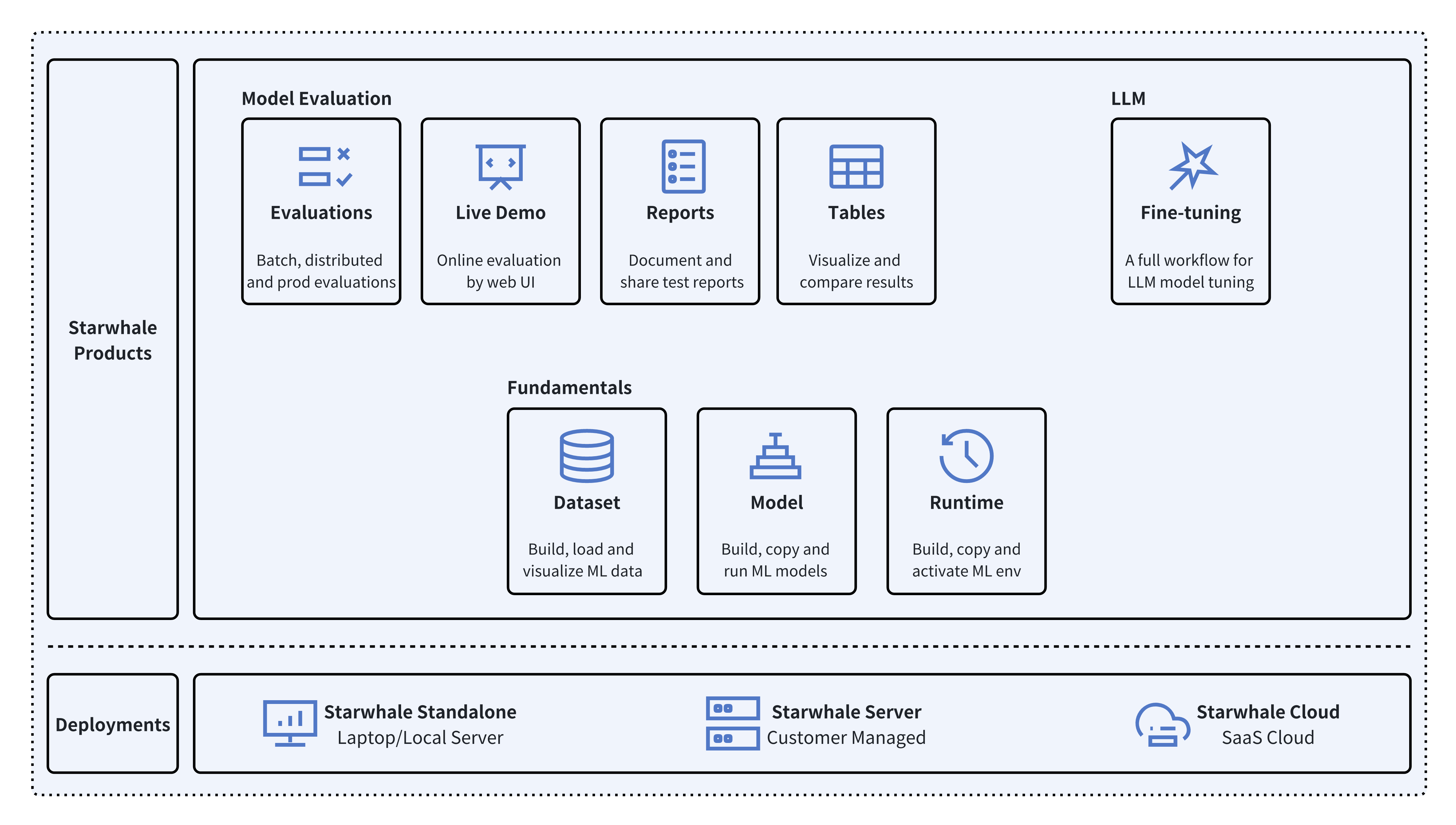
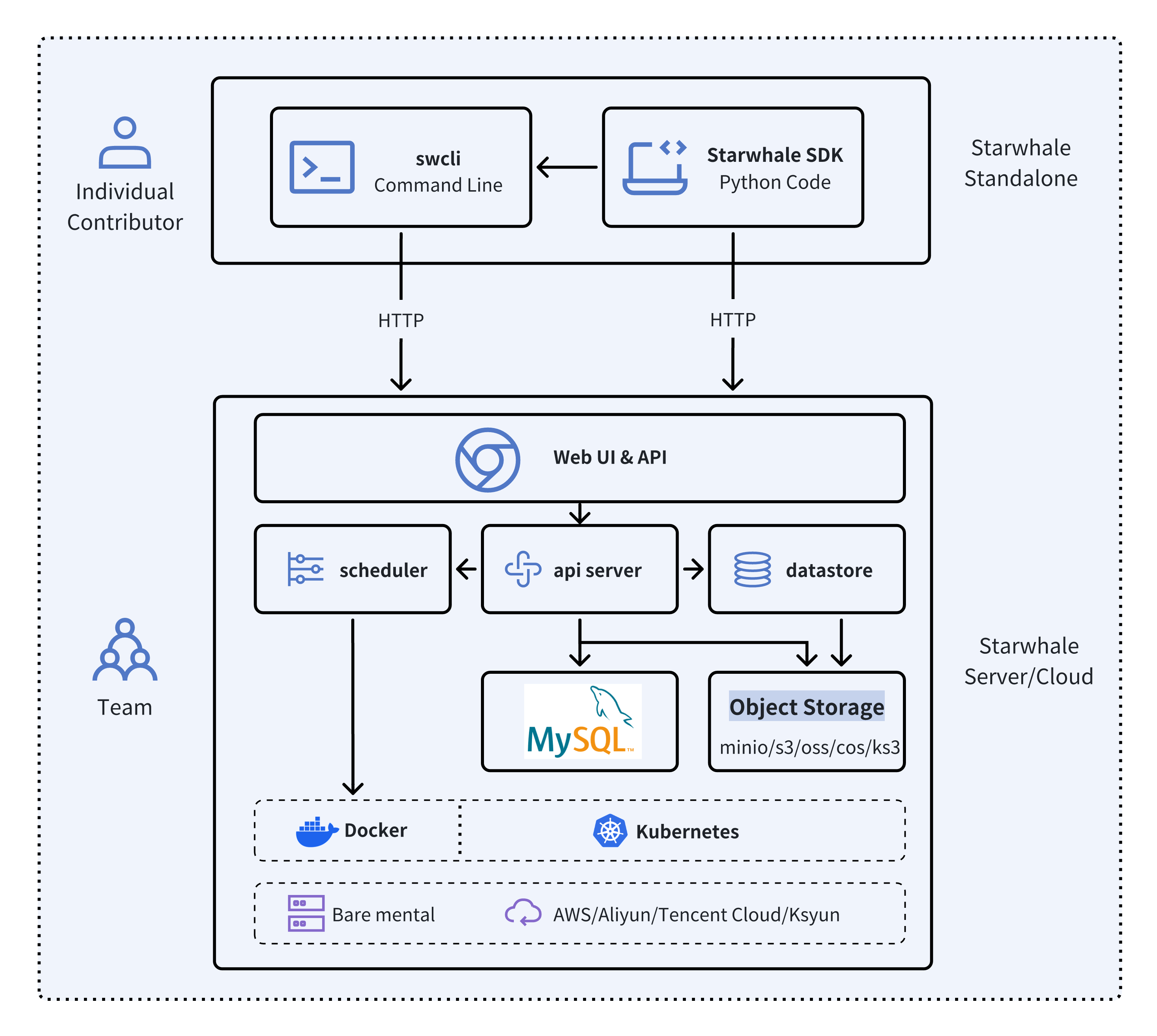
Starwhale is an MLOps/LLMOps platform that brings efficiency and standardization to machine learning operations. It streamlines the model development liftcycle, enabling teams to optimize their workflows around key areas like model building, evaluation, release and fine-tuning.
Starwhale meets diverse deployment needs with three flexible configurations:
- 🐥 Standalone - Deployed in a local development environment, managed by the
swclicommand-line tool, meeting development and debugging needs. - 🦅 Server - Deployed in a private data center, relying on a Kubernetes cluster, providing centralized, web-based, and secure services.
- 🦉 Cloud - Hosted on a public cloud, with the access address https://cloud.starwhale.cn. The Starwhale team is responsible for maintenance, and no installation is required. You can start using it after registering an account.
As its core, Starwhale abstracts Model, Runtime and Dataset as first-class citizens - providing the fundamentals for streamlined operations. Starwhale further delivers tailored capabilities for common workflow scenarios including:
- 🔥 Models Evaluation - Implement robust, production-scale evaluations with minimal coding through the Python SDK.
- 🌟 Live Demo - Interactively assess model performance through user-friendly web interfaces.
- 🌊 LLM Fine-tuning - End-to-end toolchain from efficient fine-tuning to comparative benchmarking and publishing.
Starwhale is also an open source platform, using the Apache-2.0 license. The Starwhale framework is designed for clarity and ease of use, empowering developers to build customized MLOps features tailored to their needs.
Starwhale Dataset offers efficient data storage, loading, and visualization capabilities, making it a dedicated data management tool tailored for the field of machine learning and deep learning
import torch
from starwhale import dataset, Image
# build dataset for starwhale cloud instance
with dataset("https://cloud.starwhale.cn/project/starwhale:public/dataset/test-image", create="empty") as ds:
for i in range(100):
ds.append({"image": Image(f"{i}.png"), "label": i})
ds.commit()
# load dataset
ds = dataset("https://cloud.starwhale.cn/project/starwhale:public/dataset/test-image")
print(len(ds))
print(ds[0].features.image.to_pil())
print(ds[0].features.label)
torch_ds = ds.to_pytorch()
torch_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(torch_ds, batch_size=5)
print(next(iter(torch_loader)))Starwhale Model is a standard format for packaging machine learning models that can be used for various purposes, like model fine-tuning, model evaluation, and online serving. A Starwhale Model contains the model file, inference codes, configuration files, and any other files required to run the model.
# model build
swcli model build . --module mnist.evaluate --runtime pytorch/version/v1 --name mnist
# model copy from standalone to cloud
swcli model cp mnist https://cloud.starwhale.cn/project/starwhale:public
# model run
swcli model run --uri mnist --runtime pytorch --dataset mnist
swcli model run --workdir . --module mnist.evaluator --handler mnist.evaluator:MNISTInference.cmpStarwhale Runtime aims to provide a reproducible and sharable running environment for python programs. You can easily share your working environment with your teammates or outsiders, and vice versa. Furthermore, you can run your programs on Starwhale Server or Starwhale Cloud without bothering with the dependencies.
# build from runtime.yaml, conda env, docker image or shell
swcli runtime build --yaml runtime.yaml
swcli runtime build --conda pytorch --name pytorch-runtime --cuda 11.4
swcli runtime build --docker pytorch/pytorch:1.9.0-cuda11.1-cudnn8-runtime
swcli runtime build --shell --name pytorch-runtime
# runtime activate
swcli runtime activate pytorch
# integrated with model and dataset
swcli model run --uri test --runtime pytorch
swcli model build . --runtime pytorch
swcli dataset build --runtime pytorchStarwhale Evaluation enables users to evaluate sophisticated, production-ready distributed models by writing just a few lines of code with Starwhale Python SDK.
import typing as t
import gradio
from starwhale import evaluation
from starwhale.api.service import api
def model_generate(image):
...
return predict_value, probability_matrix
@evaluation.predict(
resources={"nvidia.com/gpu": 1},
replicas=4,
)
def predict_image(data: dict, external: dict) -> None:
return model_generate(data["image"])
@evaluation.evaluate(use_predict_auto_log=True, needs=[predict_image])
def evaluate_results(predict_result_iter: t.Iterator):
for _data in predict_result_iter:
...
evaluation.log_summary({"accuracy": 0.95, "benchmark": "test"})
@api(gradio.File(), gradio.Label())
def predict_view(file: t.Any) -> t.Any:
with open(file.name, "rb") as f:
data = Image(f.read(), shape=(28, 28, 1))
_, prob = predict_image({"image": data})
return {i: p for i, p in enumerate(prob)}Starwhale Fine-tuning provides a full workflow for Large Language Model(LLM) tuning, including batch model evaluation, live demo and model release capabilities. Starwhale Fine-tuning Python SDK is very simple.
import typing as t
from starwhale import finetune, Dataset
from transformers import Trainer
@finetune(
resources={"nvidia.com/gpu":4, "memory": "32G"},
require_train_datasets=True,
require_validation_datasets=True,
model_modules=["evaluation", "finetune"],
)
def lora_finetune(train_datasets: t.List[Dataset], val_datasets: t.List[Dataset]) -> None:
# init model and tokenizer
trainer = Trainer(
model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer,
train_dataset=train_datasets[0].to_pytorch(), # convert Starwhale Dataset into Pytorch Dataset
eval_dataset=val_datasets[0].to_pytorch())
trainer.train()
trainer.save_state()
trainer.save_model()
# save weights, then Starwhale SDK will package them into Starwhale ModelRequirements: Python 3.7~3.11 in the Linux or macOS os.
python3 -m pip install starwhaleStarwhale Server is delivered as a Docker image, which can be run with Docker directly or deployed to a Kubernetes cluster. For the laptop environment, using swcli server start command is a appropriate choice that depends on Docker and Docker-Compose.
swcli server startWe use MNIST as the hello world example to show the basic Starwhale Model workflow.
- Use your own Python environment, follow the Standalone quickstart doc.
- Use Google Colab environment, follow the Jupyter notebook example.
- Run it in the your private Starwhale Server instance, please read Server installation(minikube) and Server quickstart docs.
- Run it in the Starwhale Cloud, please read Cloud quickstart doc.
-
🚀 LLM:
- 🐊 OpenSource LLMs Leaderboard: Evaluation, Code
- 🐢 Llama2: Run llama2 chat in five minutes, Code
- 🦎 Stable Diffusion: Cloud Demo, Code
- 🦙 LLAMA evaluation and fine-tune
- 🎹 Text-to-Music: Cloud Demo, Code
- 🍏 Code Generation: Cloud Demo, Code
-
🌋 Fine-tuning:
- 🐏 Baichuan2: Cloud Demo, Code
- 🐫 ChatGLM3: Cloud Demo, Code
- 🦏 Stable Diffusion: Cloud Demo, Code
-
🦦 Image Classification:
- 🐻❄️ MNIST: Cloud Demo, Code.
- 🦫 CIFAR10
- 🦓 Vision Transformer(ViT): Cloud Demo, Code
-
🐃 Image Segmentation:
- Segment Anything(SAM): Cloud Demo, Code
-
🐦 Object Detection:
- 🦊 YOLO: Cloud Demo, Code
- 🐯 Pedestrian Detection
-
📽️ Video Recognition: UCF101
-
🦋 Machine Translation: Neural machine translation
-
🐜 Text Classification: AG News
-
🎙️ Speech Recognition: Speech Command
-
Visit Starwhale HomePage.
-
More information in the official documentation.
-
For general questions and support, join the Slack.
-
For bug reports and feature requests, please use Github Issue.
-
To get community updates, follow @starwhaleai on Twitter.
-
For Starwhale artifacts, please visit:
- Python Package on Pypi.
- Helm Charts on Artifacthub.
- Docker Images on Docker Hub, Github Packages and Starwhale Registry.
-
Additionally, you can always find us at [email protected].
🌼👏PRs are always welcomed 👍🍺. See Contribution to Starwhale for more details.
Starwhale is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.