A Windows utility for managing your PATH environment variable through both a context menu and command line interface.
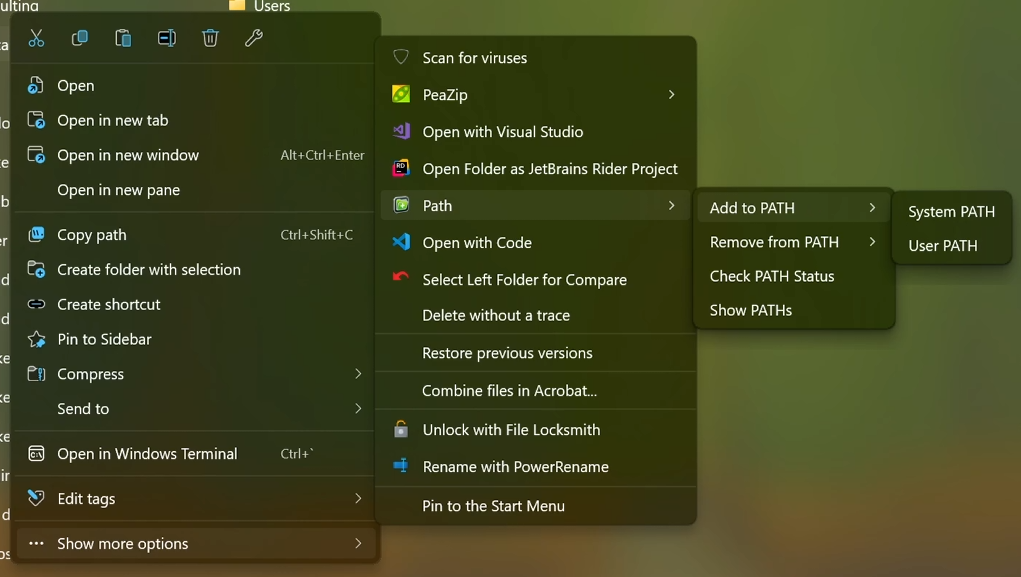
AddToPath context menu integration in Windows Explorer
- Requirements
- Quick Start
- Features
- Installation
- CLI Usage
- Uninstall
- Troubleshooting
- Development
- License
- Windows 10 or later
- .NET Framework 4.7.2 (pre-installed on Windows 10)
- Administrator rights for system PATH modifications
- Download latest release
- Run
AddToPath.exeas administrator - Click "Install Tools"
- Right-click any folder → Path → Add to PATH
-
Two ways to manage PATH:
-
Context Menu (GUI)
- Right-click any folder and use the "Path" menu
- Add folders to system or user PATH
- Remove folders from PATH
- Check if folders are in PATH
- View all PATH entries
-
Command Line (CLI)
- Use
a2pcommand from any terminal - Simple commands for PATH management:
# Add current directory to user PATH a2p add . # Add a directory to system PATH (needs admin) a2p add -s "C:\Tools" # Remove from user PATH a2p remove "C:\Tools" # Check if directory is in PATH a2p check "C:\Tools"
- Use
-
-
No external dependencies - everything is embedded
-
UAC elevation for admin operations
-
Works with both user and system PATH
-
Changes take effect immediately in new terminals
-
Includes scripts to refresh PATH in existing terminals
- Download the latest release
- Run
AddToPath.exeas administrator and choose "Install Tools"- Both tools will be installed to Program Files
- Creates context menu entries
- Adds installation directory to system PATH
- Creates
updatepathcommand for refreshing PATH in current terminals
- You can now:
- Right-click folders and use the "Path" menu
- Use
a2pcommands in any terminal - Use
updatepathto refresh PATH in current terminal
The a2p command supports the following operations:
a2p add <path> # Add to user PATH
a2p add -s <path> # Add to system PATH (needs admin)
a2p remove <path> # Remove from user PATH
a2p remove -s <path># Remove from system PATH (needs admin)
a2p check <path> # Check if path is in PATH
a2p list # List all PATH entriesAfter modifying PATH, you can either:
- Open new terminals to see the changes, or
- Refresh PATH in current terminal:
updatepath
To completely remove both tools, you can either:
- Run
AddToPath.exeand choose "Uninstall" - Run
AddToPath.exe --uninstallas administrator
Either way:
- Removes context menu entries
- Removes both tools from Program Files
- Removes installation directory from PATH
The tool automatically detects common issues and will show a "Reinstall Tools" button if it finds any problems. This can fix:
- Missing context menu entries
- Missing PATH entries
- Incorrect installation directory
- Missing or outdated components
For specific issues:
-
"Access denied" when modifying system PATH
- Run the tool as administrator
- For CLI, use an elevated command prompt
-
Changes not visible in current terminal
- PATH changes only affect new terminals
- Close and reopen your terminal
- Use
updatepathto refresh PATH
-
Any other issues
- Run
AddToPath.exe- it will detect problems and offer to fix them - Click "Reinstall Tools" if offered
- The tool will repair all components and restore functionality
- Run
This project is built using:
- C# Windows Forms & Console Apps
- .NET Framework 4.7.2
- Visual Studio 2022 or later
See CONTRIBUTING.md for development setup and guidelines.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.



