-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 268
v0.28: Pagination guide #1753
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Merged
Merged
v0.28: Pagination guide #1753
Changes from 2 commits
Commits
Show all changes
11 commits
Select commit
Hold shift + click to select a range
f3f36ec
pagination guide: zeroth draft
guimachiavelli 4f76ad2
pagination guide: slightly improved draft
guimachiavelli 9250fc0
Apply suggestions from code review
guimachiavelli a99a123
Apply suggestions from code review
guimachiavelli d63d87d
Apply suggestions from code review
guimachiavelli 9d070d1
pagination guide: first draft
guimachiavelli 655c262
Update learn/advanced/pagination.md
guimachiavelli 60890b6
Address review feedback
guimachiavelli 1693ada
Apply suggestions from code review
guimachiavelli 7b8fbc7
Apply suggestions from code review
guimachiavelli a12ddd3
address review feedback
guimachiavelli File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Failed to load comments.
Loading
Jump to
Jump to file
Failed to load files.
Loading
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,117 @@ | ||
| # Pagination of search results | ||
|
|
||
| In a perfect world, users would not need to look beyond the first search result to find what they were looking for. In practice, this is difficult to achieve due to design constraints, performance trade-offs, and even inneffective query terms. Because of that, it is usually necessary to create a pagination interface so users can browse through long lists of results. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| In this guide, we will discuss some of Meilisearch's current limitations, how these limitations impact common pagination interface patterns, and the recommended way of handling pagination when using Meilisearch. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Choosing the right pagination UI | ||
|
|
||
| For performance reasons, Meilisearch cannot provide the exact number of possible results for a query. When using the search endpoint, responses contain an `estimatedTotalHits` field. As its name indicates, `estimatedTotalHits` is only an estimate of how many documents match your user's query. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| Because of this, we do not recommend creating interfaces with page selectors that allow users to jump to an arbitrary results page. If page selection is crucial to the software you are developing, this document's last section lists a number of tips that might help you work around Meilisearch's current limitations. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| Instead of a full page selector, [we recommend creating pagination interfaces centered around previous and next buttons](#recommended-previous-and-next-buttons). | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ::: note | ||
| By default, Meilisearch returns a maximum of 1000 search results. Consult our [index setting reference](/reference/api/settings.md) if you need to change this. | ||
| ::: | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Recommended: Previous and next buttons | ||
|
|
||
| Pagination interfaces that rely solely on previous and next buttons are similar to page selectors, but do not allow users to jump to an arbitrary results page. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ![Placeholder image for prev/next interface]() | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| Though this approach offers less precision than a full-blown page selector, it does not require knowing the number of total search results. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Implementation | ||
|
|
||
| Previous and next buttons can be implemented using the [`limit`](/reference/api/search.md#limit) and [`offset`](/reference/api/search.md#offset) search parameters. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| Paginating requires providing an `offset` that is equal to your `limit` times the page number times: `offset = limit * page number`. We recommend starting page count from 0 instead of 1 when calculating offset values. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| For example, if you set `limit` to `20` and want the first page of search results, your `offset` must be 0: `offset = 0 * 20`. | ||
|
|
||
| ```js | ||
| const results = await index.search("x", { limit: 20, offset: 0 }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| If you keep the same `limit` and want the third page of results, `offset` must be `40`: `offset = 2 * 20`. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ```js | ||
| const results = await index.search("x", { limit: 20, offset: 40 }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Once a query returns less than your configured `limit`, you have reached the last results page. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| It is often helpful to disable navigation buttons when the user cannot move to the "next" or "previous" page. The "previous" button should be disabled whenever your `offset` is 0. | ||
|
|
||
| To disable the "next" button, we recommend setting your query's `limit` to the number of displayed results plus one. The extra result indicates that you have at least one item beyond what you can display in a single results page: | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| ```js | ||
| const results = await index.search("x", { limit: 21, offset: 0 }) | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| if (offset === 0 ) { | ||
| // If offset equals 0, we're on the first results page | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| // and can disable the "previous" buttons | ||
| document.querySelector("#previous_button").disabled = true; | ||
| } else { | ||
| document.querySelector("#previous_button").disabled = false; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| if (results.hits.length < 21 ) { | ||
| // If Meilisearch returns 20 items or less, | ||
| // we don't have any more results to | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| // and can disable the "next" | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| document.querySelector("#next_button").disabled = true; | ||
| } else { | ||
| // If Meilisearch returns exactly 21 results | ||
| // and our page can only show 20 items at a time, | ||
| // we have at least one more page with 1 result in it | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| document.querySelector("#next_button").disabled = false; | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Not recommended: Page selection | ||
|
|
||
| As its name states, this type of pagination is made of a numbered list of pages accompanied by next and previous buttons. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| 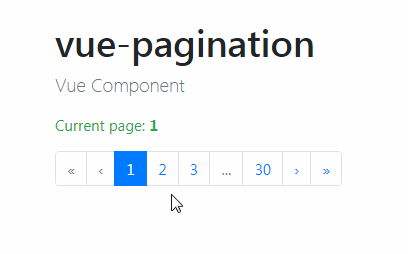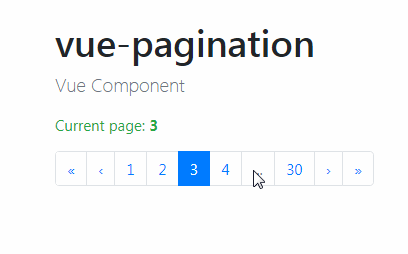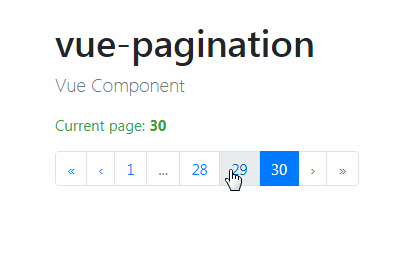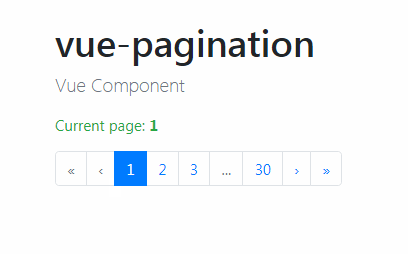 | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| This is is a common UI pattern that offers users a significant amount of precision when navigating results. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Implementation | ||
|
|
||
| The general implementation of a page selection interface is similar to our [recommended solution](#recommended-previous-and-next-buttons), but you must also display a page list. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| To create the page list, however, you must know the exact number of total results. For example, if you have 100 results and your search result pages contain 10 results each, your selector must show a list of numbers going from 1 to 10. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| Since Meilisearch can only give you an estimate of total search results, it can be difficult to implement page selectors when using Meilisearch. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| We recommend two different workarounds to create this kind of pagination interface with Meilisearch. | ||
|
|
||
| #### Set a hard limit of results during your search | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| By default, a search request returns 20 search results. You can change this value to a much higher number and treat it as the effective maximum of search results you will show a user. Doing so means the size of your `hits` array is the exact number of search results you have to paginate. | ||
|
|
||
| For example, if you set `limit` to 300, every search request made to Meilisearch returns at most 300 documents. If a query returns a `hits` array with 200 items and you want each page to display 20 results, you can create a page selector with 10 pages. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| // perhaps a code sample here? | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| This method provides control and reliability. It also prevents users from paginating too far, which avoids performance loss. However, this limits the number of results your users can see. | ||
|
|
||
| ::: note | ||
| We do not recommend caution when setting high values for `limit` as it can negatively impact performance. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| #### Accept the unreliable number | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| You use `estimatedTotalHits` to calculate the number of search result pages. This means your page count is likely to change until Meilisearch retrives the last search result. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| For example, a query's `estimatedTotalHits` might be `100` when you fetch the first page of search results. If you are showing 20 results per page, this means your interface will display a page selector with 5 pages. When you fetch the fifth and last page according to Meilisearch's current estimate, however, `estimatedTotalHits` might change to `300`. Your page list, previously displaying 5 pages, must now show 10 total pages. | ||
|
|
||
| This method gives users access to all search results. However, it also results in an interface that might feel unreliable due to constant and unpredictable changes. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Unsatisfied? Let us know | ||
|
|
||
| Is the current state of pagination in Meilisearch negatively impacting you? Please share your thoughts with us in this [GitHub discussion](https://github.com/meilisearch/product/discussions/483). We are actively working on improving this aspect of Meilisearch and your input is greatly appreciated. | ||
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
guimachiavelli marked this conversation as resolved.
Outdated
Show resolved
Hide resolved
|
||
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.