-
-
browser have a global window object, console.log and any function created with function keyword are in global but node use global object to store global property. By default function declared in node js file in included in global object
-
all js files are module and have module property which is used to export and import file
-
module have exports property, we can assign object or function in this module.exports property to export the functionality of that js file
-
to import js file we need to use require method with the file name with path. ie: require("./filename") or require("./filename.js")
-
the imported require method will return same data that was assigned in module.exports in that file
-
-
-
documentation https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v16.x/docs/api/
-
to import filesystem we use
require('fs')by convention we store it inconst fs=require('fs')- fs.readFileSync("fileNameWithPath","file-encoder")
- fs.writeFileSync("fileNameWithPath", StringToWrite);
-
Events
-
module name events
-
it returns a class
-
by convention we store it in
EventEmitter -
then we make an object
const emitter= new EventEmitter(); -
to add a listener we called it on method which takes the event name and a callback function
-
emitter.on("event1",()=>console.log("event1 called")) -
to trigger event we use
emitter.emit("event name"); -
to use event we can extends EvenEmitter class then we can export the object
const EventEmitter = require("events"); class MyEvent extends EventEmitter { emitLog() { this.emit("log"); } } const events = new MyEvent(); module.exports = events;
-
using http module: import
httpmodule,then usecreateServermethod to create server, create server needs ahandler functionwhich takesrequestandresponseas parameters.then matchrequest.url, then if matched useresponse.write()to write response then useresponse.end()to send the response, then listen to desire portserver.listen(port);const http = require("http"); const server = http.createServer(serverHandler); server.listen(3000, () => console.log("listening on port 3000")); function serverHandler(request, response) { switch (request.url) { case "/": response.write("hello nodeJs Server"); return response.end(); case "/users": const users = [{ name: "user1" }, { name: "user2" }]; response.write(JSON.stringify(users)); return response.end(); default: response.write("404 not found"); return response.end(); } }
-
-
-
-
- initializing node package
- npm - Node Package Manager, node package repository, auto installed with node
- address npmjs.com
- node -v / node --version to get installed node version
- npm -v to check installed npm version
- npm i -g [email protected] , to install npm version 6.14.5 globally, i shorthand for install and -g shorthand for global
- npm init to initialize npm project, this will ask some question about the project like project name, version,author etc,
- npm init --yes / npm init -y to init the project with all default answer
-
- Installing packages and package dependency
- will use date-format package
- search date-format in npmjs.com
- address https://www.npmjs.com/package/date-format
- uses instruction is given in the documentation
npm i date-formatto install date-format- under node_modules date-format file will be installed
- there will also change in package.json, the date-format property will be added under dependency property
- in package-lock.json, there will be package installation url
- under node_modules folder inside date-format there is another package.json file, inside this if any other dependency package is needed that file is also be installed under node_modules folder
- so after working on project and adding or install any packages will increase the size of node_modules folder
-
- using packages
- require(''), lookup order:
- first it will check built-in modules
- then it will check any installed module in local node_modules folder
- if we need to import our own module then we will use relative path of that file, "./relative_path/filename"
- documentation address https://www.npmjs.com/package/date-format
- to use the date-format module we use
const dateFormat=require('date-format')
-
- Semantic Versioning
- npm i // will install all required package that is in package.json file
- npm list // will display the modules that is installed by npm
- npm list // will also display the installed dependency
- versioning
- sample version values:
"date-format": "^3.0.0" - the numbers are Major.Minor.Patch
- this versioning process is called semantic versioning
- bug fix is Patch update, it will increase Patch part by 1
- old feature with new feature will update Minor version 1.1.1=>1.2.0
- existing functionality change with added new feature,or the api is changed,then update major, 1.1.1->2.0.0
- sign before version:
- ^ Caret sign : will update to latest minor version // shorthand 1.x
- ~ tilde [Teelda]: will update latest patched version // shorthand 1.1.x
- 1.1.1 is exact version, is written without any sign
- in npm => npm i [email protected] to specify exact version
- sample version values:
-
- DevDependencies and Global Package
- dev dependency is used when we need the package while developing not while running the app
- to install package as dev dependency we use
npm i package-name --save-dev - package will be saved under dedDependency property
- some package needs to be installed globally, ie: nodemon is a global package of npm, it helps to reload development server after code change
- the flag for global package is
-gor--global npm list -gto view globally installed packages- root option will show the root of the app
npm root npm root -gwill show the root of global package
-
- Updating and Uninstalling Packages
npm outdatedwill show packages updatable information like current version, wanted latest version and actual latest versionnpm updatewill update package if it updatable- for global packages
npm outdated -gnpm update -g
- to uninstall package use npm
uninstallorunthen package name, if the package is global then add-gflag
-
- Publishing Packages
npm adduserto register to npmjsnpm loginto login to npmjs- then make sure the package name in unique in npmjs to check for package name use
npm search package-name, and have a index.js withmodule.exports - then
npm publishto publish, must verify email address before publish npm version major|minor|patchwill update the version, or we can manually update package.json
-
-
-
- version controlling system keep tracks of file modification and can revert changes and helps managing a project including multiple person developing same project
- install git from https://git-scm.com/downloads
- just stick to default is enough
- to check if git is installed
git --version - then add few config to configure git
git config --global user.name "Name Of The User"git config --global user.email [email protected]git config --listto see all configs
-
- to initialize git
git init git statusto check the status- untracked file is also called unstaged file
- to add changed file into staged file use
git add filename1 filename2 ...orgit add . git commit -m"commit message"to make a new pointgit loggit detail loggit log --onelinegit log in oneline // sort version- head works like cursor pointer in a text editor, where the head is pointing the files will be on that version
- to initialize git
-
git checkout commit-id filenameto see that old committed filegit checkout -- filename.extto revert to the latest file version- use a
.gitignorefile to list any files or directory to ignore from git, it help full for ignoring dependency that can be installed from file, any build directory, or any log file that is not mandatory for project. - for only filename we use just
filename.ext - for directory we use forward slash '/'
/ignore-directory-name - 'node_modules' is an example we can ignore it in gitignore
/node_modules
-
- git is a version controlling system, while github provide online or cloud version of git system.
-
-
-
-
var and let
-
var is function scoped and let is block scoped
-
var has Hoisted, or it can be used before declaration
-
x = 5; var x;
-
let is not hoisted, variable declared in let cant be used before
-
const is same as let but cannot be reassigned
-
const a=20;then we cannot doa=10 -
const array and object can be modified though
-
-
-
- arrow functions are bind this where it created but normal functions are not bind this property
- syntax
()=>1; // is same as function(){ return 1 } // if there is only one parameter we can ignore the first bracket pair number=>number*2; //is same as function (number){ return number*2; } ()=>({ name:1, id:2 }) //is same as function (){ return { ..... } } // if there is other statement inside function block then we need to use curly brackets ()=>{ let random=Math.random(); return random; }
-
- class example
class MyClass { madeIn = "Bangladesh"; // this is new feature it will automatically add to constructor function // a constructor function is method of class which get called when a new object is created using the class constructor(color, passenger) { this.color = color; // here this is referred to the object this.passenger = passenger; } whatColor() { console.log(this.color); } } class MyEnhancedClass extends MyClass { constructor(modelName, color, passenger) { super(color, passenger); // must call super inside derivate class constructor, also need to supply super class constructor argument or else those will be empty this.modelName = modelName; } }
-
- Spread operator, ... before array or object name. it will make the array or object flat one level, like ...[1,2,3] will be 1,2,3 no array
- ie: array=[1,2,3] , newArray=[...array,4,5,6];// result will be newArray=[1,2,3,4,5,6];
- it will work same on object
- rest operator/parameter, The rest parameter syntax allows a function to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array, providing a way to represent variadic functions in JavaScript.
- (number1,number2,...rest)// then any other argument send to this function other then number1 and number2 will be in rest array, rest is variable name, so this name can be any name, also number1 and number2 is not mandatory
-
- ie array=[1,2,3]; const [a,b,c]=array; or , const [a,b]=array; or const [a,,c]=array; or object={name:"rahat"}, const {name}=object
-
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const squares = numbers.map((number) => number * number);
-
-
-
- synchronous or blocking pattern, waits for statement to be finished
- asynchronous or non blocking pattern, does not wait for a statement to finished, we need it when we works with any io, ie: fetching data from db.
-
-
sync approach:
const students=getStudents(); console.log(students);// here students is undefined // mock function to get data from db function getStudents(){ console.log("getting data from db"); return setTimeout(()=>{name:"rahim",id:1},500); }
-
the problem with this approach is js uses non-blocking or async pattern by default.it will not wait for setTimeout function to be finished. thats why students will have a undefined value.
-
to solve this problem we can use a callback function, when a function accept another function as parameter is call callback function. here inside setTimeout the function is used is a callback function.
-
async approach:
getStudents((students)=>console.log(students); function getStudents(callback){ setTimeout(()=>callback({name:"rahim",id:1}),500); }
-
-
-
this happens when we need to wait for some data, and based on that data if we need to again use any i/o intensive work or get data from a db then we need to use the callback again. this will become very complex in no time. this callback inside a callback approach is called callback hell. there can be many callback inside another callback.
-
ie
getUser((userName) => getGitRepository(userName, (repository) => getRepositoryItems(repository) ) );
-
-
-
ie: instead of using anonymous function we can use named function
getUser((userName,getGitRepository(repository,getRepositoryItems(repository)));
-
-
-
-
-
real life promise
- we promise to do a job in future, until we do this job it is in not done state
- in future if the job is done then we say promise is completed or fulfilled
- if not completed we say did not keep the promise
-
in js the promise object will have a in pending state until the promise return a complete or failed status
-
if it complete then the state is resolved
-
if it failed then the state is rejected
-
example code:
const jobDone = new Promise(jobDonePromiseHandler); function jobDonePromiseHandler(resolve, reject) { setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000); //this will resolve in 1 seconds setTimeout(() => reject(0), 2000); //this will reject in 2 seconds } jobDone .then((data) => console.log(data)) .catch((error) => console.log(error));
-
-
-
getUser(userName) .then(getGitRepository) .then(getRepositoryItems) .catch(catchError);
-
-
- async-await helps asynchronous code look like synchronous, that help for better understanding
async function getUserData() { try { const userDetails = await getUser(userId); const repository = await getGitRepository(userDetails); const repositoryItems = await getRepositoryItems(repository); } catch (error) { console.log(error); } }
- async-await helps asynchronous code look like synchronous, that help for better understanding
-
-
-
- browser=>client/user
- server=> where the expected resource/ web site stored
- URL -> Uniform Resource locator, ie: www.google.com
-
- application 1 <--API--> application 2
- API -> Application Programming Interface
- Among many there is REST API
- REST -> Representational State Transfer
- RESTful api uses HTTP Request and HTTP Response
- RESTful concept
- Resource/Nouns
- Any information provided by rest api or endpoint
- uses URI to communicate
- ie
- example.com/books
- example.com/books/4
- example.com/authors
- Methods/Verb
- actions to be perform on resource
- perform CRUD (Create Read Update Delete) operation
- HTTP POST -> Create
- HTTP GET -> Read
- HTTP PUT/PATCH -> Update
- HTTP DELETE -> Delete
- Representation
- How to data is presented, or how client will get the data when perform an action to the api
- most used format is JSON and XML
- Resource/Nouns
- Crud Operation details
- GET https://example.com/books // this will get all book information in Json format
- GET https://example.com/books/1 // get book details of book id 1
- POST https://example.com/books {"bookName":"book name"} // will create new book
- PUT or PATCH https://example.com/books/1 {"bookName":"new book name"} // will update book name of id 1
- Delete https://example.com/books/1 // will delete book of id 1
-
- rest api link and example https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/
-
-
-
-
init npm :
npm init -y -
use the basic http module
-
create a basic http
const http = require("http"); const server = http.createServer(serverHandler); function serverHandler(request, response) { switch (request.url) { case "/": response.write("this is index page"); return response.end(); case "/home": response.write("this is home page"); return response.end(); default: response.write("404 page not found"); return response.end(); } } server.listen(3000, () => console.log("listening to port 3000...."));
-
it is not suitable to maintain http server using built-in http module
-
instead we will use express package
-
install the express package
npm i express
-
-
-
-
created server using express,
-
first require express and put it in a constant
-
then call the express and store it in app constant
-
here is the sample code
const express = require("express"); const app = express(); app.get("/", (req, res) => { res.send("hello from express"); }); app.get("/students", (req, res) => { const students = ["rahim", "karim"]; res.send(JSON.stringify(students)); }); app.listen(3000, () => console.log("listening on port 3000"));
-
we need to install nodemon, nodemon is a global package, it watch for changes in file and if changed automatically restart the file.
-
install nodemon globally
npm i nodemon -g -
run app file using nodemon
nodemon app.js
-
-
-
download postman and install it,postman help to send http request,like post,patch,delete. In browser we can do the same but we need to setup custom page/script to send different http request. But postman have all features.
-
used mocked db.json file to replace db
-
read the db.json file using fs module
-
code
fs.readFile("./db.json", "utf-8", (err, data) => { const students = JSON.parse(data).students; res.send(JSON.stringify(students)); });
-
-
-
used
app.post("/api/students",()=>{})method to receive post request, post request on same uri is used to create new resource, in this case will create new student object -
to get the sended data to this uri we used a middleware express.json(),
app.use(express.json()), after this we can receive data inreq.body -
we first loaded the db.json, and inserted the new student object in db by
db.students.push(student) -
then we save the db object as json using
fs.writeFile("filename", JSON.stringify(db), (error) => { // now the file is saved, we need to return the created student data using `res.send()` });
-
-
- db.json is formatted as only array of student object
- created new db module to handle db.json file read and write
- create two promises to handel read and write, getStudent and insertStudent
- imported new db module in app.js and used new function in async-await syntax
-
- we used hard coded uri, using route parameter we can use dynamic uri
- syntax
uri/:variable-nameie: for getting a id from uri we can use/api/students/:id - this id is accessed by
req.params.id - then we simply used the find method of array to find the id and then send the student data;
- we converted id string to integer
- if student not found we send a status code of 404, ie:
res.status(404).send("any message")
-
- used app.put to handle put request which is used to update a resource
- created new function updateStudent
- updated the index if the given id is there
-
- used app.delete to handle delete request
- created deleteStudent function
- to keep the id valid, no element has been deleted just added deleted flag
-
-
-
- all callback function of are replaced with named function then moved them to separate file under controllers folder
- them exported them
-
- the routes are grouped using
app.route - then moved the route to separate file under Routes
- imported students from controllers and provided the named function accordingly
- then used Router from express
Router=express.Router()and replace app by Router - then exported the Router object
- the routes are grouped using
-
- in app.js imported the Student router file.
- then used
app.use("/api/students",studentsRoutes)to replace old students router - in student routes file we change the uri to
/api/studentsto/because when we used the app.use we already specified the uri for that resource, if we still keep the/api/studentsinRoutes/students.jsfile then our endpoint will become/api/students/api/studentswhich we don't want
-
-
-
-
middleware is a function that execute before sending response to client,
-
we already used three middlewares,
app.use(express.json()),app.use("",studentRoutes)andapp.get("/",(req.res)=>res.send("hello world")); -
these are built-in middlewares, we can make our own middleware, middlewares are used to apply restriction to our endpoint, to receive json object etc,
-
middleware take 3 parameters,
request,response and nextwe already know request and response, the next is callback, we need to call next to say we want to continue the pipeline of middlewares, -
after using res.send there will be no next call, the response will be send
-
example
app.use((req, res, next) => { req.body.app = "Node"; // add this property to all request next(); //then call next middleware });
-
middlewares are called in the serial it written - top to bottom
-
-
- done in previous section
-
- the request object is when a client send a request
- the response object is server is sending the data to client
- express use almost everything as middleware
- a middleware have the access of request and response object and a callback next function that we use to pass control to next middleware in the pipeline
- then when we send the response it complete the request-response cycle
- after completing request-response cycle it all not process any middleware after response.send
-
-
express.urlencoded({extended:true})to handle data passed in url ?data1=hello&data2=world -
to send this type of data in postman we need to use the
x-www-form-urlencodedsection while sending data instead of json -
to use static file we use
express.static("root-folder-name"); -
ie :
express.static("public");our static files will be served from public folder-
example
app.use(express.static("public")); app.use("/static", express.static("public"));
-
the folder is relative to app file
-
if the folder is in other location is better to use absolute location
-
example
const path = require("path"); app.use("/static", express.static(path.join(__dirname, "public")));
-
-
-
-
- those middleware are not from express, they are written by others
- we will use a middleware call morgan
- it show request data in console log
- installation
npm i morganconst morgan = require("morgan")- app.use(morgan('dev'))// there is dev,tiny,combined etc
- this will console.log the request type,requested uri, respond code, response time
-
-
-
- mongo is a no-sql database, it store data as json object
- we used db.json file to store our data with the help of db.js file
- in real life we keep our data in a database
- with node we will use mongo db
- each data in mongo db is called document
- is document have a unique id and can have array with object or object with array, as wel as nested object
- same type of document is called collection
- we need to download to mongo db from its website mongodb.com
- from Software->community-server ==> free and open source
- enterprise server will be used when we use it under a company or the paid version of this server
- now download the community server for windows as msi
- select complete , uncheck install mongodb-compass
- and leave everything default and install it
-
- at this point mongoDB server will try to run as a windows service, but the default setup store db data to
c:\data\dbthats why we need to create a folder calldatain c: directory, then inside data folder we need to create a folder named db - now we can restart mongoDB service from windows service manager or from task manager
- default mongodb listen to 127.0.0.1:27017
- add mongo db to environment path
- open advanced system setting
- under
advancedtab openEnvironment variablesbutton - now edit path from system variable
- then new and paste the copied monogodb path , my path is
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\5.0\bin - now restart terminal or cmd window and type mongo
- if you get a mongo console then its working
- otherwise you need to check if mongoDB service is running or not, the path is added to system environment variable
- you can also restart your pc if above is ok but still mongo console is not working
- you can manually run mongodb server by running mongod command, and leave it open until you finished your work
- at this point mongoDB server will try to run as a windows service, but the default setup store db data to
-
- in terminal or cmd type mongo and enter in mongo console
use my-dbwill select my-db if my-db exist or will create and then select my-dbdb.collectionwill create the collection or exist will use that collection and then select that collection- db.collection have many methods, among them
insertOneandinsertMany. insertOnewill use when we want to insert only one document.insertManywill use when we want to insert more than one document, and must be in array- the json data can be js object, mongo then will convert to json object
- while inserting data mongo will automatically insert a unique id for that document
db.collection.students.insertOne({name:"saikot",age:20,hobbies:["music","gardening"]})insertMany([student1,student2])....db.collection.students.find()will give all students documentshow dbswill show all database list- again to switch a database we use
use db-name
- in terminal or cmd type mongo and enter in mongo console
-
db.collection.students.find()to show all documents of students collection.find().pretty()will show json with prettier.find({name:"saikot"})will show only documents exact matchedname:"saikot"property and value.find().limit(1)will limit the result to limit- using greater than and less than we will pass an object rather than exact value with
$keyword:value- keyword: lt->less than, gt->greater than, gte and lte , e is or equal
{age: {$gte:18}}here this will find all document with age greater than or equal 18
- multiple key:value find
find({name:"saikot",age:{$gt:18}})this will works asandfind({$or:[{name:"saikot"},{age:{$gt:18}}])will works asorwe need to useorkeyword and pass the or object as array
-
- when we use $ sign is call operator
- db.collection.students.updateOne({name:"saikot"},{$set:{age:21}})
- this will return an object of the operation
{ "acknowledged" : true, "matchedCount" : 1, "modifiedCount" : 1 }- updateOne will update only one document
- we will use
.updateMany()if we want to update more than one documents replaceOneandreplaceManywill replace whole document, not just update provided object- delete
.deleteOne({filter}),deleteMany({filter})will delete document/(s) that match filter
- Official doc for crud
-
- download mongodb compass from mongodb website
- go here and download stable zip version for windows
- extract the zip file and open mongodbCompass.exe file
- on new connection page there will be an option
fill in connection fields individuallyclick there to open individual field - from default installation of mongodb we know that server location is 127.0.0.1 or localhost and the port 27017
- these default fields will there already so we just need to click on connect to connect with mongodb server
- from the app we can perform all crud operation we did on mongo console
-
-
-
-
in an empty mondo folder init npm and install mongoose
-
npm init -ynpm i mongoose -
simple use of mongoose
const mongoose = require("mongoose"); mongoose .connect("mongodb://localhost:27017") .then(() => console.log("connected to mongodb")) .catch((error) => console.error("couldn't connect to mongodb"));
-
so we require and put in in mongoose const
-
then we call mongoose connect method and pass mongodb uri
-
since it return a promise we can chain it with a then and catch block
-
-
-
-
see documentation mongooseJs.com
-
schema
-
define the document structure of a collection
-
mongoose start or work with schema
-
each schema mapped to a mongoDB collection
-
mongoose.Schema() is a class
-
Schema accept an object of property types
-
for example
const testSchema = mongoose.Schema({ title: String, // String is shorthand for {type: String} author: { type: String }, body: String, comments: [{ body: String, date: Date }], date: { type: Date, default: Date.now }, hidden: Boolean, meta: { votes: Number, }, });
-
{keyName:keyType}
-
there are String,Number,Boolean,Date
-
we can also do like: body:{type:String,default:"this is great content"}
-
so we can use an object to describe the type and also the default value
-
another example
const testSchema = mongoose.Schema({ firstName: String, lastName: String, dob: Date, entryDate: { type: Date, default: Date.now }, passed: Boolean, hobbies: [String], parents: { father: String, mother: String, }, subject: [ { name: String, marks: { type: Number, min: 0, max: 100 } }, ], });
-
when the property has an object with type property then it treat it as type, else it treat it as structure
-
-
-
-
-
- schema types is configuration object of individual property
- the types are
- String, Number, Date, Buffer(binary data), Boolean, Mixed(all types are mixed), ObjectId, Array, Decimal128(128 bit decimal), Map(map structure), Schema
- Mixed,ObjectId,Decimal128 uses Schema.Types.Mixed/Objectid/Decimal128
- if we need a property named
typewe need to define that property with configuration object, ie:{type:{type:String}}
-
-
using the schema file we can make model of a collection
-
Student=model("Student",studentSchema) -
model returns a class, then we can use this class to make an object
-
ie:
const Student = model("Student", studentSchema); const newStudent = new Student({ firstName: "Karim", lastName: "Sarkar", dob: new Date("21 April 1996"), passed: true, hobbies: ["traveling"], parents: { father: "A", mother: "B", }, subject: [ { name: "Math", marks: 79 }, { name: "English", marks: 84 }, ], }); newStudent.save().then((data) => console.log(data));
-
then we can call it save method. the save method return a promise, we can use then catch chain or use async-await syntax
-
-
-
create example,
const newStudent = new Student(studentObject); const [saved, error] = await of(newStudent.save());
-
read example, will use find method, will work all mongo console example
-
limit will limit the result, sort will sort the document 1 is ascending ,-1 descending
const [students, error] = await of( Student.find() .select("firstName lastName") .limit(4) .sort({ firstName: -1 }) );
-
-
-
-
find().countDocuments()will return the count of documents return by find -
example
const updateStudent = async (id, updateObject) => { const [updateResult, updateError] = await of( Student.updateOne( { _id: id }, { $set: updateObject, } ) ); if (updateError) return console.error(`There was this error: `, updateError); console.log(`Update successfully, result`, updateResult); }; updateStudent("613a12a035240311bc9eb527", { passed: false });
-
delete example
const deleteStudent = async (id) => { const [deleteResult, deleteError] = await of( Student.deleteOne({ _id: id }) ); if (deleteError) return console.error(`There was this error: `, deleteError); console.log(`Delete successfully, result`, deleteResult); }; deleteStudent("613a5c56781af74eee88a81b");
-
-
-
example
const breakfastSchema = new Schema({ eggs: { type: Number, min: [6, "Too few eggs"], max: 12, }, bacon: { type: Number, required: [true, "Why no bacon?"], }, drink: { type: String, enum: ["Coffee", "Tea"], required: function () { return this.bacon > 3; }, }, }); const Breakfast = db.model("Breakfast", breakfastSchema); const badBreakfast = new Breakfast({ eggs: 2, bacon: 0, drink: "Milk", }); let error = badBreakfast.validateSync(); assert.equal(error.errors["eggs"].message, "Too few eggs");
-
-
custom error
const breakfastSchema = new Schema({ eggs: { type: Number, min: [6, "Must be at least 6, got {VALUE}"], max: 12, }, drink: { type: String, enum: { values: ["Coffee", "Tea"], message: "{VALUE} is not supported", }, }, dob: { type: Date, validator: { validate: (value) => value > new Date("1 January 1950"), message: "you are too old for this program", }, }, }); const Breakfast = db.model("Breakfast", breakfastSchema); const badBreakfast = new Breakfast({ eggs: 2, drink: "Milk", }); let error = badBreakfast.validateSync(); assert.equal(error.errors["eggs"].message, "Must be at least 6, got 2"); assert.equal(error.errors["drink"].message, "Milk is not supported");
-
-
example
//single line console.log(error.message); // multiple validation errors or error have errors property // error.errors, the error key is is the key defined in the schema for (const errorKey in error.errors) { console.log(error.errors[errorKey], error.errors[errorKey].message); }
-
-
-
- copied my-express project, changed it name to my-express-mongo
- cleanup db.json and db.js related files
- cleanup any other unused codes
- created models folder for mongoose
- this model will link mongoose to mongodb
-
-
const { Schema, model } = require("mongoose"); const studentSchema = Schema({ name: { type: String, required: true }, age: { type: Number, min: 0 }, hobbies: { type: Array, of: String, validate: { validator: (value) => value.length > 0, message: "There must be at least 1 hobby!", }, }, }); const Student = model("Student", studentSchema); module.exports.Student = Student;
-
-
-
code,
const mongoose = require("mongoose"); mongoose .connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/my-express-mongo") .then((e) => console.log("connected to mongo db")) .catch((e) => console.error("couldn't connect to mongodb"));
-
removed few
db.jsimport
-
-
-
const errorBadRequest = (res, { errors }) => { const message = []; for (const errorKey in errors) { message.push(errors[errorKey].message); } return res.status(400).send(message); };
-
create
const create = async (req, res) => { const studentName = req.body.name; const [saveResult, saveError] = await of(new Student(req.body).save()); if (saveError) return errorBadRequest(res, saveError); res.send(saveResult); };
-
postman request incorrect
{ "name": "sultan saikot", "age": -1, "hobbies": [] } -
correct
{ "name": "sultan saikot", "age": 30, "hobbies": ["music", "gardening"] }
-
-
- example code ```js const errorNotFound = (res) => { return res.status(404).send("Resource not found!"); }; const list = async (req, res) => { const [students] = await of(Student.find().sort({ name: 1 })); res.send(students); }; const item = async (req, res) => { const [findStudent, findStudentError] = await of( Student.findById(req.params.id) ); if (findStudentError || !findStudent) return errorNotFound(res); res.send(findStudent); }; ``` -
-
put example
const update = async (req, res) => { const [updateResult, updateError] = await of( Student.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, req.body, { new: true }) ); if (updateError || !updateResult) return errorNotFound(res); res.send(updateResult); };
-
delete example
const remove = async (req, res) => { const [deleteResult, deleteError] = await of( Student.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id) ); if (deleteError || !deleteResult) return errorNotFound(res); res.send(deleteResult); };
-
-
-
-
-
authentication: can login
-
authorization : have access to content/data
-
code
const userSchema = Schema({ name: { type: String, required: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 100, }, email: { type: String, require: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 255, unique: true, }, password: { type: String, required: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 1024, }, }); exports.User = model("User", userSchema);
-
-
-
model
const userSchema = Schema({ name: { type: String, required: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 100, }, email: { type: String, require: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 255, unique: true, }, password: { type: String, required: true, minlength: 5, maxlength: 1024, }, }); exports.User = model("User", userSchema);
-
controller - create
const create = async (req, res) => { const [findResult, findError] = await of( User.findOne({ email: req.body.email }) ); if (findError) return errorBadRequest(res, findError); const [saveResult, saveError] = await of(new User(req.body).save()); if (saveError) return errorBadRequest(res, saveError); const { email, name } = saveResult; res.send({ email, name }); };
-
fixed helper controller,
const errorBadRequest = (res, error) => { const { errors } = error; if (!errors) return res.status(400).send(error.message); //... };
-
-
- code
const bcrypt = require("bcrypt"); // create const [newUser, newUserError] = await of(new User(req.body).validate()); if (newUserError) return errorBadRequest(res, newUserError); const salt = await bcrypt.genSalt(10); const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(req.body.password, salt); const { email, name } = req.body; const password = hashedPassword; const [save, saveError] = await of( new User({ email, name, password }).save() );
-
example
const bcrypt = require("bcrypt"); const hashPassword = async (password) => { const salt = await bcrypt.genSalt(10); await bcrypt.hash(password, salt); return await bcrypt.hash(password, salt); }; hashPassword("saikot").then((pass) => console.log(pass));
-
-
/api/authwill receive email and password to authenticate user -
used save create user code but now to check it against server
-
code
const create = async (req, res) => { const [user, findError] = await of( User.findOne({ email: req.body.email }) ); if (findError || !user) return errorBadRequest(res, { message: "invalid email/password" }); const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.compare( req.body.password, user.password ); if (!hashedPassword) return errorBadRequest(res, { message: "invalid email/password" }); res.send({ message: "Logged in successfully" }); };
-
-
- jwt is like a passport and the validator is server, so is nearly impossible to modify this token and it helps the stateless architecture
- more on jwt.io
- is three part encoded string
- #1 is algorithm type,#2 payload/data #3 verify signature
- the part 3 is important, it ensures the data is generated from server, on server it uses a private key to sign the data, this makes sure no one from outside can't generate the signature
npm i jsonwebtokenconst jwt=require("jsonwebtoken")const jwtToken=jwt.sign(data,secretKey);
-
-
separate app file into app and server file, express related files are in app file and other files are in server file
-
install dotenv
npm i dotenv -
import and apply configs from
config.envfile -
code
const dotenv = require("dotenv"); dotenv.config({ path: "./config.env" }); // alternate require("dotenv").config({ path: "./config.env" });
-
now we can get the variable from
process.env.VARIABLE_NAME -
env variable name should be all uppercase like const variable naming convention
-
used
morganif app is in development mode
-
-
- added JWT_SECRET in config.env
- get the jwt_secret from env
process.env.JWT_SECRET
-
- in user controller
res.send({ message: "Signed up successfully", token: save.generateJWTToken(), data: { email, name }, });
-
in auth controller
res.send({ message: "Logged in successfully", token: user.generateJWTToken(), });
-
in user model
userSchema.methods.generateJWTToken = function () { return jwt.sign( { _id: this._id, email: this.email }, process.env.JWT_SECRET ); };
-
-
-
- see the
req.header()method - it extract the value of header key , ie:
req.header('Authorization')
- see the
-
-
authorize middleware
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken"); module.exports = function (req, res, next) { const token = req.header("Authorization"); const jwtToken = token ? token.split(" ")[1] : null; if (!jwtToken) res.status(401).send("Not Authorized"); try { req.user = jwt.verify(jwtToken, process.env.JWT_SECRET); next(); } catch (error) { res.status(400).send("Bad request"); } };
-
-
created users/me end point
-
there is no need to build any logout endpoint, since we only generating token and not storing it elsewhere the token can be removed easily from client side to make the logout functionality
-
-
updated user model
```js role: { type: String, enum: ["admin", "user"], default: "user", }, //// jwt.sign( { _id: this._id, email: this.email, role: this.role }, process.env.JWT_SECRET ) ``` -
added admin middleware
module.exports = function (req, res, next) { console.log(req.user); if (req.user.role !== "admin") return res.status(403).send("Forbidden"); next(); ;
-
note must update jwtToken generator to have role field and must call authorize middleware before admin middleware, admin middleware use req.user object set by authorize middleware
-
for multiple middlewares we pass array of middlewares
-
-
-
-
-
created a burger-builder-api folder under section f
-
initiate npm
npm init --yes -
installed needed packages
npm i dotenv express morgan bcrypt jsonwebtoken joi cors lodash -
created new folder and files
-
files: app.js server.js .env .gitignore
-
folders: controllers,models,routes,middlewares
-
-
-
-
created user schema and model and added a method generateJWT
-
added 3rd parameter in jwt.sign method, passed {expiresIn:time}, here time in second as int and in hour like "1h" as string
jwt.sign({ _id: this._id, email: this.email }, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: "1h", // time in second ie: 60*60 for 1 hour, or string like "1h" });
-
-
-
import Joi from 'joi'
-
code example
const userValidationSchema = Joi.object({ email: Joi.string().email().max(255).required(), password: Joi.string().max(255).min(8).required(), }); const validateUser = function (user) { const { error } = userValidationSchema.validate(user, { abortEarly: false, }); return error ? error.details.reduce( (previous, current) => [ ...previous, { key: current.context.key, message: current.message }, ], [] ) : null; };
-
exported validateUser from user model
-
used abortEarly:false in joi schema validate to grub all error message at once
-
-
-
bcrypt.genSalt(10)must needs to await -
example code
const create = async function (req, res) { const error = validateUser(req.body); if (error) return res.status(400).send(error); const { email, password } = req.body; const [userExist] = await of(User.findOne({ email })); if (userExist) return res.status(400).send("user already exists"); // console.log(User); // const hashedPassword = await User.hashedPassword(password); const newUser = new User({ email, password }); newUser.password = await newUser.hashedPassword(); const token = newUser.generateJWT(); const [, saveError] = await of(newUser.save()); if (saveError) return res .status(400) .send("something failed while creating account"); // console.log("pick", _pick(newUser, ["email", "_id"])); const result = { token, data: _pick(newUser, ["email", "_id"]), }; res.send(result); };
-
created new _pick function alternate to lodash
function _pick(object, ...keys) { keys = keys.flat(); const result = {}; for (let key in object) { if (keys.includes(key)) { result[key] = object[key]; } } return result; }
-
have look on
npm joi-password-complexity
-
-
-
example code
const auth = async function (req, res) { const error = validateUser(req.body); if (error) return res.status(400).send(error); const { email, password } = req.body; const [user, userError] = await of(User.findOne({ email })); if (userError || !user) return res.status(400).send("Invalid user or password"); const validUser = await user.validatePassword(password); if (!validUser) return res.status(400).send("Invalid user or password"); const token = user.generateJWT(); const result = { token, data: _pick(user, ["email", "_id"]), }; res.send(result); };
-
-
-
needed to use
typeproperty, since it is a special keyword in mongoose schema, we simple mention its type object, ie:{type:{type:String}} -
code
const orderSchema = Schema({ userId: Schema.Types.ObjectId, ingredients: [ { type: { type: String }, amount: Number, }, ], customer: { deliveryAddress: String, phone: String, paymentType: String, }, price: Number, orderTime: { type: Date, default: Date.now(), }, }); const Order = model("Order", orderSchema);
-
-
- created order controllers, create, list, item
- used authorize middleware
-
- tested all api's endpoints
-
-
-
- copied src and public folder and package.json file from react burger-builder project
- added .gitignore file
-
- changed auth and login endpoint,
- saved base endpoint in env file
- changed data structure in model( backend or node)
- processed errors and got the message from
error.response
-
- Fixed order fetch and save order uri
-
-
-
- deployment details
- need to revisit it for more details, i literally was sloppy for more than 30 days
- deployment details
-
-
-
- a server for mongodb, we can choose a server from google storage, or aws or azure
-
- just need to update the link of monodb atlas link
-
- in mongodb atlas we need to specify the ip address from where the app running and accessing mongodb
-
-
-
- we need to perform some changes to prepare it for heroku
-
- just some introductory information about heroku
-
- how to deploy apps to heroku
-
- setting the environment variable
- environment variable needs to be set separately in web control panel or from cli
-
-
-
- discussed details about the e-com assignment
- we need to implement these additional feature in our e-com project
- Order Ascending-Descending (Dropdown)
- Show product By Sold -> dropdown
- load more button
- Product search
- product review
- Coupon option-> model => name, discount
- show purchase history
- validate payment
-
- models and relations total 6 models
- User-1--1-Profile
- Category-1---N-Profile
- User--->Cart Item<---Product
- Order<---Cart Item
-
- created .env , app.js and server.js file
- in .env we stored our private variable like mongodb url, jwt secret key, port and Node_env value
- in app we exported app constant from express and used cors and express.json middleware, we loaded morgan conditionally
- in server.js file we connected to mongodb and created the server
-
-
-
- user model, required fields
- name,email,password,role
- role is enum of admin and user
- role has default value
- passed third parameter , timestamps= true, which will add and update the timestamps automatically
- created validateUser function using Joi
- added generateJWT method to User model
- user model, required fields
-
- created user router and signup controller
- signup controller
- validate signup data
- check if user exist
- for new user
- generate password hash
- try to save it
- return only '_id,name,email'
- used vanillaJs pick function
-
- created user signin controller
- will check if there is user
- then compare hash of the input password with user password
- fixed some typos and error in code
- tested endpoints with postman
- created user signin controller
-
- we can use
express-async-errorsmodule to catch unhandled rejected promise - we need to require the module
- then we need to write a custom middleware to catch the error
- then we can send response according to error
- we can group error message by error.message
- we can use
-
- created authorization and admin middleware
- in authorization middle, we picked the token from
Authorizationheader and verify against jwt token - if token verified successfully then we set the
req.userto decoded token value and called next - in admin middleware we checked if req have user object and then we checked if its role is admin,if not admin then 403 forbidden else call next
-
-
-
- created category model, validate with joi, created
createindexmethod for controller - created category routes, where post with
authorizeandadminmiddleware and get without any authorization - then added in app.js
- created category model, validate with joi, created
-
- completed create and index functions in category controllers file
- fixed few typos and logic in
authorizeusermiddleware and category routes model
-
- created product model
- product model have
namedescriptionprice,categoryquantityphoto - category is Schema.Types.objectId and ref
Category - photo is object of data(type buffer) and contentType
-
-
to use file upload we need to use a package call formidable
-
first we initiate formidable
const form = new formidable.IncomingForm(); form.keepExtensions = true;
-
then we call parse
form.parse(req, parseReq); -
parseReq accept three parameter
(err, fields, files) -
in fields we get datas like json
-
in files we need to handle it with fs if any file is send like
<file name="photo">we get it by files.photo -
we pass the path of that file in fs
fs.readFile(files.photo.path, async (err, data) => {} -
then save the data in
product.photoie:product.photo = { data, contentType: files.photo.type }; -
then we try to save the data and if success then we return the data without photo field
-
we need to add some extra field or id to mention that the photo was saved successfully
-
-
- created index method
- test data with postman
- used formdata in postman
fs.readFile(files.photo.filepath, async (err, data) => {thefiles.photo.pathneeds to befiles.photo.filepath- fixed some typos
-
- used the populate method in find filtering
- since we used the ref in
Schema.Types.objectIdwe can use populate method to directly fetch the category data - we used req.query to capture the query data from the request
- collect only needed data
-
- fixed error in create product method
product.photo = { data, contentType: files.photo.mimetype };files.photo.type needs to be files.photo.mimetype - added single product and product picture
- to response product picture as image file we set its contentType to photo mimetype
- added photoById into module export in controller and import in router
- added photo router
- fixed req type post to put for update/store product
- fixed error in create product method
-
- updated product update
- used same function for create and update since they share some codes
- this is not ideal and need some optimization
- used
Object.assigninstead of lodash _assign - need to validate update data, or else there will be some error
- global unhandled promise rejection not working
-
- implemented filter post router in product
- this need to use for more specific filtration
- same as query filter with skip option
- skip simply skip the given amount from the result
- skip is used in load or next page functionality
-
-
added advanced filter, filter by range and filter by in/ matched fields
-
sample data send
{ "order": "desc", "sortBy": "price", "limit": 2, "skip": 0, "filter": { "range": { "price": [10, 1000], "quantity": [1, 40] }, "in": { "category": ["6193ef84d60e63b3596cb353"] } } } -
filter processing functions
const processFilterRange = (range) => { const args = {}; for (let key in range) { args[key] = { $gte: range[key][0], $lte: range[key][1], }; } return args; }; const processFilterIn = (range) => { const args = {}; for (let key in range) { args[key] = { $in: range[key], }; } return args; };
-
-
-
-
- app.js file is refactored
- all middleware are moved in index.js of middleware file,which takes app
- same with routing
-
- model have product,price,count,user,purchased,deleted
-
- created cart controller and router files, not implemented controller functions
-
- implemented crud operation
- used {user} filter to make sure same user if performing the action
- used a property deleted to work with delete instead of deleting cartItem data
-
- created profile model, router and controller
- implemented get and create profile without validation
- tested with postman
-
-
-
- created react app in section h "e-com-frontend"
npx create-react-app e-com-frontend- cleaned up structure, removed unnecessary files
- change title of index page in public folder
- added bootstrap cdn link
- added e-com favicon
- installed dependent packages
npm i react-router-dom axios jwt-decode
-
- added .env in .gitignore
- in app.js imported BrowserRouter from react-router-dom
- wrapped Main component inside BrowserRouter component
- added API_BASE from env in src>utils>config.js
- created a Layout component to add custom title and structure
- added Home component src>home>Home.jsx
- updated Main component added Home to Routes(previously Switch)
- Switch is replaced with routes in react-router-dom 6
- and instead component we need to use element and element prop receive element
<Routes> <Route path="/" element={<Home />} /> </Routes>- there is no exact, or exact is default, there is wildcard path="/*"
-
- inserted before menu file from tutorial
- imported and added Menu component in Layout component
- created Login and Register page in src>components>user
- created CustomLink component to have active and inactive style in Menu component
let resolved = useResolvedPath(to); let style = useMatch({ path: resolved.pathname, end: true }) ? { color: "#f90" } : { color: "grey" };- used useResolvedPath and useMatch hooks to detect matched path or active path
-
- imported before Login and Register component
- created ShowMessage and Loading component src>utils>messages.jsx
- created api auth function login and register src>api>auth.js
- created handleOnSubmit and handleOnChange in Register component src>user>Register.jsx
-
- fixed async error handler in backend, to make the error parameter work we need to send 4 parameter
error,request,response,next - updated ShowMessage to ShowErrorMessage to ease the use
- implemented handleOnSubmit, show error message, loading and show success message in Register component
- same as Register but with login
- fixed async error handler in backend, to make the error parameter work we need to send 4 parameter
-
- added auth.js in utils folder
- implemented authenticate,isAuthenticate and userInfo and signout;
-
- added signout entry in menu with span
- used useNavigation hook to redirect to signin page when signout clicked
-
- implemented a RequireAuth component
- we can use this element when we want to protect authenticated page
- it is simple higher order component
isAuthenticate() ? children : <Navigate to="/login" />; - updated Dashboard component from tutorial, added dashboard to menu
- from Login component successfully login redirect to dashboard
-
- added AdminDashboard as the tutorial, copied from user dashboard and changed it
- implemented RequireAdmin custom route
- in Main component added user and admin dashboard
- in menu created dashboard link dynamic from
userinfo().role - updated Login component, will Navigate to user/admin dashboard dynamically from
userinfo().role
-
-
-
- imported CreateCategory from tutorial
- implemented ShowSuccessMessage
- changed code to use ShowSuccessMessage and ShowErrorMessage
- added loading state and Loading component
- added
/admin/create/categoryinside RequireAdmin - link updated in AdminDashboard
- commit before
- fixed backend admin middleware changed
bearertoBearer - fixed auth save token and get token
- implemented handleOnSubmit and handleOnChange
-
- added CreateProduct from tutorial material
- added CreateProduct to Route in Main component
- updated create product link in CreateProduct component
- in admin api refactored functions and added createProduct and getCategories
- in CreateProduct component implemented dynamic category list generation
-
- implemented handleOnSubmit
- api>admin fixed createProduct uri
- improved axiosAdminPost to accept contentType, default
application/json
- improved axiosAdminPost to accept contentType, default
-
- added `<Route path="/product/:id" element={<ProductDetails />} /> ` to Main component - added ProductDetails in home folder - replaced ShowErrorMessage and others - used useParams hook to get the params id -
- this should be 6.4
- added Card component in Home and updated variable and component
- implemented Home component
- added getProducts method in admin api
- the finally is not asynchronous, so do not use it with try,catch block
- added intensional .5 seconds delay in backend to visualize delay
-
- created HomeCategories component
- loaded category on document load in useEffect
- imported HomeCategories in Home component
-
- implemented checkbox click function
-
- implemented product filter,easier logic
-
- implemented PriceFilter component
- implemented filter by price
- fixed issue with none selected in category
-
-
-
- added createCart function in admin api
- implemented handleCart and use same function in home and product details
- should be use in hook and central function
-
- imported Cart and CartItem component from tutorial
- loaded user cart from api
- need to
response.data.databecause api send the data with message and data{message,data} - added to Main component
-
- added update cart and remove cart
- added cart to menu for authorize user
-
- imported template from tutorial
- added to Main private component
- updated Proceed To Checkout link
- fixed profile controller, used FindOne
- implemented profile load and update
- temporary redirect or new react-router-dom 6 useNavigate
-
- imported Checkout component from tutorial
- updated shipping address save and continue to checkout
- updated Main component
- fixed issue with imported Checkout page
-
-
-
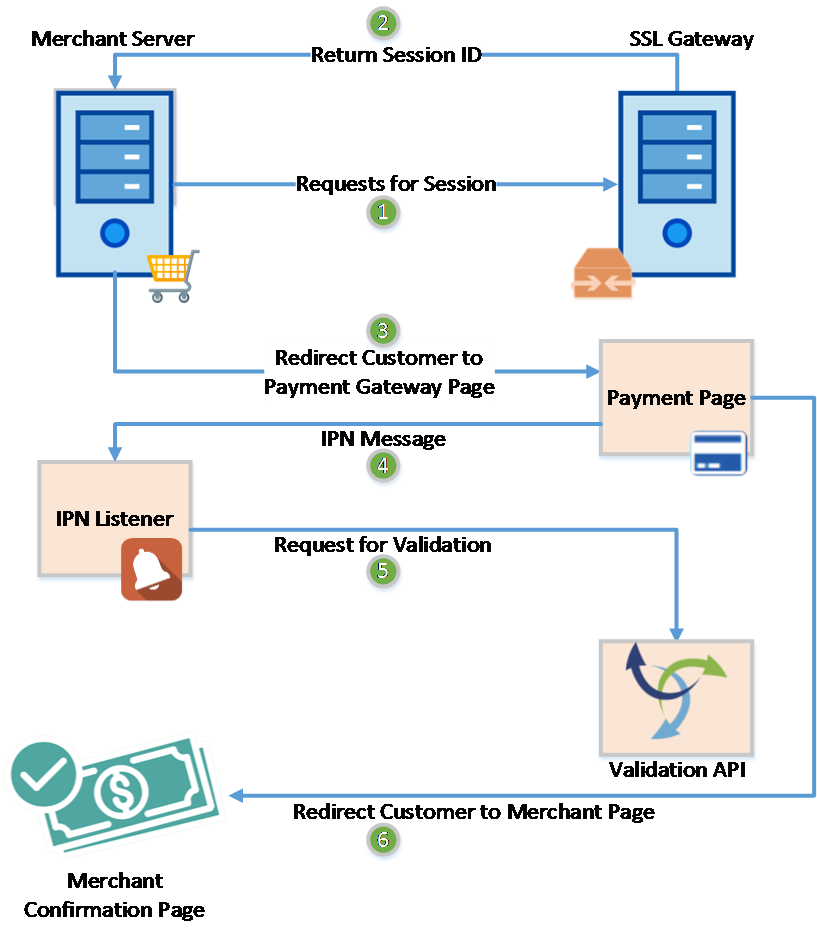
- register here for sandbox account https://developer.sslcommerz.com/
- sandbox is same as real but without real payment
- signup with real email and other fields can be fake
-
- sandbox login url https://sandbox.sslcommerz.com/manage
- store_id and secret_key will be provided to registered email
- documentation url https://developer.sslcommerz.com/doc/v4/
- node github url : https://github.com/sslcommerz/SSLCommerz-NodeJS
-
- init npm in sslcommerz-test folder
- used npm package sslcommerz-lts
- used their sample initiate code
- used "body-parser" to receive form-data submission form ssl commerz
- added functionality to accept data from ssl commerz
-
- added payment to controller and routes
- implementing payment init
- imported user cartsItem
- calculated total price
-
- imported profile
- given required data to data variable
- created function to add
setCustomerInfosetShippingInfosetItemInfo
-
- created payment component in order
- initiate payment api
- redirected to gateway url
- fixed some bugs in payment controller in backend
-
-
-
-
- init npm and
npm i cors dotenv express express-async-error joi jsonwebtoken mongoose morgan - copied tutorial files
- init npm and
-
-
-
- created user model and added generateJWT method
-
- browser endpoint->app handler->OAuth provider(ie:google)->redirect to app path-> receive info->Mongodb->token->storage
-
- added google auth routes
- for passport we need to implement
/auth/googleand/auth/google/redirectfor get request
-
- goto google developer console
- create a project
- create oauth consent screen
- select user type external
- add test user email
- obtain oauth credential
- create credential=>oAuth client id-> web application(or other type)-> add Authorised JavaScript origins[http://localhost:3001]->add redirect uris[http://localhost:3001/auth/google/redirect]
- then save the google client id and client secret to env file
-
- install passport and passport-google-oauth20
npm i passport and passport-google-oauth20 - documentation http://www.passportjs.org/packages/passport-google-oauth20/
- create authGoogle config
- import passport and GoogleStrategy
- create strategy object
- Strategy class accept an object with {clientID,clientSecret,callbackURL} and a callback
- then we use the strategy object with passport, passport.use(strategy)
- install passport and passport-google-oauth20
-
- used config authGoogle passport in authGoogle client
- we need to pass
passport.authenticate("google", { scope: ["profile"] }) - here we use passport.authenticate first parameter "google", strategy type, then second object with scope parameter which accept array of scopes, here we used
profile - then we test our auth/google endpoint
-
- added redirect passport middleware
- added email scope in /auth/google uri
- added index page with login button
- google strategy cb function accept
accessToken,refreshToken,profile,cbmust use these four parameters
-
- find the user, store the user if user not exist
-
- generate JWT in google strategy after saving user
- now send the user email and _id along with token data by calling cb
- cb(error,data), first parameter is any error and the second parameter will pass to next request pipe line and it will be store in req.user
- then we can use the data in redirect routing block
-
-
-
-
install multer
npm i multer -
config the multer in multer middleware
-
create the multer storage object
-
storage object will have destination and filename
-
these two items takes a function with req,file and cb parameter
-
in destination we call cb to set the storage location
cb(null, "media/img"); -
filename function :
const ext = file.mimetype.split("/")[1]; const uniqueSuffix = new Date.now() + "-" + Math.round(Math.random() * 1e9); const filename = `${file.filename}-${uniqueSuffix}.${ext}`; cb(null, filename);
-
the we export the multer `module.export = multer({ storage: multerStorage }).single("photo");
-
-
- created upload function in photos post
- upload function take req,res and err
- if err is instance of multer.MulterError
- if any other error
- if no error we have req.file and req.body
-
- there was error with the tutorial code
- needed to use upload as middleware to handle with multerError
-