🏗️👷♂️ 2013 iOS MTImageMapView Android port 🏡
An image view to select a complex polygon (map henceforth) out of many.
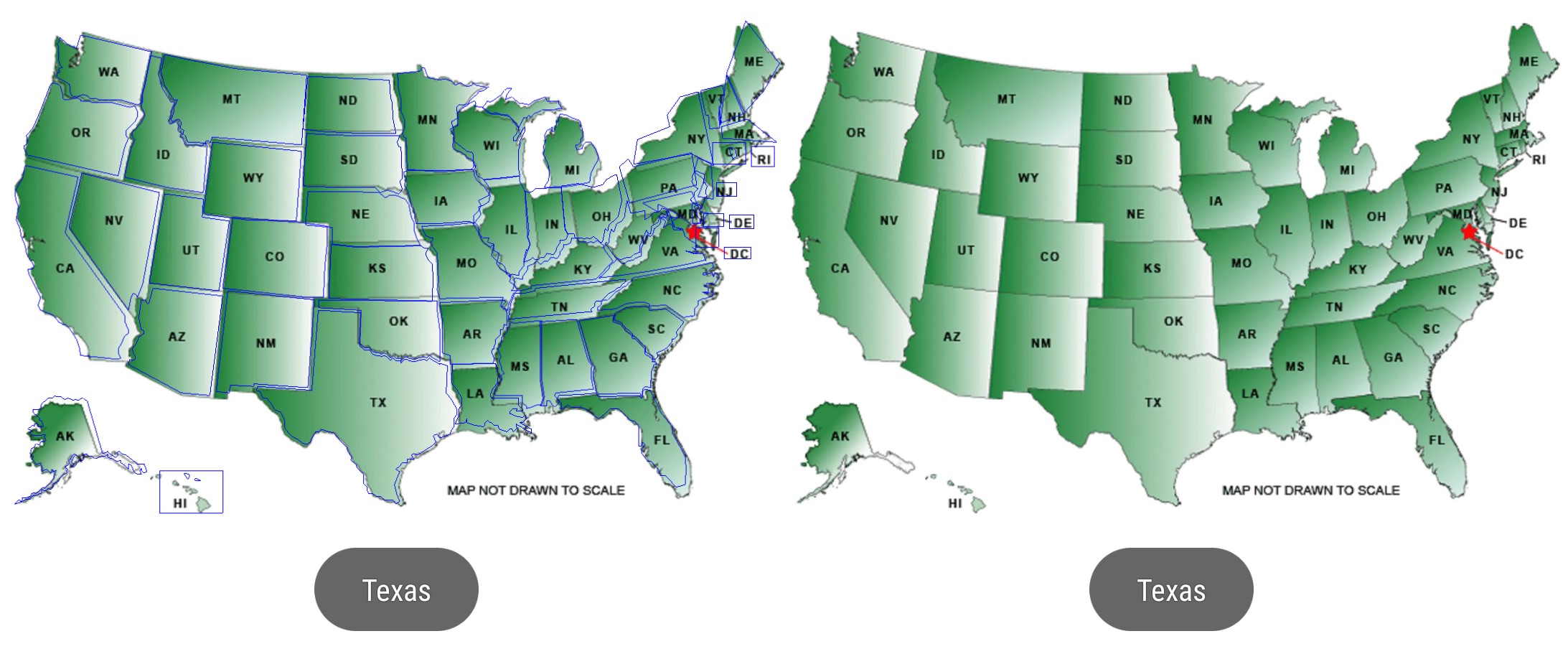
Extremely useful for handling touches on, for example, Europe map, or an eye of owl.
- Handling multiple maps on an image1, just like html <area> tag
- Batch mapping
- Interface to provide selected map id
- Debug mode to superimpose maps' polygon path on an image (the left in the screenshot)
- There is no limit but you need to be reasonable. In this example, I put about 50 polygon maps on the map in the screenshot above.
- From Android API 24
- Download
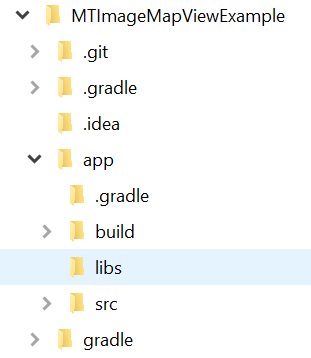
MTImageMapView-0.1-rc3.aar - Place it in the
libsfolder
- Edit
build.gradle.kts
dependencies {
...
implementation(fileTree(mapOf("dir" to "libs", "include" to listOf("*.aar", "*.jar"))))
}- or
build.gradle
dependencies {
...
implementation(fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['.aar', '.jar']))
}cleanandbuild
- Use tools like Gimp and generate a image map.
- Take only
[x,y]coordinate pairs of the map (e.g.[[123,456],[789,123],[456,789]]). - Write JSON in the following format.
[
{
"id": "Alabama",
"vertices": [[409,298],[409,298],[411,292],[409,279]]
},
{
"id": {
"name": "Alaska",
"code": "AZ",
"dial": 907,
"desc": "Alaska State Polygon Map"
},
"vertices": [[58,294],[56,293],[55,292],[54,292],[51,294]]
},
{
"vertices": [[163,213],[153,290],[131,288],[90,266]],
"description": "An area map without an id"
}
]- For the
idfield, you can use good-old string, object, or totally eliminate it if you want to. You can mix up with other fields such asdescription. - Nonetheless, the
verticesfield has to be there, and it should maintain coordinates in the aforementioned array format in #2. The field and format will be enforced in the future versions. - Instantiate
MTImageMapViewand implementMTImageMapTouchinterface. Then pass the map to the instance ofMTImageMapView. - In the example app, Square moshi is used for JSON decoding, but you can use whatever JSON decoder of your choice such as kotlinx.serialization as long as
List<MTPolygon>is produced.
val jsonMaps = assets.open("us_states.json")
.bufferedReader()
.use { it.readText() }
val moshi = Moshi.Builder()
.add(PolygonAdapter())
.build()
val mapList: List<MTPolygon> = moshi
.adapter<List<MTPolygon>>()
.fromJson(jsonMaps) as List<MTPolygon>
val usState : Drawable? = AppCompatResources
.getDrawable(applicationContext, R.drawable.us_states)
val mapView : MTImageMapView = findViewById(R.id.imageMapView)
mapView.setImageDrawable(usState)
mapView.setTouchedMapReceiver(this)
mapView.setShowPath(true)
mapView.setPolygons(mapList)- A US states image in size of 600 x 383 px.
- The polygon maps of the US states in JSON.
- ✨ The coordinates of a polygon map must be provided in an array of
[x, y]pairs inverticesfield. For the compatibility of upcoming updates, this format will be enforced. 🌟 - When you're to debug, it is convinient to split the screen space where touch event takes place from the logical space of
dpunit where you draw polygon maps on an image with graphic tools. It is necessary due to the situation in which every Android device has different screen dpi. MTImageMapTouchinterface delivers- Android native touch event in the screen pixel space,
- the point of touch in logical space, and
- the polygon map selected.
- At least 3 pairs of coordinates must present to form a polygon map.
- No "rect", "circle" type map is supported. "polygon" only at this time being.
- Dan Sunday's Fast Winding Number Algorithm
Copyright 2000 softSurfer, 2012 Dan Sunday
This code may be freely used and modified for any purpose
providing that this copyright notice is included with it.
SoftSurfer makes no warranty for this code, and cannot be held
liable for any real or imagined damage resulting from its use.
Users of this code must verify correctness for their application.
isLeft(): tests if the object's point (hence the point) is Left|On|Right of an infinite line.
Input : the point, P0, and P1
Return : >0 for the point is at the left of the line through P0 and P1
=0 for the point is on the line
<0 for the point is at the right of the line
fastWindingNumber(): winding number test for a point in a polygon
Input : polygon = vertex points of a polygon V[n+1] with V[n]=V[0]
point = a point
Return : wn = the winding number (=0 only when the point is outside)
- US states image and all coordinates are credited to Illinois Center for Information Technology and Web Accessibility
VER : 0.1-rc3
UPDATED : Mar. 6, 2024