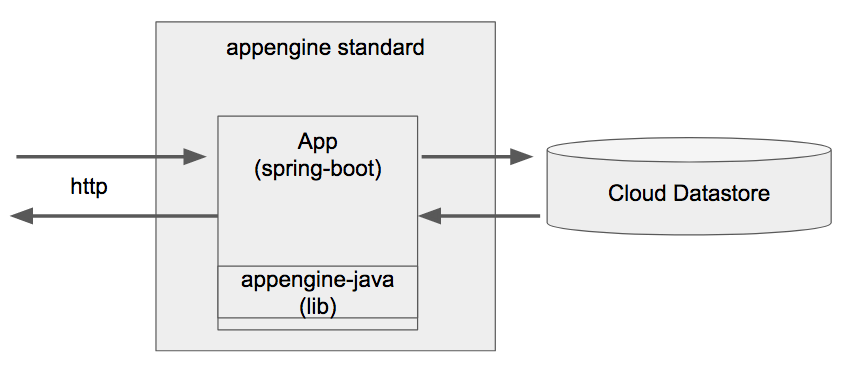
- CRUD RESTFul API
- Spring Boot
- Google cloud datastore
- Google appengine Standard environment
- Gradle
$ gcloud init
# ...
$ gradle appengineRun # run locally
$ gradle appengineDeploy # deploy on GCP
Firstly, create HelloController which returns only Hello, World! text by GET Request.
This is same as spring boot's guide
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping(path = "/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}In order to run as spring-boot, ServletInitializer and SpringApplication requires.
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringBootApplication.class);
}
}@org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApplication.class, args);
}
}To allow the application run in appengine, we need appengine-web.xml in src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/appengine-web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<appengine-web-app xmlns="http://appengine.google.com/ns/1.0">
<threadsafe>true</threadsafe>
<runtime>java8</runtime>
</appengine-web-app>Run this in appengine. You can see something like below.
$ mvn appengine:run
$ curl -i 'localhost:8080/hello'
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 31 Aug 2017 21:13:13 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 13
Server: Jetty(9.3.3.v20150827)
Hello, World!For example, TaskController(which is kind of RestController) handles GET/POST/DELETE/PUT HTTP Request where datastore (or persistansis) is not assumed to simplify. TaskController(which is RestController) handles GET/POST/DELETE/PUT HTTP Request. Take advantage of spring's annotations to work as RestController.
@RestController
public class TaskController {
// Use RequestMapping annotation to map a specific path to a function
@RequestMapping(path = "/tasks", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public List<TaskEntity> gets() {
return Arrays.asList(new TaskEntity("0", "TEST", 0, "2017/08/31"));
}
// Use placeholder in path and PathVariable annotation
// in order to pass id inside path through an argument
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "/task/{id}", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public TaskEntity get(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
return new TaskEntity("0", "TEST", 0, "2017/08/31");
}
// RequestBody annotation indicates an argument `task` is supposed to receive requst body
// Of course, to convert TaskEntity class from JSON/request_body automatically
@RequestMapping(path = "/task", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public void create(@RequestBody TaskEntity task) {
logger.info("TaskEntity: "+task);
return;
}
}Here's an entity class.
public class TaskEntity {
private String id;
private String description;
private Integer priority;
private String untilDate;
// a constructor with no arguments is necesary
public TaskEntity() {
}
public TaskEntity(String id, String description, Integer priority, String untilDate) {
this.id = id;
this.description = description;
this.priority = priority;
this.untilDate = untilDate;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
// define all getters and setters
}Let's think about error handling. App should be supposed to be received wrong incorrect input or go with unexpected behaivor. Then make app return 400, 404, 503 and among other arbitary response code.
First, create our tailored exception class.
public class ApplicationException extends RuntimeException {
}Next implement a part handling an exception. It needed to implement in all handlers but BaseController will be introduce, which becomes a base class of all of them.
public class BaseController {
protected final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(getClass());
@ExceptionHandler({ ApplicationException.class })
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleError(
ApplicationException ex, WebRequest request) {
return new ResponseEntity<Object>(new ErrorResponseModel(ex.getStatus().toString(), ex.getMessage()), new HttpHeaders(), ex.getStatus());
}
}All controllers should be like here.
public class TaskController extends BaseController {See this article if you want to know more.
Work with Google cloud datastore
Append the following dependency into dependency part in pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.appengine</groupId>
<artifactId>appengine-api-1.0-sdk</artifactId>
<version>1.9.50</version>
</dependency>We use datastore through appengine-api library instead of following cloud library because cloud library can't be worked with local devserver's datastore.
<dependency> <!-- Google Cloud Client Library for Java -->
<groupId>com.google.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>google-cloud</artifactId>
<version>0.25.0-alpha</version>
</dependency>Second of all, let's create interface and service class for access to datastore. You can see TaskSercie and DatastoreService.
Next, introduce Autowired member into TaskController which is [DI] variable. It means that it can be changeable in runtime.
Autowired annotation shows this member is supposed to be accept any TaskService instances.
Spring boot's DI is described here.
@RestController
public class TaskController extends BaseController {
@Autowired
TaskService datastoreService;At same time there's one more autowired member in Datastore class.
This datastore member is an actual client for appengine to communicate with the datastore.
@Service
public class DatastoreService implements TaskService {
@Autowired
com.google.appengine.api.datastore.DatastoreService datastore;In addition, This configulation in SpringApplication required to run google cloud datastore.
@Bean
public DatastoreService cloudDatastoreService() {
return DatastoreServiceFactory.getDatastoreService();
}AppEngine has task-based push/pull queue.
First of all, we need to specify a queue in queue.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<queue-entries>
<queue>
<name>queue-blue</name>
<target>v2.task-module</target>
</queue></target></name>
</queue>
<queue-entries>