node js-coverage using mocha, beta 0.2.0
You can easily get it installed by following steps
Visit Nodejs
sudo npm install -g Mr.Coverage
sudo and -g are necessary because a global executable command mr-coverage will be generated in your /usr/local/bin/ path.
There are two ways to install it. 1. download and install by yourself from jscoverage. 2. I have prepared a install.sh for you.
cd /usr/local/lib/node_modules/Mr.Coverage/bin
Then
sudo bash install.sh
After three steps above, you can try mr-coverage command in your terminal. Good Luck!
PS: All installation tests are done in Mac.
For command mr-coverage.
USAGE: mr-coverage [project-directory] [spec-folders/-files] + (mocha Options below, no need to set file path)
+ is important to split additional mr-coverage params and original mocha params.
You must set a coverage.json file under the root folder. The content of that is a array to mark which file or folder Mr.Coverage should track.
[
'script.js',
'xxx_folder'
]
Right now, coverage.json only support the file and folder format, and it's a white list, that means if you set nothing, coverage report will not show. Btw, the format should not start with ./. It's always relative to the root folder.
Normally, mr-coverage can be used like this. Suppose you have a nodejs project called "nodeproj" in ~/Desktop/, and have a file structures below:
nodeproj
├─ package.json
├─ script.js
├─ coverage.json
├─ node_modules
└─ spec
└─ script.spec.js
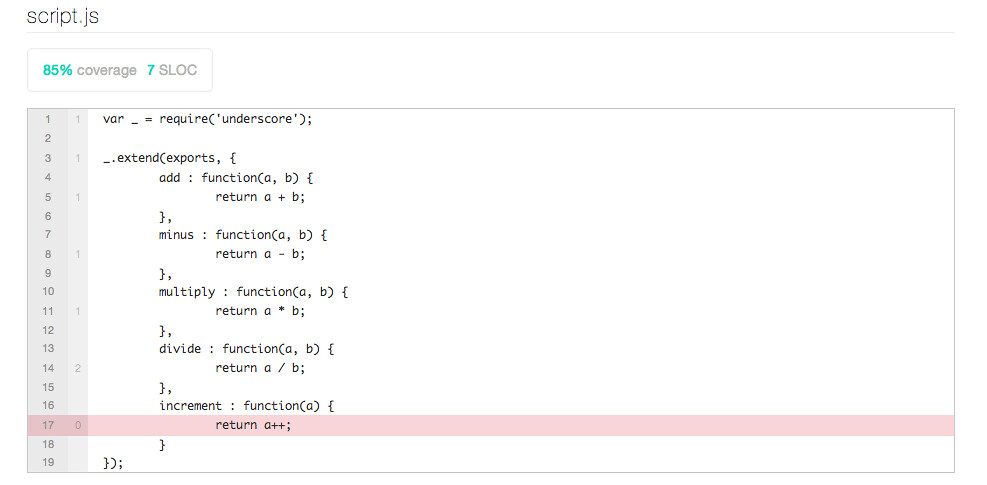
Here is the code in script.js, simple add/minus/multiply/divide
var _ = require('underscore');
_.extend(exports, {
add : function(a, b) {
return a + b;
},
minus : function(a, b) {
return a - b;
},
multiply : function(a, b) {
return a * b;
},
divide : function(a, b) {
return a / b;
},
increment : function(a) {
return a++;
}
});Here is the code in spec/script.spec.js, only tested add/minus/multiply/divide, the increment method isn't included.
describe("script", function() {
var script = require('../script');
var should = require('chai').should();
it("#add", function(done) {
script.add(1, 1).should.equal(2);
done();
});
it("#minus", function(done) {
script.minus(1, 1).should.equal(0);
done();
});
it("#multiply", function(done) {
script.multiply(1, 1).should.equal(1);
done();
});
describe("#divide", function() {
it("1 / 1", function(done) {
script.divide(1, 1).should.equal(1);
done();
});
it("1 / 0", function(done) {
setTimeout(function(argument) {
script.divide(1, 0).should.equal(Infinity);
done();
}, 500);
});
});
});Here is config in coverage.json
[ 'script.js' ]
After that, you can run command to get result.
mr-coverage ~/Desktop/nodeproj spec + -R html-cov > ~/Desktop/reports.html
You can open the reports.html file to see the result:
Report format like html-cov or json-cov is used for the testing of JavaScript coverage. Except these two formats, if user uses format like spec, list, tap, progress and so on, mr-coverage will run using mocha, and because mr-coverage supports using spec-folders and spec-files in console arguments, it's more useful than mocha.
If we run command with the 'spec' report format.
mr-coverage ~/Desktop/nodeproj spec + -R spec