This repository contains the code to reproduce all the figures in our paper:
The Shape of Learning Curves: a Review
T J Viering, M Loog,
arxiv 2021
If you found this code useful in your work, please cite our paper.
This code has been tested with Matlab (R2019b).
- Clone repository to your local PC:
git clone https://github.com/tomviering/ill-behaved-learning-curves.git
- Navigate to the root directory of the project and execute in Matlab
download_dependencies('all')
to download all additional dependencies for all experiments (total 107mb).
- Optional: download and extract panel-2.14 in the directory 'panel-2.14' (for pretty version of Fig 3).
The function download_dependencies takes a single string argument that indicates what should be downloaded, extracted, and added to the Matlab path. Options are:
-
'prtools': matlab pattern recognition toolbox - prtools.net (4 mb)
-
'riskmt': risk monotonicity - https://github.com/tomviering/RiskMonotonicity/ (20kb)
-
'gpml': gaussian process toolbox - http://gaussianprocess.org/gpml/ (3mb)
-
'makingmt': making monotone IDA - https://github.com/tomviering/monotone/ (20mb)
-
'author_results': downloads the author results for all experiments (80mb)
-
'export_fig': for exporting figures - https://github.com/altmany/export_fig (100kb)
-
'all': downloads everything (107mb)
-
'all_except_author_results': downloads everything except author results (27mb)
The experiments that produce the learning curves for the figures of the paper are sometimes time consuming because many repitions are required to obtain smooth learning curves. Therefore, we have prepared two versions of all the experiments:
- run_experiments_fast.m - total running time about 10 minutes. all the results are saved to the folder 'results_fast'.
- run_experiments_long.m - total running time about 6 hours. all the results are saved to the folder 'results_long'.
Besides saving the results to disk, these scripts also make all plots. We have performed these computations for you and we provide them with this repository. To download the results, execute
download_dependencies('author_results')
They are automatically placed in the folders 'results_fast' and 'results_long'.
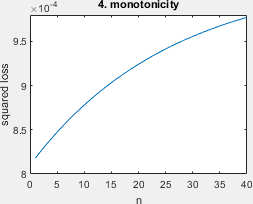
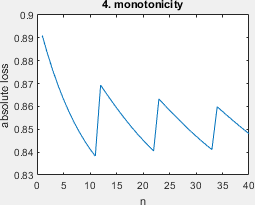
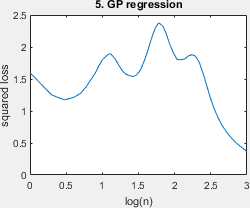
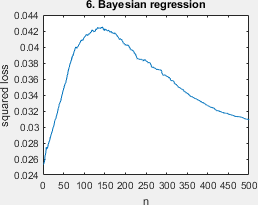
A simplified script that shows all ill-behaved learning curves (Fig 3) and the surface plot (Fig 2) with minimal styling. Requires all result files in the folders 'results_fast' or 'results_long'. Example output below.
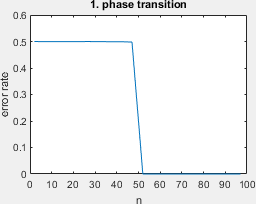
The crossing learning curves of Fig 1 (not based on actual data).
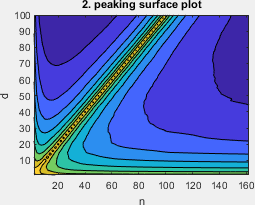
The pretty version of the surface plot of Figure 2, requires the result file `2_peaking.mat'.
The pretty version of all ill-behaved learning curves of Figure 3, requires all result files.
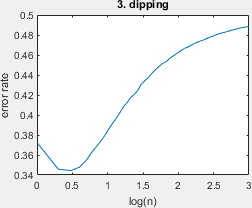
Visualizes the distribution for the dipping learning curve.
If you run into any issues, you can email me: t.j.my_surname_here AT tudelft DOT nl
The learning problems given in this repository are not all novel, instead, we aimed to provide accesible implementations for all of them. Below are the respective references and additional details that describe the experiments.
- phase transition: this is a novel learning problem, described at the end of section 6.1 in our paper.
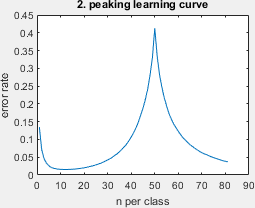
- peaking: this learning problem has a long history, please see M. Loog, T. Viering, A. Mey, J. H. Krijthe, and D. M. Tax, “A brief prehistory of double descent,” PNAS, vol. 117, no. 20, pp. 10 625–10 626, 2020.
- dipping: this learning problem was inspired by Marco Loog and Robert P W Duin. The dipping phenomenon. In S+SSPR, pages 310–317, Hiroshima, Japan, 2012. it is slightly different however, the actual learning problem is given by Figure 4 in our paper.
- monotonicity: the learning problem was given by Marco Loog, Tom Viering, and Alexander Mey. Minimizers of the empirical risk and risk monotonicity. In NeurISP, pages 7478–7487, 2019.
- GP regression: this is the learning problem where the student uses the correct noise level, but the wrong sigma, where data is uniform on the unit hypercube, originating from Peter Sollich. Gaussian Process Regression with Mismatched Models. In NeurIPS, pages 519–526, 2002.
- Bayesian regression. this is the learning problem with the fourier basis, with the non-hierarchical bayesian regression model, given by Peter Grünwald and Thijs van Ommen. Inconsistency of bayesian inference for misspecified linear models, and a proposal for repairing it. Bayesian Analysis, 12(4):1069–1103, 2017.
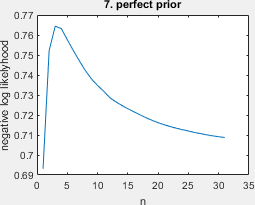
- perfect prior. this learning problem was discussed the paragraph 'Decreasing risk!?' in Peter D. Grünwald and Wojciech Kotłowski. Bounds on individual risk for log-loss predictors. JMLR, 19:813–816, 2011.
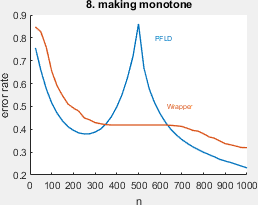
- making monotone. this experiment is taken from Tom Julian Viering, Alexander Mey, and Marco Loog. Making learners (more) monotone. In IDA, pages 535–547. Springer, 2020.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2021 T J Viering
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.