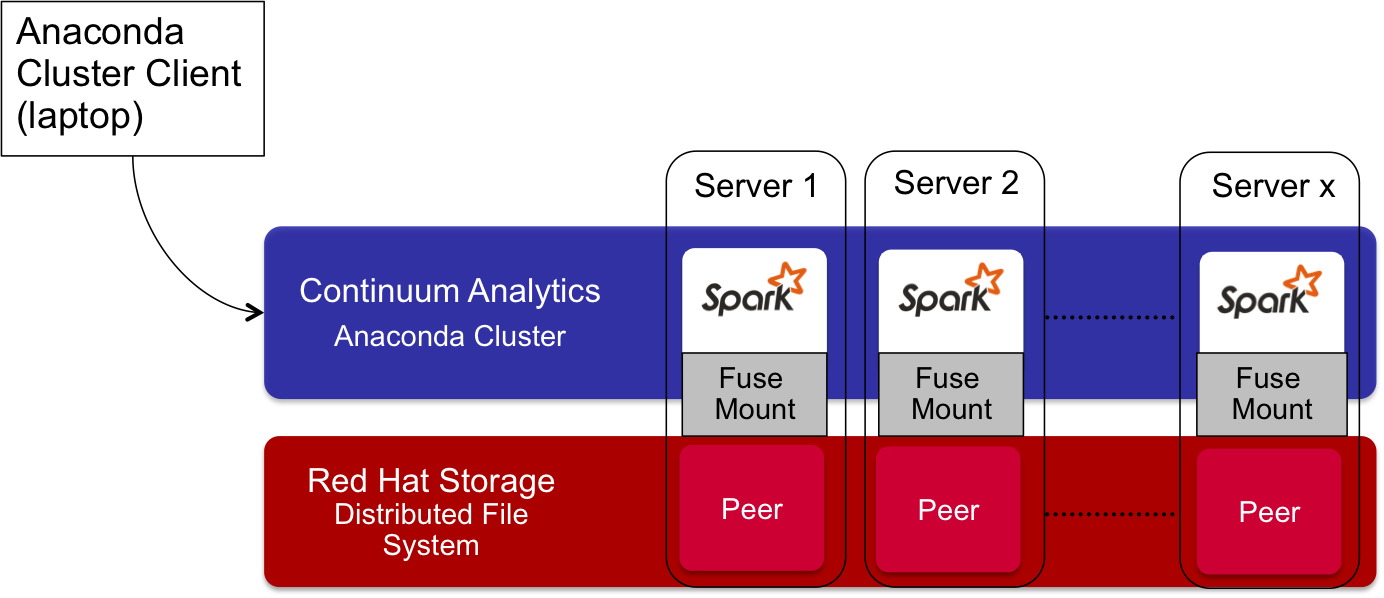
This tutorial describes how to deploy Anaconda Cluster and PySpark on top of Red Hat Storage GlusterFS.
You'll first need a GlusterFS cluster. You can get the commercial version from Red Hat or you can use a vagrant script from Jay Vyas to spin up a simple 2 Node GlusterFS cluster and volume.
Designate a random node in your GlusterFS Cluster to be your Anaconda Cluster Master. From the master, setup passwordless SSH access into the other GlusterFS nodes in the cluster and into itself.
Install Anaconda 2.7 on a laptop (or client machine) that can reach the cluster. You can download this here and its free.
A license token can be obtained for Anaconda Cluster can contacting Continuum Analytics at this link. Once you have the token, Anaconda Cluster can be installed by running the following commands on your client machine.
# TOKEN={ You will need to get this from Continuum Analytics }
# conda install -c https://conda.binstar.org/t/$TOKEN/conda-cluster conda-cluster
-
From the server you designated to be the Anaconda Cluster Master, copy its private SSH Key to your client to ~/.conda/clusters.d/rhs-spark.key and set the permissions on it to chmod 600.
-
From the client, create the Cluster YAML file for your intended Spark Cluster that conda cluster will be managing:
The head IP listed below is the Anaconda Cluster Master we designated. The private_key value is its private key that we copied from the Master onto the client. The compute IP is the other node in the GlusterFS cluster. Add it but ignore the simple_aws provider. Lastly, the name of the file and the name of the cluster (rhs-spark) must match.
# vi ~/.conda/clusters.d/rhs-spark.yaml
rhs-spark:
private_key : ~/.conda/clusters.d/rhs-spark.key
user : root
machines :
head : ['192.168.58.219']
compute : ['192.168.58.218']
provider : simple_aws
- From the client, verify conda cluster can find the newly defined cluster:
# conda cluster list; conda cluster manage rhs-spark status
- From the client, bootstrap the cluster (This install conda cluster on GlusterFS servers)
# conda cluster manage rhs-spark bootstrap --conda --loglevel DEBUG
- From the client, deploy the PySpark runtime on the GlusterFS Servers.
# conda cluster manage rhs-spark bootstrap --spark --loglevel DEBUG
You have now completed setting up the Cluster. It is ready to ready PySpark Jobs.
- Copy some data (“Grimm’s Fairy Tales”) into the GlusterFS Volume so that we can analyze with a PySpark Job:
# mkdir -p /mnt/glusterfs/grimm
# cd /mnt/glusterfs/grimm
# wget https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/2591/pg2591.txt --no-check-certificate
-
Write a PySpark Job and copy it up to the Anaconda Master in the cluster. I have included a spark-wordcount.py in this repo that you can use. Note that it expects files to exist within the /mnt/glusterfs/grimm directory in the GlusterFS Volume. You will need to edit the file to change the setMaster value to your Anaconda Master hostname.
-
From the Anaconda Master, run the PySpark Job
# python spark-wordcount.py