Config Engine generates network configurations and docker images for all nodes of VPN network from a single config.json file. This is time saving approach when you need to deploy Tinc for numerous remote nodes. So you can share config folders or you can create docker images for each configs (using provided scripts) to disribute and directly connect to VPN network.
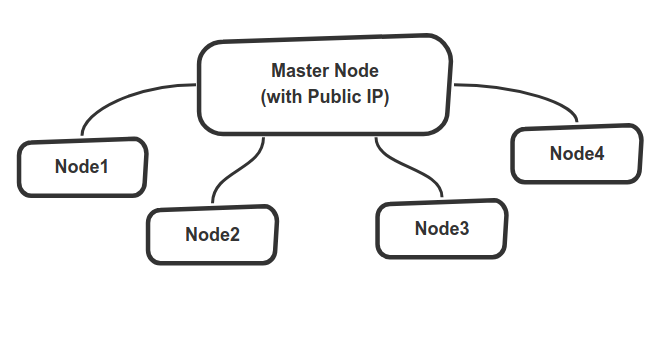
For now; it only supports simple topology depicted on schematic below which has one node with a public IP (namely master node) and multiple other Tinc client nodes without need of public IP. It may converted into mesh network if you provide more master nodes in your network as Tinc claims to form Mesh VPN Network where nodes directly talk to each other without traffic passing through interim nodes "regardless of how you set up the tinc daemons to connect to each other" [1].
├── config_outs/ # configurations will be generated under this directory
├── image_outs/ # docker images will be generted under this directory
├── templates/ # tinc config file templates; Jinja2 used as template engine
│ ├── hostfile.tmpl
│ ├── tinc-down.tmpl
│ ├── tinc-up.tmpl
│ └── tinc.conf.tmpl
├── test/ # docker-compose files to test tinc setup
│ ├── docker-compose.yml # test setup with externally mounting config
│ └── tinc.conf.tmpl # test setup with image with embedded config
├── images/ # shematics
├── Dockerfile # Dockerfile for config generator script
├── Dockerfile_node # Dockerfile to build tinc client image with embedded configuration
├── build_all_nodes.sh # Build tinc docker images with embedded configuration
├── config.json # configure all networks this json file
├── docker.compose.yml # docker-compose file to trigger config generation
├── gen_config.py # python code to generates configs
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
Check config.json file to configure your network. Currently i've only tested with simple start topology where there is only one master node and other nodes connected to it.
If you are lazy, just change master_public_ip variable with your server IP and leave rest of config as it is :
"master_public_ip": "198.199.124.51",
Sample config.json will create 20 nodes with master node and other vpn nodes connected to it. It will use IP pool from 10.0.26.1 to 10.0.26.20 for nodes.
Warning! DO NOT USE "-" character in network name.
Run docker-compose on project root folder
docker-compose up
If everything goes fine; Tinc configurations will be generated under config_outs/config_< unique_id >
Such as :
ls config_outs/config_3e2e721b-d29d-4158-9f81-cb3d6cf5d8ee/*
You can either use these network configs by sharing them to other host PCs' /etc/tinc/
folder :
cp -r config_outs/<config-id>/<node-name>/<netowork-name>/ /etc/tinc/
Or you can use with Docker file as it is shown on test/docker-compose.yml
If you like to create docker images for each node with embedded configurations inside it. You can use build_all_nodes.sh script.
To test command to see what commands to be issued for each config :
./build_all_nodes.sh config_outs/<config-id> <your-name> test
To build images :
./build_all_nodes.sh config_outs/<config-id> <your-name> build
In case you dont have private docker registry server (you should not user docker hub for obvious reasons), you might like to share docker images manually. So to export docker images into image_outs folder :
./build_all_nodes.sh config_outs/<config-id> <your-name> save
To test; change docker image name : image: <your-name>/<image-name>:latest in test/docker-compose_w_node.yml file.
And run :
docker-compose -f test/docker-compose_w_node.yml
Transfer your image to other client. (You may use scp).
Load Docker image :
docker load --input <path-to-your-image>/<config-id>.img
Check your image :
docker images
And use test/docker-compose_w_node.yml file similarly.