-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
5f53df5
commit fdb1911
Showing
8 changed files
with
346 additions
and
1 deletion.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ | ||
| FROM --platform=linux/amd64 golang:1.18 as builder | ||
| FROM --platform=linux/amd64 golang:1.22 as builder | ||
|
|
||
| ARG APP | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,45 @@ | ||
| # KEDA concepts | ||
|
|
||
| https://keda.sh/docs/2.11/concepts/scaling-deployments/#scaling-of-deployments-and-statefulsets | ||
|
|
||
| KEDA is a Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaler. With KEDA, you can drive the scaling of any container in Kubernetes based on the number of events needing to be processed. | ||
|
|
||
| - With KEDA you can explicitly map the apps you want to use event-driven scale, with other apps continuing to function. | ||
|
|
||
| Agent - keda-operator runs with keda install | ||
| Metrics - The metric serving is the primary role of the keda-operator-metrics-apiserver container that runs when you install KEDA. | ||
| Admission Webhooks - it will prevent multiple ScaledObjects to target the same scale target. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| 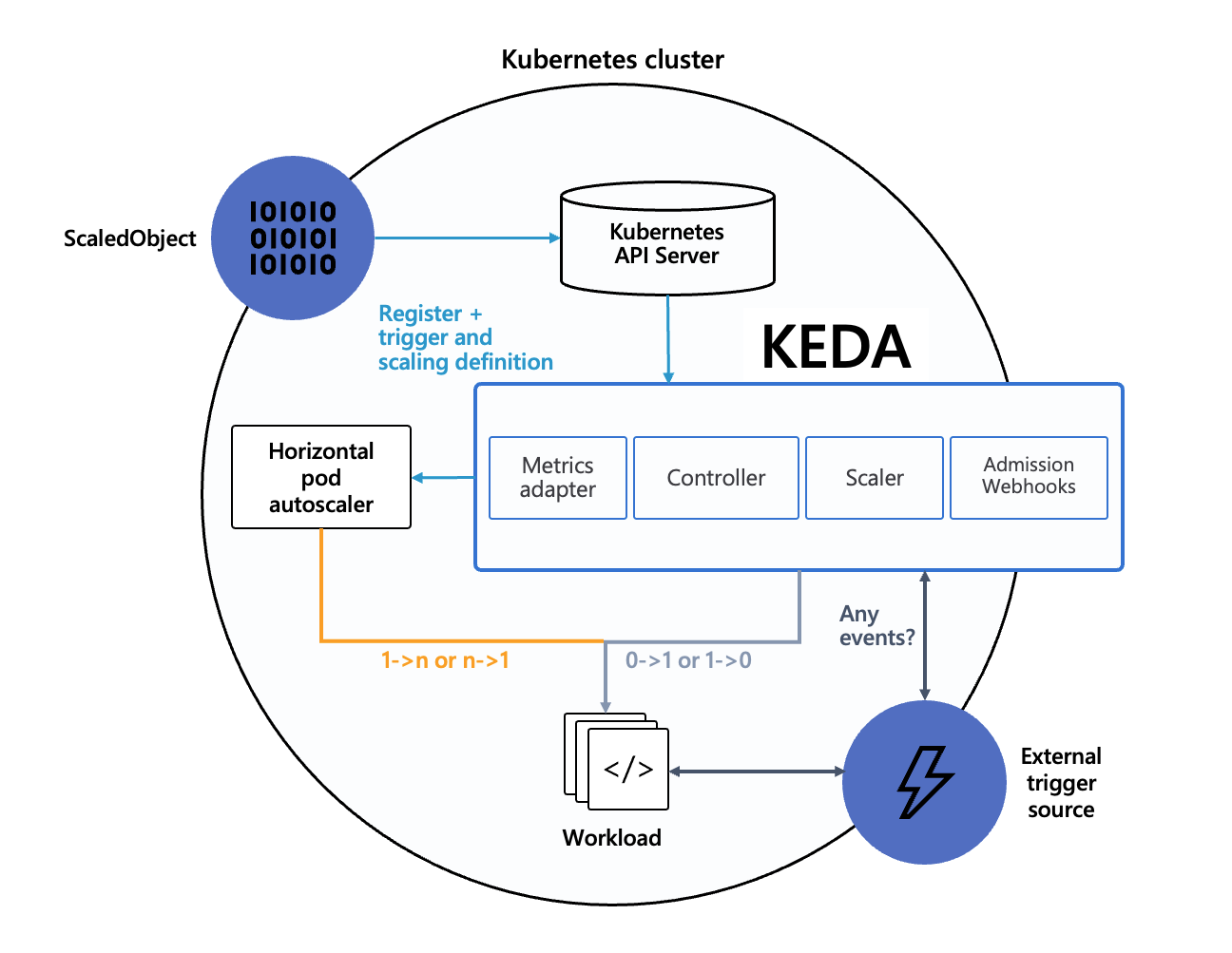 | ||
|
|
||
| #TODO Try to explain this arch again | ||
|
|
||
| ### Event sources and scalers | ||
|
|
||
| - CPU/Memory | ||
| - MSSQL | ||
| - PostgreSQL etc... | ||
|
|
||
| ### Custom Resources (CRD) | ||
|
|
||
| - scaledobjects.keda.sh | ||
| - scaledjobs.keda.sh (Not used) | ||
| - triggerauthentications.keda.sh | ||
| - clustertriggerauthentications.keda.sh (not used) | ||
|
|
||
| ScaledObjects represent the desired mapping between an event source (e.g. Rabbit MQ) and the Kubernetes Deployment, StatefulSet or any Custom Resource that defines /scale subresource. | ||
|
|
||
| ScaledJobs represent the mapping between event source and Kubernetes Job. | ||
|
|
||
| ScaledObject/ScaledJob may also reference a TriggerAuthentication or ClusterTriggerAuthentication which contains the authentication configuration or secrets to monitor the event source. | ||
|
|
||
| Authentication scopes: Namespace vs. Cluster (ClusterTriggerAuthentication) | ||
|
|
||
| - Each TriggerAuthentication is defined in one namespace and can only be used by a ScaledObject in that same namespace. | ||
|
|
||
| - For cases where you want to share a single set of credentials between scalers in many namespaces, you can instead create a ClusterTriggerAuthentication. | ||
|
|
||
| - As a global object, this can be used from any namespace. | ||
|
|
||
| - To set a trigger to use a ClusterTriggerAuthentication, add a kind field to the authentication reference: |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,106 @@ | ||
| ## Scaling Deployments, StatefulSets & Custom Resources | ||
|
|
||
| - Deployments and StatefulSets are the most common way to scale workloads with KEDA. | ||
| - It allows you to define the Kubernetes Deployment or StatefulSet that you want KEDA to scale based on a scale trigger | ||
| - KEDA will monitor that service(Deployment/Statefullset) and based on the events that occur it will automatically scale your resource out/in accordingly. | ||
|
|
||
| ### ScaledObject spec | ||
|
|
||
| https://keda.sh/docs/2.11/concepts/scaling-deployments/#scaledobject-spec | ||
|
|
||
| ```yaml | ||
| apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 | ||
| kind: ScaledObject | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: {scaled-object-name} | ||
| annotations: | ||
| scaledobject.keda.sh/transfer-hpa-ownership: "true" # Optional. Use to transfer an existing HPA ownership to this ScaledObject | ||
| autoscaling.keda.sh/paused-replicas: "0" # Optional. Use to pause autoscaling of objects | ||
| spec: | ||
| scaleTargetRef: | ||
| apiVersion: {api-version-of-target-resource} # Optional. Default: apps/v1 | ||
| kind: {kind-of-target-resource} # Optional. Default: Deployment | ||
| name: {name-of-target-resource} # Mandatory. Must be in the same namespace as the ScaledObject | ||
| envSourceContainerName: {container-name} # Optional. Default: .spec.template.spec.containers[0] | ||
| pollingInterval: 30 # Optional. Default: 30 seconds | ||
| cooldownPeriod: 300 # Optional. Default: 300 seconds | ||
| idleReplicaCount: 0 # Optional. Default: ignored, must be less than minReplicaCount | ||
| minReplicaCount: 1 # Optional. Default: 0 | ||
| maxReplicaCount: 100 # Optional. Default: 100 | ||
| fallback: # Optional. Section to specify fallback options | ||
| failureThreshold: 3 # Mandatory if fallback section is included | ||
| replicas: 6 # Mandatory if fallback section is included | ||
| advanced: # Optional. Section to specify advanced options | ||
| restoreToOriginalReplicaCount: true/false # Optional. Default: false | ||
| horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig: # Optional. Section to specify HPA related options | ||
| name: {name-of-hpa-resource} # Optional. Default: keda-hpa-{scaled-object-name} | ||
| behavior: # Optional. Use to modify HPA's scaling behavior | ||
| scaleDown: | ||
| stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300 | ||
| policies: | ||
| - type: Percent | ||
| value: 100 | ||
| periodSeconds: 15 | ||
| triggers: | ||
| # {list of triggers to activate scaling of the target resource} | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```yaml | ||
| spec: | ||
| scaleTargetRef: | ||
| apiVersion: {api-version-of-target-resource} # Optional. Default: apps/v1 | ||
| kind: {kind-of-target-resource} # Optional. Default: Deployment | ||
| name: {name-of-target-resource} # Mandatory. Must be in the same namespace as the ScaledObject | ||
| envSourceContainerName: {container-name} # Optional. Default: .spec.template.spec.containers[0] | ||
| ``` | ||
| https://keda.sh/docs/2.11/concepts/scaling-deployments/#fallback | ||
| ### fallback | ||
| - The fallback section is optional. It defines a number of replicas to fall back to if a scaler is in an error state. | ||
| ### Triggers | ||
| https://keda.sh/docs/2.11/scalers/ | ||
| - type | ||
| - metadata | ||
| - name | ||
| - useCachedMetrics | ||
| - authenticationRef | ||
| - metricType: AverageValues, Value, Utlization | ||
| ### Caching Metrics | ||
| Polling Interval -> HPA -> Metrics -> KEDA Metrics server | ||
| - Enabling this feature can significantly reduce the load on the scaler service. | ||
| ### Pause AutoScaling | ||
| ```yaml | ||
| metadata: | ||
| annotations: | ||
| autoscaling.keda.sh/paused-replicas: "0" | ||
| ``` | ||
| ### Activating and Scaling thresholds | ||
| - Activation Phase: Defines when the scaler is active or not and scales from/to 0 based on it. | ||
| - Scaling Phase: 1 to n vice versa | ||
| ### Existing HPA | ||
| ```yaml | ||
| metadata: | ||
| annotations: | ||
| scaledobject.keda.sh/transfer-hpa-ownership: "true" | ||
| spec: | ||
| advanced: | ||
| horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig: | ||
| name: {name-of-hpa-resource} | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,45 @@ | ||
| ### Scaling Jobs | ||
|
|
||
| The primary reason to consider this option is to handle processing long-running executions. Rather than processing multiple events within a deployment, for each detected event a single Kubernetes Job is scheduled. That job will initialize, pull a single event from the message source, and process to completion and terminate. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ```yaml | ||
| apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 | ||
| kind: ScaledJob | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: {scaled-job-name} | ||
| annotations: | ||
| autoscaling.keda.sh/paused: true # Optional. Use to pause autoscaling of Jobs | ||
| spec: | ||
| jobTargetRef: | ||
| parallelism: 1 # [max number of desired pods](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/job/#controlling-parallelism) | ||
| completions: 1 # [desired number of successfully finished pods](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/job/#controlling-parallelism) | ||
| activeDeadlineSeconds: 600 # Specifies the duration in seconds relative to the startTime that the job may be active before the system tries to terminate it; value must be positive integer | ||
| backoffLimit: 6 # Specifies the number of retries before marking this job failed. Defaults to 6 | ||
| template: | ||
| # describes the [job template](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/job) | ||
| pollingInterval: 30 # Optional. Default: 30 seconds | ||
| successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 5 # Optional. Default: 100. How many completed jobs should be kept. | ||
| failedJobsHistoryLimit: 5 # Optional. Default: 100. How many failed jobs should be kept. | ||
| envSourceContainerName: {container-name} # Optional. Default: .spec.JobTargetRef.template.spec.containers[0] | ||
| minReplicaCount: 10 # Optional. Default: 0 | ||
| maxReplicaCount: 100 # Optional. Default: 100 | ||
| rolloutStrategy: gradual # Deprecated: Use rollout.strategy instead (see below). | ||
| rollout: | ||
| strategy: gradual # Optional. Default: default. Which Rollout Strategy KEDA will use. | ||
| propagationPolicy: foreground # Optional. Default: background. Kubernetes propagation policy for cleaning up existing jobs during rollout. | ||
| scalingStrategy: | ||
| strategy: "custom" # Optional. Default: default. Which Scaling Strategy to use. | ||
| customScalingQueueLengthDeduction: 1 # Optional. A parameter to optimize custom ScalingStrategy. | ||
| customScalingRunningJobPercentage: "0.5" # Optional. A parameter to optimize custom ScalingStrategy. | ||
| pendingPodConditions: # Optional. A parameter to calculate pending job count per the specified pod conditions | ||
| - "Ready" | ||
| - "PodScheduled" | ||
| - "AnyOtherCustomPodCondition" | ||
| multipleScalersCalculation : "max" # Optional. Default: max. Specifies how to calculate the target metrics when multiple scalers are defined. | ||
| triggers: | ||
| # {list of triggers to create jobs} | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| envSourceContainerName: | ||
| - This optional property specifies the name of container in the Job, from which KEDA should try to get environment properties holding secrets etc. If it is not defined it, KEDA will try to get environment properties from the first Container, ie. from .spec.JobTargetRef.template.spec.containers[0]. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ | ||
| ### Authentication | ||
|
|
||
| Often a scaler will require authentication or secrets and config to check for events. | ||
|
|
||
| KEDA provides a few secure patterns to manage authentication flows: | ||
|
|
||
| ### Defining secrets and config maps on ScaledObject | ||
|
|
||
| If using the RabbitMQ scaler, the host parameter may include passwords so is required to be a reference. | ||
|
|
||
| You can create a secret with the value of the host string, reference that secret in the deployment, and map it to the ScaledObject metadata parameter like below: | ||
|
|
||
| TriggerAuthentication resource to define authentication as a separate resource to a ScaledObject | ||
|
|
||
| ```yaml | ||
| apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 | ||
| kind: TriggerAuthentication | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: {trigger-authentication-name} | ||
| namespace: default # must be same namespace as the ScaledObject | ||
| spec: | ||
| podIdentity: | ||
| provider: none | azure | azure-workload | aws-eks | aws-kiam | gcp # Optional. Default: none | ||
| identityId: <identity-id> # Optional. Only used by azure & azure-workload providers. | ||
| secretTargetRef: # Optional. | ||
| - parameter: {scaledObject-parameter-name} # Required. | ||
| name: {secret-name} # Required. | ||
| key: {secret-key-name} # Required. | ||
| env: # Optional. | ||
| - parameter: {scaledObject-parameter-name} # Required. | ||
| name: {env-name} # Required. | ||
| containerName: {container-name} # Optional. Default: scaleTargetRef.envSourceContainerName of ScaledObject | ||
| hashiCorpVault: # Optional. | ||
| address: {hashicorp-vault-address} # Required. | ||
| namespace: {hashicorp-vault-namespace} # Optional. Default is root namespace. Useful for Vault Enterprise | ||
| authentication: token | kubernetes # Required. | ||
| role: {hashicorp-vault-role} # Optional. | ||
| mount: {hashicorp-vault-mount} # Optional. | ||
| credential: # Optional. | ||
| token: {hashicorp-vault-token} # Optional. | ||
| serviceAccount: {path-to-service-account-file} # Optional. | ||
| secrets: # Required. | ||
| - parameter: {scaledObject-parameter-name} # Required. | ||
| key: {hasicorp-vault-secret-key-name} # Required. | ||
| path: {hasicorp-vault-secret-path} | ||
| ``` | ||
| If creating a deployment yaml that references a secret, be sure the secret is created before the deployment that references it, and the scaledObject after both of them to avoid invalid references. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | ||
| ### External Scalers | ||
|
|
||
| https://keda.sh/docs/2.11/scalers/azure-service-bus/ | ||
|
|
||
| While KEDA ships with a set of built-in scalers, users can also extend KEDA through a GRPC service that implements the same interface as the built-in scalers. | ||
|
|
||
| #TODO | ||
|
|
||
| To implement external scalar, need to use the GRPC and trigger the driver to accept the scalars. | ||
|
|
||
| Will come back and implement this if required. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Admission Webhooks | ||
|
|
||
| - The scaled workload (scaledobject.spec.scaleTargetRef) is already autoscaled by another other sources (other ScaledObject or HPA). | ||
| - CPU and/or Memory trigger are used and the scaled workload doesn’t have the requests defined. This rule doesn’t apply to all the workload types, only to Deployment and StatefulSet. | ||
| - CPU and/or Memory trigger are the only used triggers and the ScaledObject defines minReplicaCount:0. This rule doesn’t apply to all the workload types, only to Deployment and StatefulSet. |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | ||
| # Demo on KEDA | ||
|
|
||
| Steps: | ||
|
|
||
| - GCO devops repo, Helm charts and FluxCD (Short Update) | ||
| - KEDA Architecture (Tutorial 01_scaling_intro.md ) | ||
| - Install KEDA in local kind cluster | ||
| - Install a sample app | ||
| - Add scaled object to scale the sample app | ||
| - Add scaled object to scale the sample app based on Azure Service Bus queue | ||
| - In Dev cluster explain the KEDA architecture | ||
|
|
||
| ```example | ||
| git:(main) ✗ kpo -n keda | ||
| NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE | ||
| keda-admission-webhooks-99d9c854-t6dsc 1/1 Running 0 2m15s | ||
| keda-operator-5f648b87fb-zhwxj 1/1 Running 1 (116s ago) 2m15s | ||
| keda-operator-metrics-apiserver-846455667b-gzdfc 1/1 Running 0 2m15s | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```example | ||
| git:(main) ✗ k get crds | ||
| NAME CREATED AT | ||
| clustertriggerauthentications.keda.sh 2023-11-30T04:39:44Z | ||
| scaledjobs.keda.sh 2023-11-30T04:39:44Z | ||
| scaledobjects.keda.sh 2023-11-30T04:39:44Z | ||
| triggerauthentications.keda.sh 2023-11-30T04:39:44 | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,55 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| apiVersion: v1 | ||
| kind: Secret | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: newsecret | ||
| type: Opaque | ||
| data: | ||
| connection: RW5kcG9pbnQ9c2I6Ly9hei1zZXJ2aWNlYnVzLW5zLXd1LWdjby1kZXYtMDAxLnNlcnZpY2VidXMud2luZG93cy5uZXQvO1NoYXJlZEFjY2Vzc0tleU5hbWU9dGVzdDtTaGFyZWRBY2Nlc3NLZXk9c1dRcUNOdTh3Zy8xVU0wZmMwUmtDSUFlclFPUDQ4R1NoK0FTYkVzeExFOD07RW50aXR5UGF0aD1xdWV1ZS1idWxrLXVwbG9hZC1ib29raW5ncy1sb2NhbA== | ||
| ## Temp secrets for the Queue, once deleted need to create again. | ||
| --- | ||
| apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 | ||
| kind: TriggerAuthentication | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: queue-bulk-upload-bookings-local-auth | ||
| spec: | ||
| secretTargetRef: | ||
| - parameter: connection | ||
| name: newsecret | ||
| key: connection | ||
| --- | ||
| apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 | ||
| kind: ScaledObject | ||
| metadata: | ||
| name: example-scaledobject | ||
| labels: | ||
| app: prd-dev | ||
| deploymentName: prd-dev | ||
| spec: | ||
| scaleTargetRef: | ||
| apiVersion: apps/v1 | ||
| kind: Deployment | ||
| name: prd-dev | ||
| idleReplicaCount: 0 | ||
| minReplicaCount: 1 | ||
| maxReplicaCount: 3 | ||
| pollingInterval: 30 | ||
| cooldownPeriod: 300 | ||
| fallback: | ||
| failureThreshold: 3 | ||
| replicas: 2 | ||
| triggers: | ||
| # - metadata: | ||
| # messageCount: "5" | ||
| # queueName: queue-bulk-upload-bookings-local | ||
| # type: azure-servicebus | ||
| - metadata: | ||
| value: "80" | ||
| metricType: Utilization | ||
| type: cpu | ||
| - metadata: | ||
| value: "80" | ||
| metricType: Utilization | ||
| type: memory | ||
| # authenticationRef: | ||
| # name: queue-bulk-upload-bookings-local-auth |