A tool that aims to detect infected hosts by analyzing NetFlow/IPFIX records. The algorithm is based on the fact that many p2p botnets use keep-alive messages to their neighbors that are sent with a fixed period.
It consists of a couple of components depicted on the scheme:
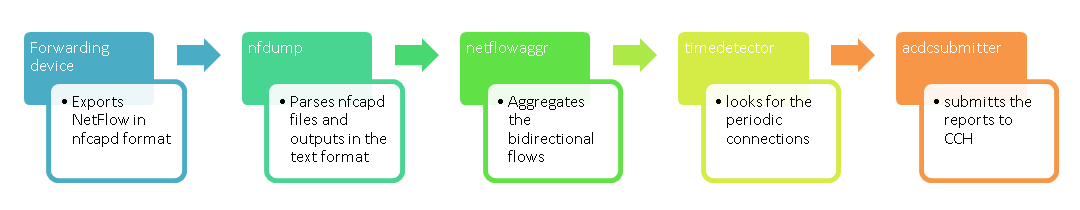
Here is what needs to be installed on a cloud Ubuntu 14.10 image to compile the project:
sudo apt-get install make g++
sudo apt-get install libboost1.54-dev libboost1.54
Also you will need nfdump tool:
sudo apt-get install nfdump
Suppose you are in the directory with the source code.
Compile:
make -C bidirectional && make -C timedetector
- Location of the netflow data
The directory containg the nfcapd files is configured in run.sh file with NFCAPDDir parameter.
Also, the first and the last file to process are also specified there:
NFCAPDDir=../../netflow/zeus
START=nfcapd.201411181315
END=nfcapd.201411181330
- Botnet types
Some p2p botnets use a fixed-time period to contact the neighbours (as pointed and summarized in a table at 7th (103rd) page of this article).
For example, 30 minutes period is used by Zeus p2p botnet.
The configuration of the time period is placed in timedetector/timedetector.conf file:
"times" :
[600000, 900000, 1800000, 2400000],
That means that the connections will be checked for the periods of 10, 15, 30 and 40 minutes.
If a periodic connections were detected, the output will give you a related ip address (could be both IPv4 or IPv6) and the number of other hosts with which it was periodically communicating. This is given for each requested period:
192.168.1.143
600000 -> 2
900000 -> 2
1800000 -> 2
2400000 -> 0
- Detection parameters
To detect the periodical connection, the timeline is split by the period intervals; and thus wrapped into two-dimentional array:
![Red dots are new flows [connections] between the two hosts Connection events for a Zeus p2p infected hosts](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tigran-a/relbot/master/zeus.png)
Here X-axis is the time, and Y-axis is a wrapping "level": a point at (x,y) means that a new connection was established at time y*period + x.
The timeline is discretized by small intervals defined in ms here:
"UNIT_MS" : 1000,
That is, a connection started at 15th seconds 125ms, is equivalent to one started on 15th second 789ms.
For each such unit interval we count the number of connections on different levels; also we may affect neighbouring unit intervals,
number of the affected neighbouring unit intervals from each side is defined by RADIUS parameter
"RADIUS" : 3,
We can prevent analysis for the hosts for which the maximal value cumullated per unit-interval does not go over MIN_VAL parameter:
"MIN_VAL" : 4.0,
Here we say that if we don't have ~4 points on different levels for at least one interval, we don't do the analysis.
Now, we calculate the maximum value between all unit-intervals (maximum), dispersion and a mean.
Then, if we have exactly one unit-interval with the value greater than FREE_COEF + MAX_COEF*maximum + DISP_COEF*dispersion + MEAN_COEF*mean, then we suppose we found a periodic connections.
It is done to ensure somehow, that it was not random connections for the unit inerval, but it's an outlier from other unit-intervals values.
![Red dots are new flows [connections] between the two hosts Within lots of connections it's not always obvious whether the periodic connections are there](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tigran-a/relbot/master/hidden.png)
One an tweak the coefficients with
"DISP_COEF" : 0.5,
"MEAN_COEF" : 0.5,
"FREE_COEF" : 0,
"MAX_COEF" : 0.5,
Note, the threads parameter is currently ignored.
After all parameters confiugred, you can run the sample pipe:
./run.sh
Tool bidirectional/netflowaggr.cpp is amed to join two related flows into one, e.g., for host A and host B,
if we have flow A:10->B:20 and flow B:20->A:10 within a given time inerval, then it will output only A:10-> B:20 (assuming it appeared first).
The default time interval is 2 minutes, and can be changed in the .cpp file:
#define TIME_WINDOW 120000
It appeared, that this aggregation is not necessary for the detection mechanism.
In order to submit a report to the ACDC's Central Clearing House, one must possess a CCH Write Key (for the details, please, refer to PyACDC, api v2 documentation).
A script for submitting a report is provided in acdcsubmitter.py.
It takes as the input at stdin the output produced by relbot (see run.sh), for example:
=============================
103.169.223.139
600000 -> 0
900000 -> 4
1800900 -> 0
2400000 -> 0
=============================
103.169.68.96
600000 -> 1
900000 -> 0
1800900 -> 0
2400000 -> 0
and will look per each host, if for at least one time period, the index ( number going after -> ), which is actually a number of hosts with whom the given one has periodic connections, is at least MIN_IDX
MIN_IDX -- filters out all suspecious hosts for which the number of periodic connections are less than MIN_IDX.
For the example abouve, MIN_IDX = 2 will skip reporting the second host, but will report the first one.
IP_MODE="plain" The mode of the source IP. This can be plain for unaltered IPs, anon for anonymised IPs, or pseudo for pseudonymised IPs.
CONFIDENCE = 0.5 The default confidence level (from 0.0 to 1.0) for the reports
More parameters can be set direcly in the build_report funtion:
def build_report(ip, confidence= CONFIDENCE , timestamp = None, version =1, ipmode = IP_MODE, reporttype="RelBot detected a suspecious host" ):
KEY is a CCH write key
CCH_HOST = "webservice.db.acdc-project.eu" is a host where the CCH is running
CCH_PORT = 3000 is the corresponding port
A simple pipe to submit the found infections can be performed as:
./run.sh | ./acdcsubmitter.py
- The work was done within ACDC by SnT (University of Luxembourg)
Current algorithm simply counts the number of flows per UNIT, but it should be better to take into account that the host can be switched off
(look at the activity of ther flows) and if not, there should be no gaps between the levels. For example,
every 30 min a new flow should be established, but currently if we have a new flow in 1h30, the fact that there are two missing flows is ignored.
Also, some small deviations from the fixed period are observed (e.g. 0.5 seconds for 30 min periods)
Thanks go to CIRCL for 30Gb of NetFlow data and to Christian Nordlohne from IF-IS for a sample of NetFlow data with known hosts infected by p2p Zeus.