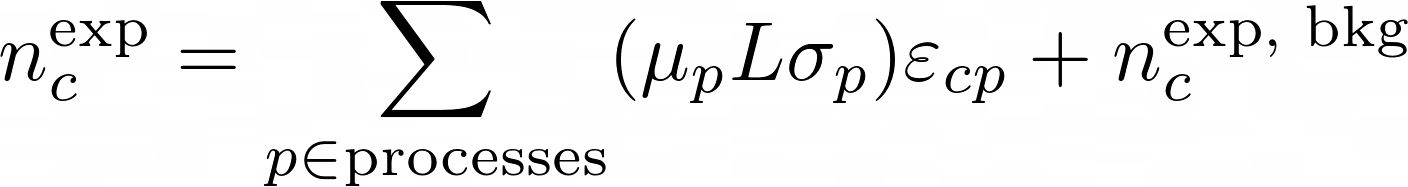Very simple python package to create very simple counting experiment RooFit workspaces.
The statistical model describes the migration of events from truth-bins (e.g. processes) and reco-category. The implemented likelihood is a product of Poissonian distributions:
The product is over all the reconstructed categories. The number of expected events in each category is:
The matrix ε implements the efficiencies and the migrations. It's matrix elements are the conditional probability to be selected and reconstructed in category-c for a process-p: P[c|p]. The generated number of events for each process can be parametrized in any way. A popular one in hep is:
here the generated number of events are equal to the product of the luminosity (the overall normalization), its cross section and the signal strength (which is the free parameter in the fit). The background is added on top of that.
Here a simple example:
import ROOT
from countingworkspace import *
NAMES_PROC = ['proc1', 'proc2']
NCATEGORIES = 3
EFFICIENCIES = [[0.3, 0.1],
[0.5, 0.4],
[0.2, 0.2]]
EXPECTED_BKG_CAT = [100, 30, 10]
LUMI = 100.
# first create the parameters needed for the parametrization. The luminosity
ws = ROOT.RooWorkspace()
ws.factory('lumi[%f]' % LUMI)
# and the cross sections:
xsections = create_variables(ws, 'xsec_{proc}', # {proc} is an index, you can call as you prefer
bins=NAMES_PROC, # the names
values=[101.5, 7.99]) # the values of the cross sections
create_workspace(NCATEGORIES, NAMES_PROC,
efficiencies=EFFICIENCIES,
nexpected_bkg_cat=EXPECTED_BKG_CAT,
expression_nsignal_gen='prod:nsignal_gen_proc{proc}(mu_{proc}[1, -4, 5], lumi, xsec_{proc})',
ws=ws)
It is also possible to add simple systematic uncertainties.
There are some utilies to run toys.
Look at the examples
pip install countingworkspace