This repository contains the command line tool rapidgzip, which can be used for parallel decompression of almost any gzip file. Other tools, such as bgzip, can only parallelize decompression of gzip files produced by themselves. rapidgzip works with all files, especially those produced by the usually installed GNU gzip. How this works can be read in the pugz paper or in the rapidgzip paper, which builds upon the former.
The Python module provides a RapidgzipFile class, which can be used to seek inside gzip files without having to decompress them first.
Alternatively, you can use this simply as a parallelized gzip decoder as a replacement for Python's builtin gzip module in order to fully utilize all your cores.
The random seeking support is the same as provided by indexed_gzip but further speedups are realized at the cost of higher memory usage thanks to a least-recently-used cache in combination with a parallelized prefetcher.
This repository is a light-weight fork of the indexed_bzip2 repository, in which the main development takes place. This repository was created for visibility reasons and in order to keep indexed_bzip2 and rapidgzip releases separate. It will be updated at least for each release. Issues regarding rapidgzip should be opened here.
You can simply install it from PyPI:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # Recommended for newer manylinux wheels
python3 -m pip install rapidgzip
rapidgzip --help
Advanced Installations
The latest unreleased development version can be tested out with:
python3 -m pip install --force-reinstall 'git+https://github.com/mxmlnkn/indexed_bzip2.git@master#egginfo=rapidgzip&subdirectory=python/rapidgzip'And to build locally, you can use build and install the wheel:
cd python/rapidgzip
rm -rf dist
python3 -m build .
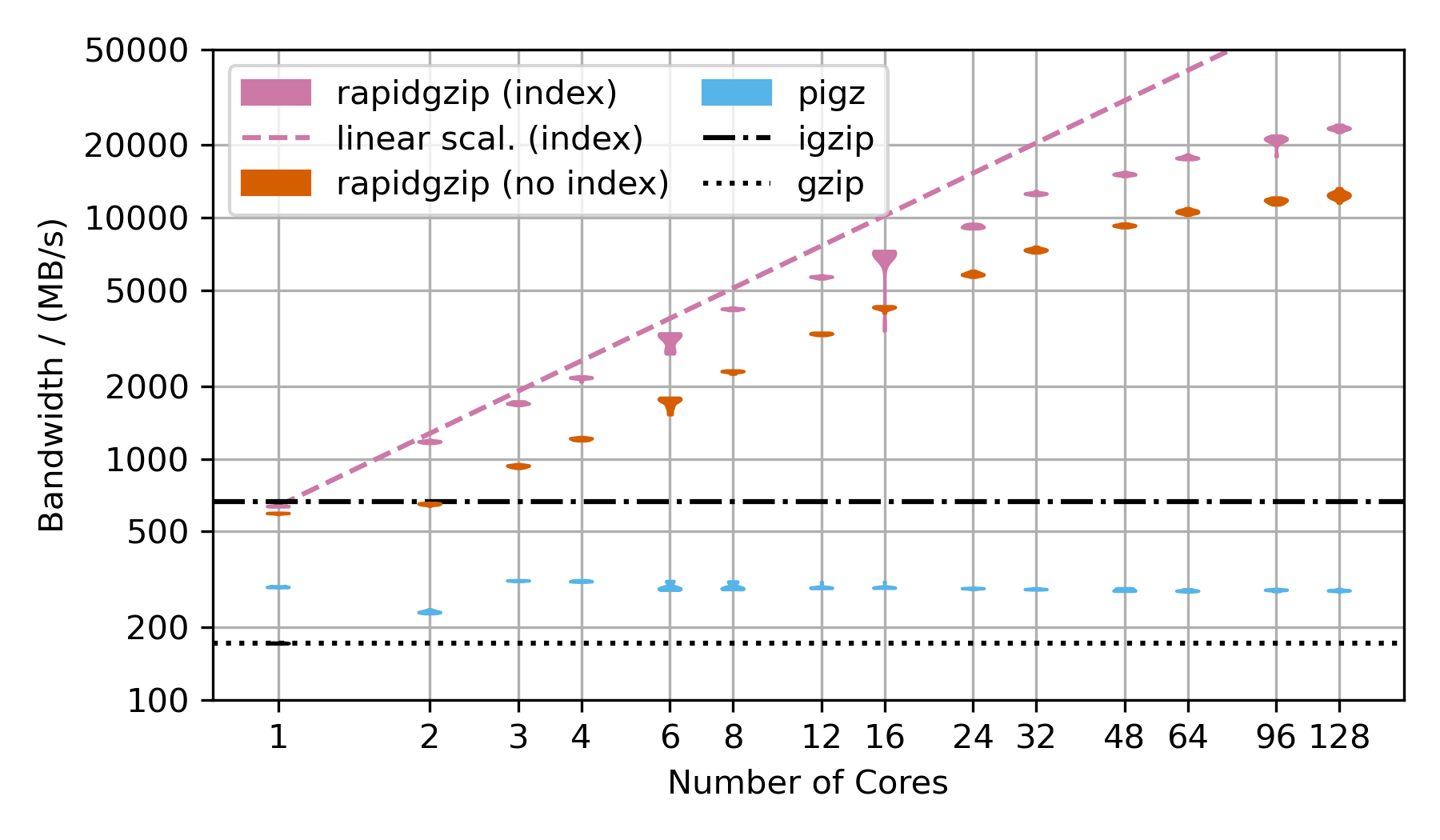
python3 -m pip install --force-reinstall --user dist/*.whlFollowing are benchmarks showing the decompression bandwidth over the number of used cores.
There are two rapidgzip variants shown: (index) and (no index).
Rapidgzip is generally faster when given an index with --import-index because it can delegate the decompression to ISA-l or zlib while it has to use its own custom-written gzip decompression engine when no index exists yet.
Furthermore, decompression can be parallelized more evenly and more effectively when an index exists because the serializing window propagation step is not necessary.
The violin plots show 20 repeated measurements as a single "blob". Thin blobs signal very reproducible timings while thick blobs signal a large variance.
This benchmark uses the Silesia corpus compressed as a .tar.gz file to show the decompression performance. However, the compressed dataset is only ~69 MB, which is not sufficiently large to show parallelization over 128 cores. That's why the TAR file is repeated as often as there are number of cores in the benchmark times 2 and then compressed into a single large gzip file, which is ~18 GB compressed and 54 GB uncompressed for 128 cores.
Rapidgzip achieves up to 24 GB/s with an index and 12 GB/s without.
Pugz is not shown as comparison because it is not able to decompress the Silesia dataset because it contains binary data, which it cannot handle.
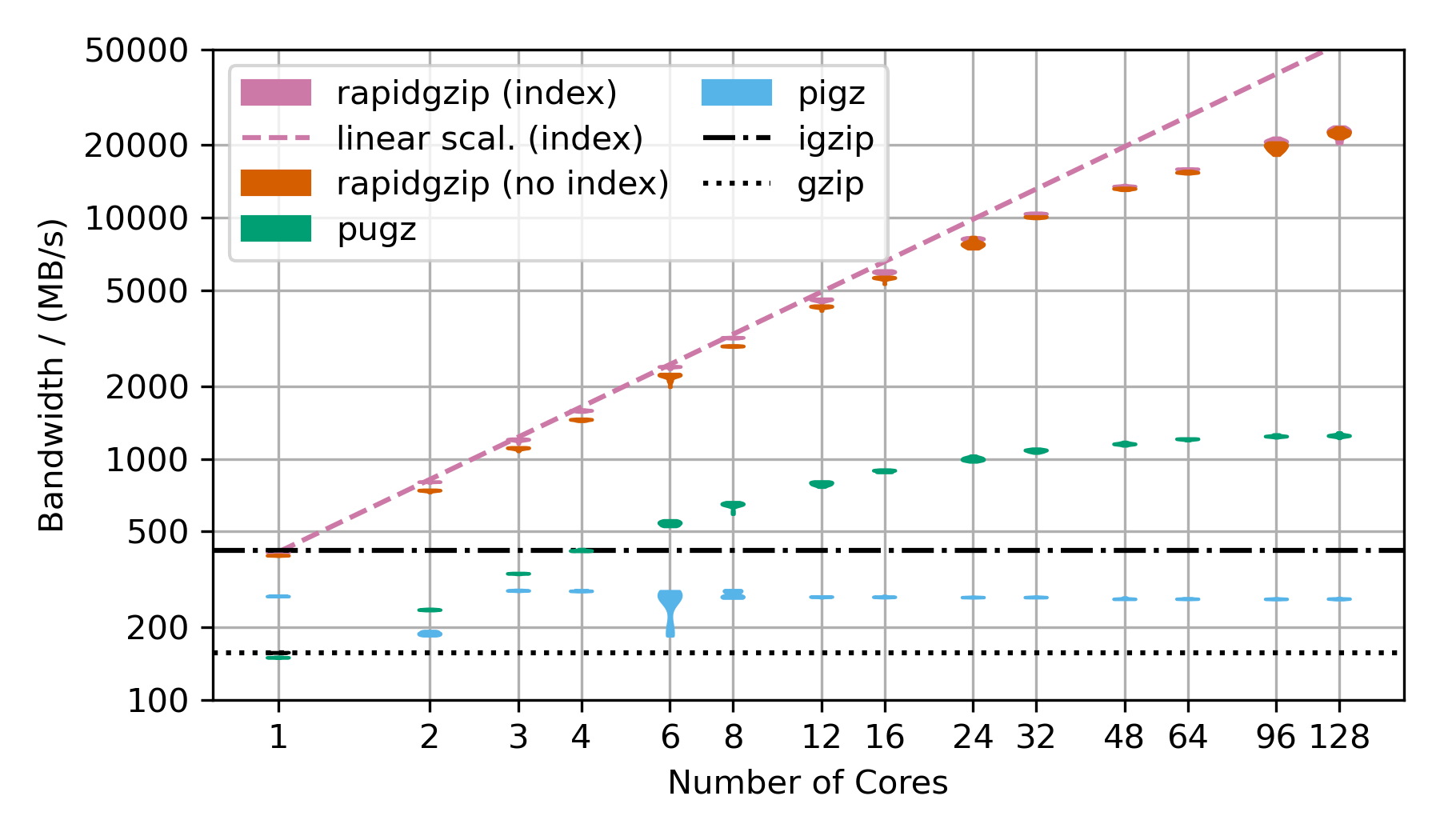
More Benchmarks
This benchmarks uses random data, that has been base64 encoded and then gzip-compressed. This is the next best case for rapidgzip after the trivial case of purely random data, which cannot be compressed and therefore can be decompressed with a simple memory copy. This next best case results in mostly Huffman-coding compressed data with only very few LZ77 back-references. Without LZ77 back-references, parallel decompression can be done more independently and therefore faster than in the case of many LZ77 back-references.
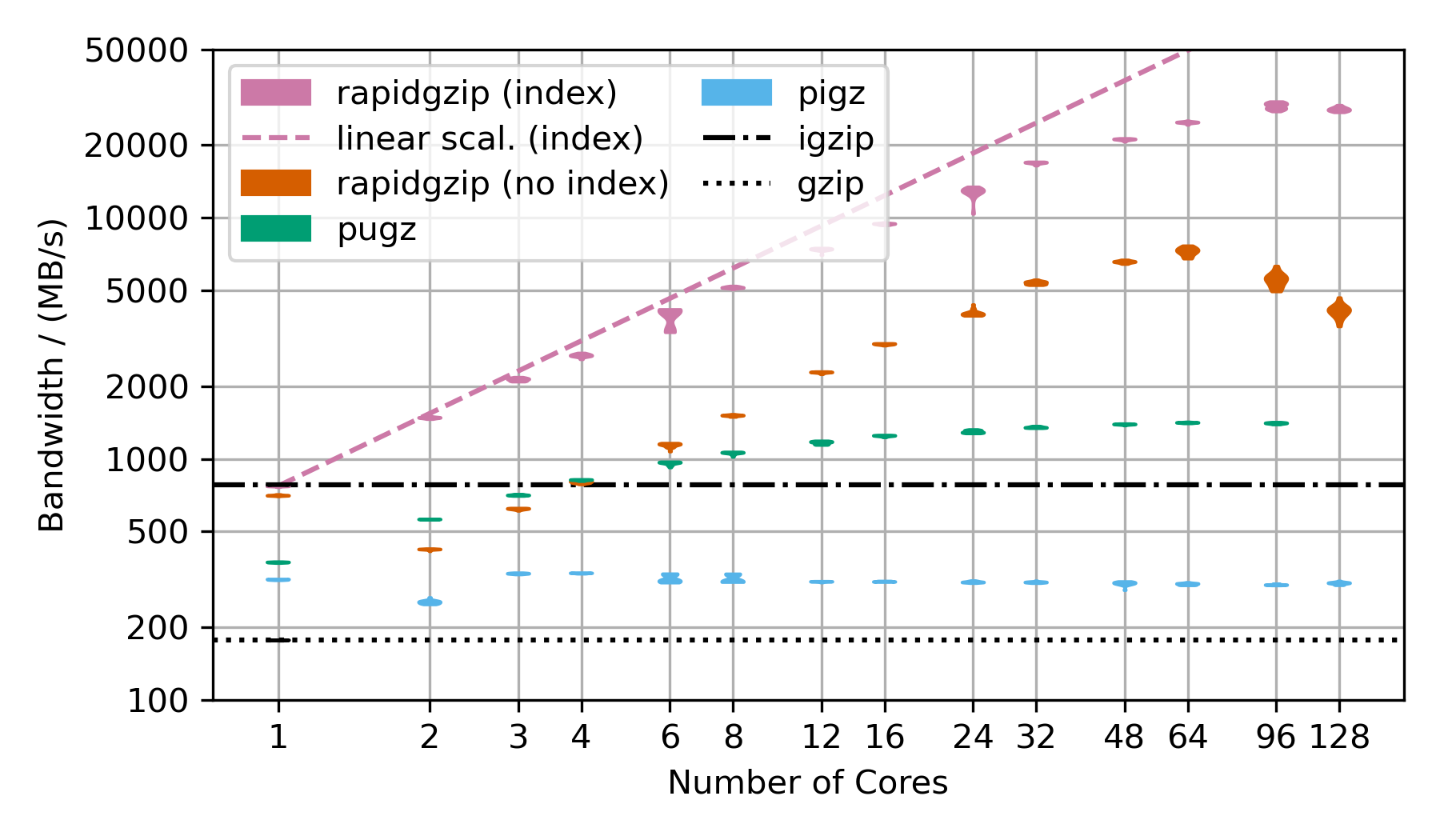
This benchmarks uses gzip-compressed FASTQ data. That's why the TAR file is repeated as often as there are number of cores in the benchmark to hold the decompression times roughly constant in order to make the benchmark over this large a range feasible. This is almost the worst case for rapidgzip because it contains many LZ77 back-references over very long ranges. This means that a fallback to ISA-L is not possible and it means that the costly two-staged decoding has to be done for almost all the data. This is also the reason why if fails to scale above 64 cores, i.e, to the second CPU socket. The first and second decompression stages are completely independently submitted to a thread pool, which on this NUMA architecture means, that data needs to be costly transferred from one processor socket to the other if the second step for a chunk is not done on the same processor as the first. This should be fixable by making the ThreadPool NUMA-aware.
These three scaling plots were created with rapidgzip 0.9.0 while the ones in the paper were created with 0.5.0.
These benchmarks on my local workstation with a Ryzen 3900X only has 12 cores (24 virtual cores) but the base frequency is much higher than the 2xAMD EPYC CPU 7702.
| 4GiB-base64 | 4GiB-base64 | 20x-silesia | 20x-silesia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncompressed Size | 4 GiB | 3.95 GiB | |||
| Compressed Size | 3.04 GiB | 1.27 GiB | |||
| Module | Bandwidth / (MB/s) |
Speedup | Bandwidth / (MB/s) |
Speedup | |
| gzip | 250 | 1 | 293 | 1 | |
| rapidgzip (0 threads) | 5179 | 20.6 | 5640 | 18.8 | |
| rapidgzip (1 threads) | 488 | 1.9 | 684 | 2.3 | |
| rapidgzip (2 threads) | 902 | 3.6 | 1200 | 4.0 | |
| rapidgzip (6 threads) | 2617 | 10.4 | 3250 | 10.9 | |
| rapidgzip (12 threads) | 4463 | 17.7 | 5600 | 18.7 | |
| rapidgzip (24 threads) | 5240 | 20.8 | 5750 | 19.2 | |
| rapidgzip (32 threads) | 4929 | 19.6 | 5300 | 17.7 |
| 4GiB-base64 | 4GiB-base64 | 20x-silesia | 20x-silesia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncompressed Size | 4 GiB | 3.95 GiB | |||
| Compressed Size | 3.04 GiB | 1.27 GiB | |||
| Module | Bandwidth / (MB/s) |
Speedup | Bandwidth / (MB/s) |
Speedup | |
| gzip | 250 | 1 | 293 | 1 | |
| rapidgzip (0 threads) | 5060 | 20.1 | 2070 | 6.9 | |
| rapidgzip (1 threads) | 487 | 1.9 | 630 | 2.1 | |
| rapidgzip (2 threads) | 839 | 3.3 | 694 | 2.3 | |
| rapidgzip (6 threads) | 2365 | 9.4 | 1740 | 5.8 | |
| rapidgzip (12 threads) | 4116 | 16.4 | 1900 | 6.4 | |
| rapidgzip (24 threads) | 4974 | 19.8 | 2040 | 6.8 | |
| rapidgzip (32 threads) | 4612 | 18.3 | 2580 | 8.6 |
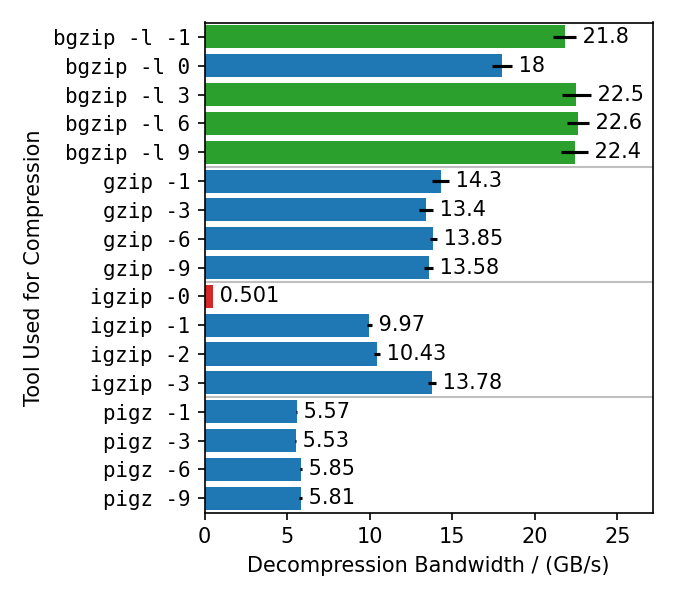
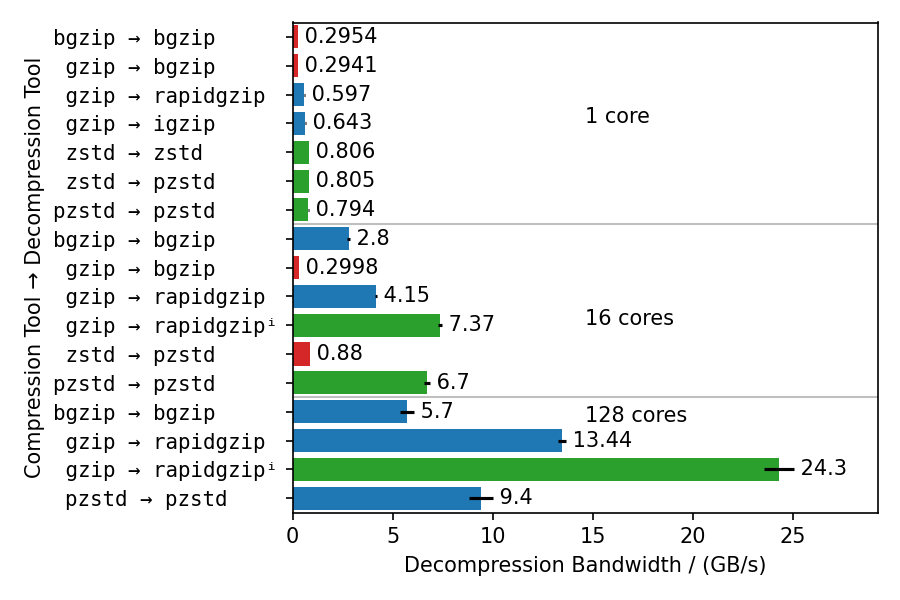
This benchmarks compresses the enlarged Silesia TAR with different gzip implementations, each with different compression levels. Rapidgzip is then used to decompress the resulting files with 128 cores.
Rapidgzip can parallelize decompression for almost all tested cases.
The only exception are files compressed with igzip -0, because these files conain only a single several gigabytes large deflate block.
This is the only known tool to produce such a pathological deflate block.
The decompression bandwidth for the other compressors, varies quite a lot.
The fastest decompression is reached with 22 GB/s for bgzip-compressed files because the bgzip format is directly supported, which enabled rapidgzip to avoid the two-staged decompression method and also enables rapidgzip to offload all of the work to ISA-L.
Files compressed with bgzip -l 0 decompress slightly slower with "only" 18 GB/s, because it creates a fully non-compressed gzip stream and therefore is more I/O bound than the other bgzip-generated files.
Decompression of pigz-generated files is the slowest with 6 GB/s as opposed to 10-14 GB/s for gzip and igzip.
It is not clear why that is.
It might be because pigz generates small deflate blocks and adds flush markers.
The values in this chart are higher than in table 3 in the paper because the measurements were done with rapidgzip 0.10.1 instead of version 0.5.0.
This benchmarks uses different compressors and different decompressors to show multiple things:
- Single-core decompression of rapidgzip is close to
igzipand roughly twice as fast asbgzip, which uses zlib. - Decompression bandwidth with ISA-L can somewhat compete with zstd and is only 25% slower.
- Both,
bgzipandpzstdcan only parallelize decompression of files compressed withbgzip/pzstd. This especially means, that files compressed with the standardzstdtool cannot be decompressed in parallel and tops out at ~800 MB/s. - Even for bgzip-compressed files, rapidgzip is always faster than
bgzipfor decompression, thanks to ISA-L and better multi-threading. - Rapidgzip scales higher than pzstd for decompression with many cores, and can be more than twice as fast when an index exists: 24.3 GB/s vs. 9.5 GB/s.
The values in this chart are higher than in table 4 in the paper because the measurements were done with rapidgzip 0.10.1 instead of version 0.5.0.
rapidgzip --help
# Parallel decoding: 1.7 s
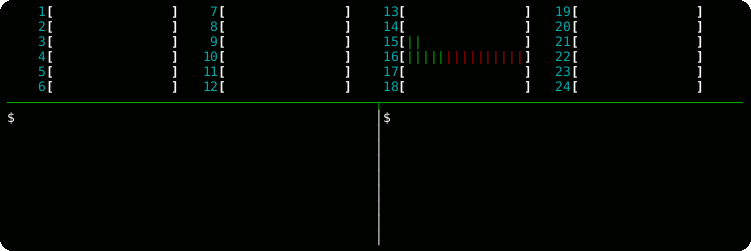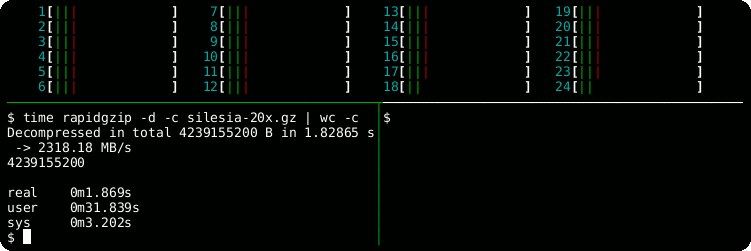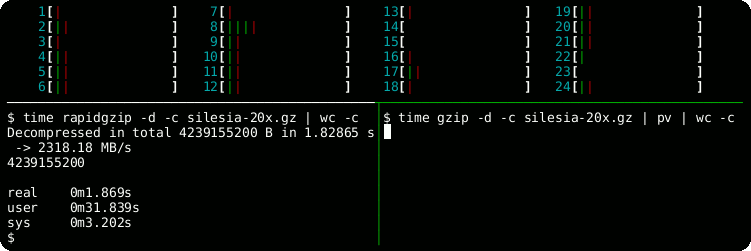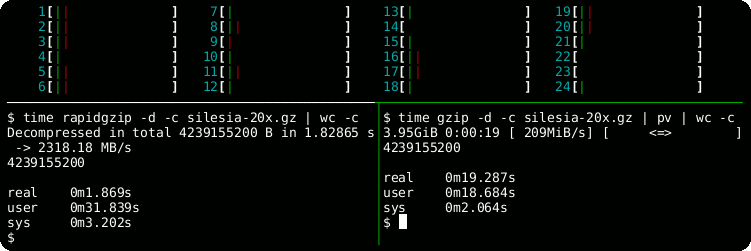
time rapidgzip -d -c -P 0 sample.gz | wc -c
# Serial decoding: 22 s
time gzip -d -c sample.gz | wc -cHelp Output
A gzip decompressor tool based on the rapidgzip backend from ratarmount
Usage:
rapidgzip [OPTION...] positional parameters
Actions options:
-d, --decompress Force decompression. Only for compatibility. No
compression supported anyways.
--import-index arg Uses an existing gzip index.
--export-index arg Write out a gzip index file.
--count Prints the decompressed size.
-l, --count-lines Prints the number of newline characters in the
decompressed data.
--analyze Print output about the internal file format
structure like the block types.
Advanced options:
--chunk-size arg The chunk size decoded by the parallel workers
in KiB. (default: 4096)
--verify Verify CRC32 checksum. Will slow down
decompression and there are already some
implicit and explicit checks like whether the
end of the file could be reached and whether
the stream size is correct.
--no-verify Do not verify CRC32 checksum. Might speed up
decompression and there are already some
implicit and explicit checks like whether the
end of the file could be reached and whether
the stream size is correct.
--io-read-method arg Option to force a certain I/O method for
reading. By default, pread will be used when
possible. Possible values: pread, sequential,
locked-read (default: pread)
--index-format arg Option to select an output index format.
Possible values: gztool, gztool-with-lines,
indexed_gzip. (default: indexed_gzip)
Decompression options:
-c, --stdout Output to standard output. This is the
default, when reading from standard input.
-f, --force Force overwriting existing output files.
Also forces decompression even when piped
to /dev/null.
-o, --output arg Output file. If none is given, use the
input file name with '.gz' stripped or
'<input file>.out'. If no input is read
from standard input and not output file is
given, then will write to standard output.
-k, --keep Keep (do not delete) input file. Only for
compatibility. This tool will not delete
anything automatically!
-P, --decoder-parallelism arg
Use the parallel decoder. If an optional
integer >= 1 is given, then that is the
number of decoder threads to use. Note that
there might be further threads being
started with non-decoding work. If 0 is
given, then the parallelism will be
determined automatically. (default: 0)
--ranges arg Decompress only the specified byte ranges.
Example: 10@0,1KiB@15KiB,5L@20L to
decompress the first 10 bytes, 1024 bytes
at offset 15 KiB, as well as the 5 lines
after skipping the first 20 lines.
Output options:
-h, --help Print this help message.
-q, --quiet Suppress noncritical error messages.
-v, --verbose Print debug output and profiling statistics.
-V, --version Display software version.
--oss-attributions Display open-source software licenses.
--oss-attributions-yaml Display open-source software licenses in
YAML format for use with Conda.
If no file names are given, rapidgzip decompresses from standard input to standard output.
If the output is discarded by piping to /dev/null, then the actual decoding step might
be omitted if neither -l nor -L nor --force are given.
Examples:
Decompress a file:
rapidgzip -d file.gz
Decompress a file in parallel:
rapidgzip -d -P 0 file.gz
List information about all gzip streams and deflate blocks:
rapidgzip --analyze file.gz
from rapidgzip import RapidgzipFile
file = RapidgzipFile("example.gz", parallelization=os.cpu_count())
# You can now use it like a normal file
file.seek(123)
data = file.read(100)
file.close()The first call to seek will ensure that the block offset list is complete and therefore might create them first. Because of this the first call to seek might take a while.
import os
import rapidgzip
with rapidgzip.open("example.gz", parallelization=os.cpu_count()) as file:
file.seek(123)
data = file.read(100)The creation of the list of gzip blocks can take a while because it has to decode the gzip file completely. To avoid this setup when opening a gzip file, the block offset list can be exported and imported.
import io
import os
import rapidgzip as rapidgzip
with open("example.gz", "rb") as file:
in_memory_file = io.BytesIO(file.read())
with rapidgzip.open(in_memory_file, parallelization=os.cpu_count()) as file:
file.seek(123)
data = file.read(100)rapidgzip is the default backend in ratarmount since version 0.14.0.
Then, you can use ratarmount to mount single gzip files easily.
base64 /dev/urandom | head -c $(( 4 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 )) | gzip > sample.gz
# Serial decoding: 23 s
time gzip -c -d sample.gz | wc -c
python3 -m pip install --user ratarmount
ratarmount sample.gz mounted
# Parallel decoding: 3.5 s
time cat mounted/sample | wc -c
# Random seeking to the middle of the file and reading 1 MiB: 0.287 s
time dd if=mounted/sample bs=$(( 1024 * 1024 )) \
iflag=skip_bytes,count_bytes skip=$(( 2 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 )) count=$(( 1024 * 1024 )) | wc -cBecause it is written in C++, it can of course also be used as a C++ library.
In order to make heavy use of templates and to simplify compiling with Python setuptools, it is mostly header-only so that integration it into another project should be easy.
The license is also permissive enough for most use cases.
I currently did not yet test integrating it into other projects other than simply manually copying the source in src/core, src/rapidgzip, and if integrated zlib is desired also src/external/zlib.
If you have suggestions and wishes like support with CMake or Conan, please open an issue.
A paper describing the implementation details and showing the scaling behavior with up to 128 cores has been submitted to and accepted in ACM HPDC'23, The 32nd International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing. The paper can also be accessed on ACM DL or Arxiv. The accompanying presentation can be found here.
If you use this software for your scientific publication, please cite it as:
@inproceedings{rapidgzip,
author = {Knespel, Maximilian and Brunst, Holger},
title = {Rapidgzip: Parallel Decompression and Seeking in Gzip Files Using Cache Prefetching},
year = {2023},
isbn = {9798400701559},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3588195.3592992},
doi = {10.1145/3588195.3592992},
abstract = {Gzip is a file compression format, which is ubiquitously used. Although a multitude of gzip implementations exist, only pugz can fully utilize current multi-core processor architectures for decompression. Yet, pugz cannot decompress arbitrary gzip files. It requires the decompressed stream to only contain byte values 9–126. In this work, we present a generalization of the parallelization scheme used by pugz that can be reliably applied to arbitrary gzip-compressed data without compromising performance. We show that the requirements on the file contents posed by pugz can be dropped by implementing an architecture based on a cache and a parallelized prefetcher. This architecture can safely handle faulty decompression results, which can appear when threads start decompressing in the middle of a gzip file by using trial and error. Using 128 cores, our implementation reaches 8.7 GB/s decompression bandwidth for gzip-compressed base64-encoded data, a speedup of 55 over the single-threaded GNU gzip, and 5.6 GB/s for the Silesia corpus, a speedup of 33 over GNU gzip.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 32nd International Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing},
pages = {295–307},
numpages = {13},
keywords = {gzip, decompression, parallel algorithm, performance, random access},
location = {Orlando, FL, USA},
series = {HPDC '23},
}This tool originated as a backend for ratarmount. After writing the bzip2 backend for ratarmount, my hesitation about reimplementing custom decoders for existing file formats has vastly diminished. And, while random access to gzip files did exist with indexed_gzip, it did not support parallel decompression neither for the index creation nor when the index already exists. The latter of which is trivial, when ignoring load balancing issues, but parallelizing even the index creation is vastly more complicated because decompressing data requires the previous 32 KiB of decompressed data to be known.
After implementing a production-ready version by improving upon the algorithm used by pugz, I submitted a paper. The review process was double-blind and I was unsure whether to pseudonymize Pragzip because it has already been uploaded to Github. In the end, I used "rapidgzip" during the review process and because I was not sure, which form fields should be filled with the pseudonymized title, I simply stuck with it. Rapidgzip was chosen for similar reason to pragzip, namely the P and RA are acronyms for Parallel and Random Access. As rapgzip, did not stick, I used rapidgzip, which now also contains the foremost design goal in its name: being rapidly faster than single-threaded implementations. Furthermore, the additional ID could be interpreted to stand for Index and Decompression, making "rapid" a partial backronym.
The main part of the internal architecture used for parallelizing is the same as used for indexed_bzip2.
Performance profiling and tracing is done with Score-P for instrumentation and Vampir for visualization. This is one way, you could install Score-P with most of the functionalities on Ubuntu 22.04.
Installation steps for Score-P
sudo apt-get install libopenmpi-dev openmpi-bin gcc-11-plugin-dev llvm-dev libclang-dev libunwind-dev \
libopen-trace-format-dev otf-trace libpapi-dev
# Install Score-P (to /opt/scorep)
SCOREP_VERSION=8.0
wget "https://perftools.pages.jsc.fz-juelich.de/cicd/scorep/tags/scorep-${SCOREP_VERSION}/scorep-${SCOREP_VERSION}.tar.gz"
tar -xf "scorep-${SCOREP_VERSION}.tar.gz"
cd "scorep-${SCOREP_VERSION}"
./configure --with-mpi=openmpi --enable-shared --without-llvm --without-shmem --without-cubelib --prefix="/opt/scorep-${SCOREP_VERSION}"
make -j $( nproc )
make install
# Add /opt/scorep to your path variables on shell start
cat <<EOF >> ~/.bashrc
if test -d /opt/scorep; then
export SCOREP_ROOT=/opt/scorep
export PATH=$SCOREP_ROOT/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$SCOREP_ROOT/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
fi
EOF
echo -1 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/perf_event_paranoid
# Check whether it works
scorep --version
scorep-info config-summary