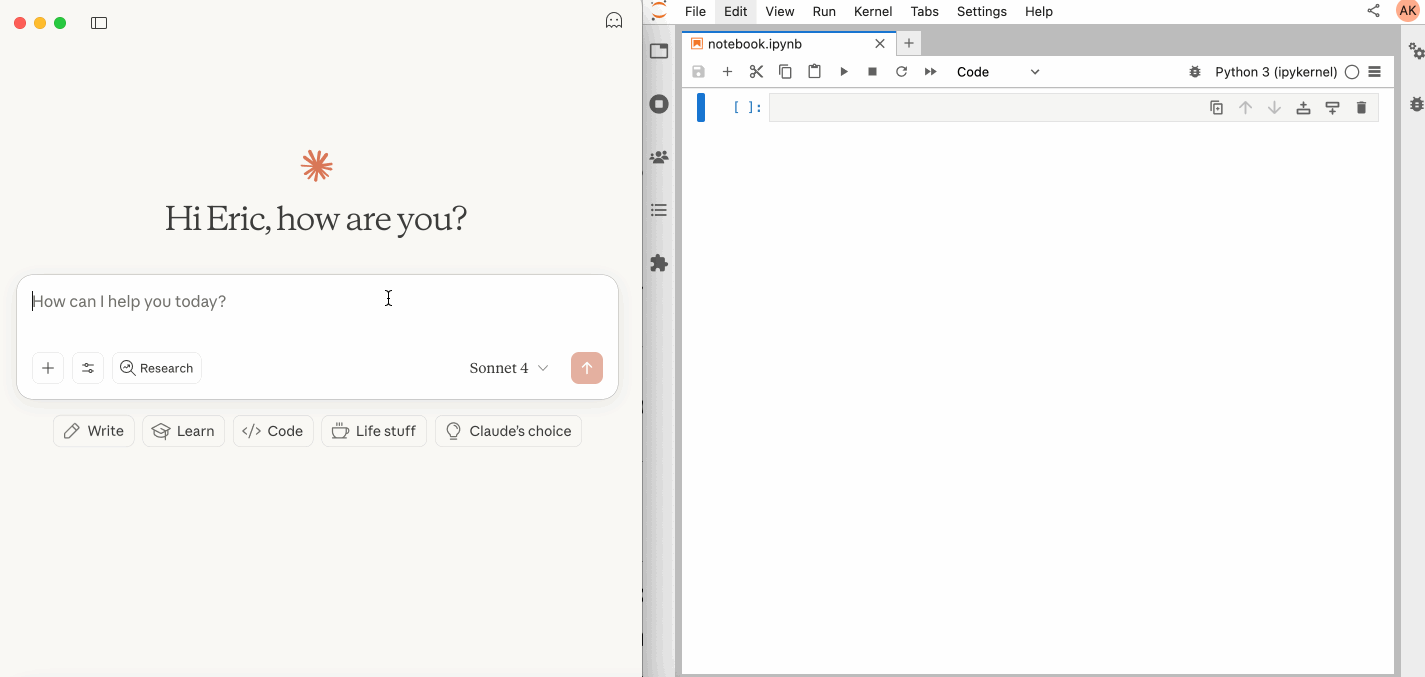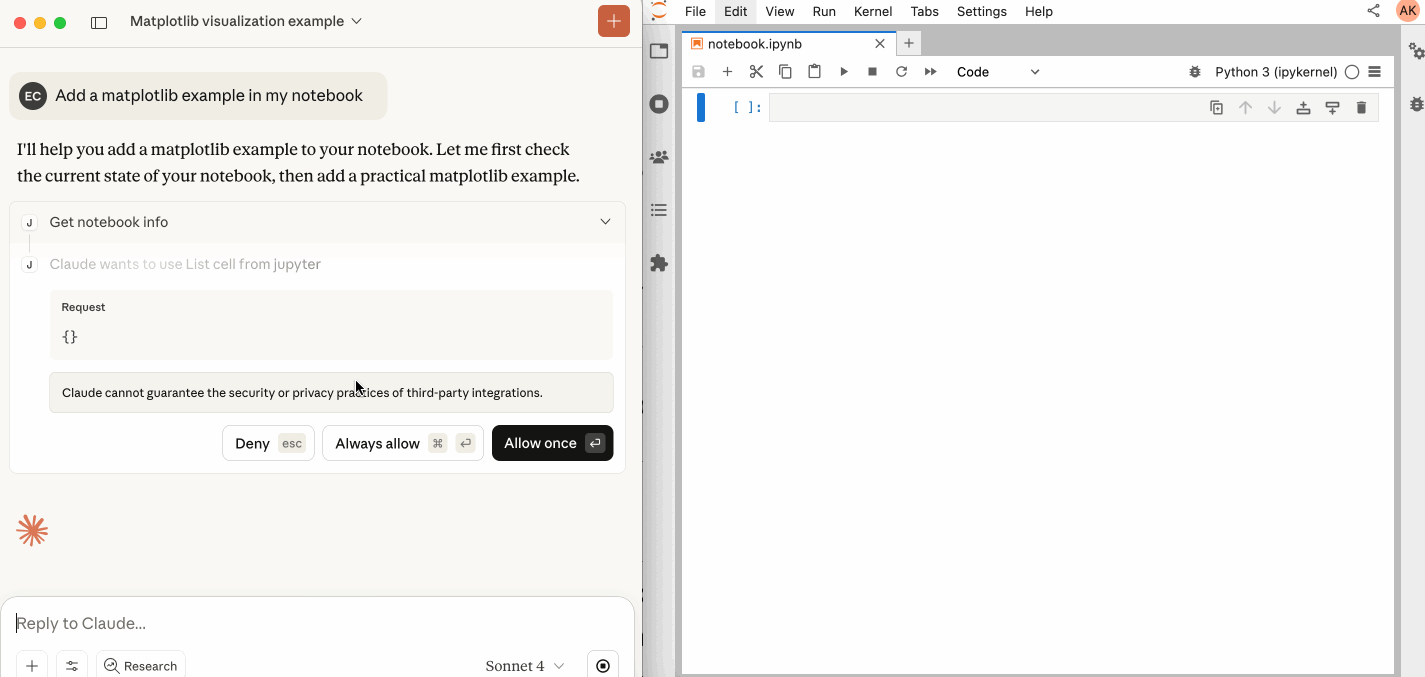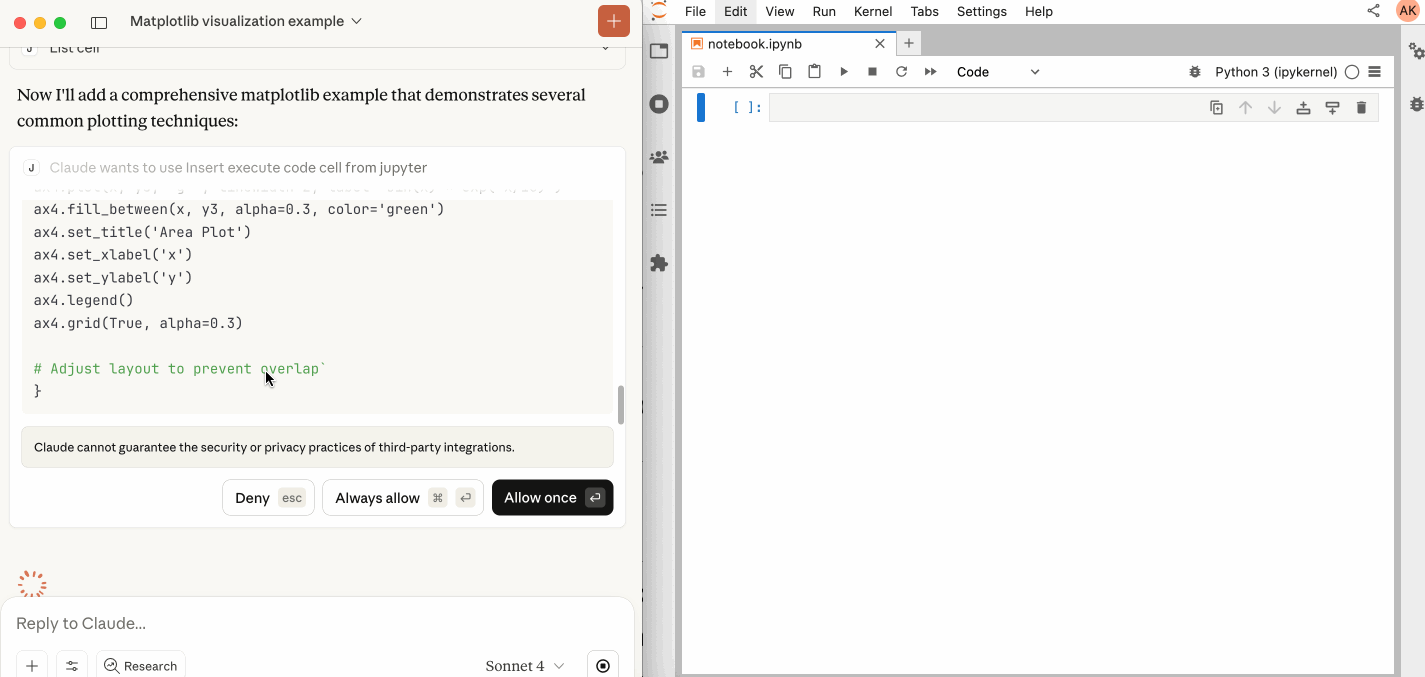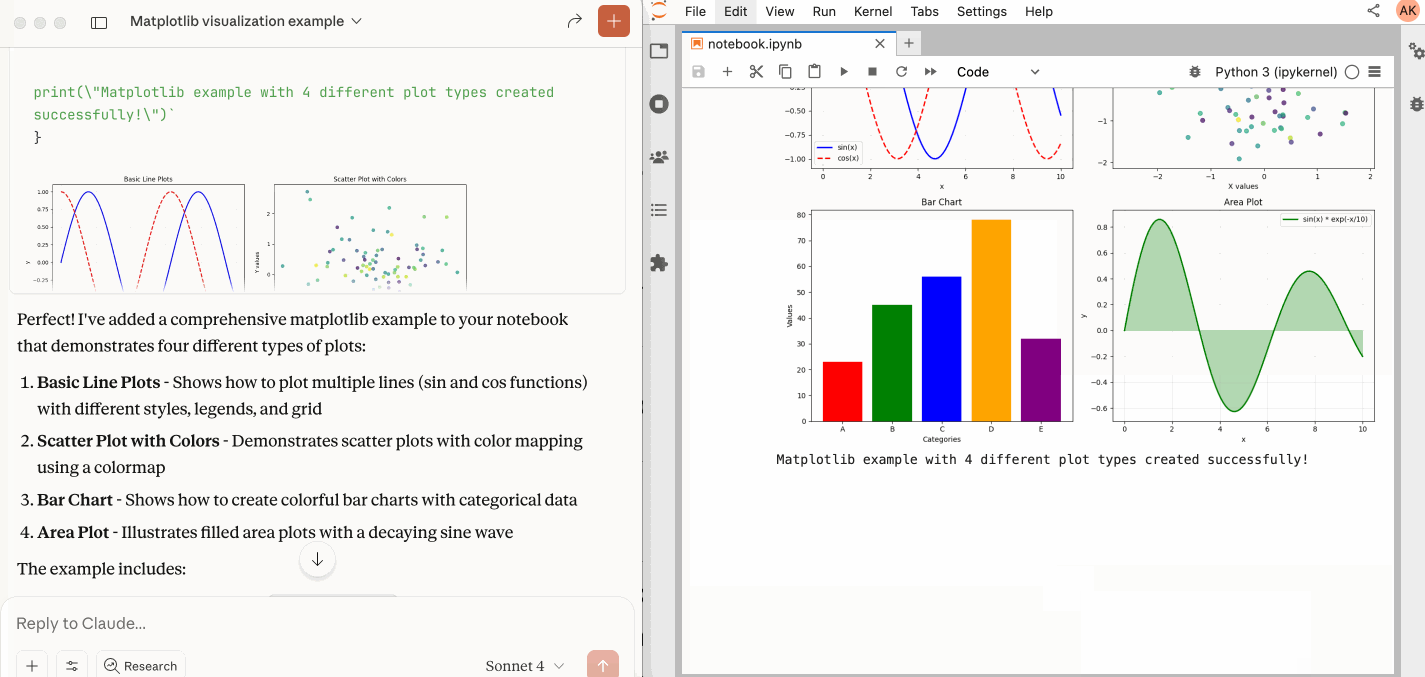
An MCP server developed for AI to connect and manage Jupyter Notebooks in real-time
Developed by Datalayer
- ⚡ Real-time control: Instantly view notebook changes as they happen.
- 🔁 Smart execution: Automatically adjusts when a cell run fails thanks to cell output feedback.
- 🧠 Context-aware: Understands the entire notebook context for more relevant interactions.
- 📊 Multimodal support: Support different output types, including images, plots, and text.
- 📚 Multi-notebook support: Seamlessly switch between multiple notebooks.
- 🎨 JupyterLab integration: Enhanced UI integration like automatic notebook opening.
- 🤝 MCP-compatible: Works with any MCP client, such as Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf, and more.
Compatible with any Jupyter deployment (local, JupyterHub, ...) and with Datalayer hosted Notebooks.
The server provides a rich set of tools for interacting with Jupyter notebooks, categorized as follows:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
list_files |
List files and directories in the Jupyter server's file system. |
list_kernels |
List all available and running kernel sessions on the Jupyter server. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
use_notebook |
Connect to a notebook file, create a new one, or switch between notebooks. |
list_notebooks |
List all notebooks available on the Jupyter server and their status |
restart_notebook |
Restart the kernel for a specific managed notebook. |
unuse_notebook |
Disconnect from a specific notebook and release its resources. |
read_notebook |
Read notebook cells source content with brief or detailed format options. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
read_cell |
Read the full content (Metadata, Source and Outputs) of a single cell. |
insert_cell |
Insert a new code or markdown cell at a specified position. |
delete_cell |
Delete a cell at a specified index. |
overwrite_cell_source |
Overwrite the source code of an existing cell. |
execute_cell |
Execute a cell with timeout, supports multimodal output including images. |
insert_execute_code_cell |
Insert a new code cell and execute it in one step. |
execute_code |
Execute code directly in the kernel, supports magic commands and shell commands. |
Available only when JupyterLab mode is enabled. It is enabled by default.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
notebook_run-all-cells |
Execute all cells in the current notebook sequentially |
For more details on each tool, their parameters, and return values, please refer to the official Tools documentation.
The server also supports prompt feature of MCP, providing a easy way for user to interact with Jupyter notebooks.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
jupyter-cite |
Cite specific cells from specified notebook (like @ in Coding IDE or CLI) |
For more details on each prompt, their input parameters, and return content, please refer to the official Prompt documentation.
For comprehensive setup instructions—including Streamable HTTP transport, running as a Jupyter Server extension and advanced configuration—check out our documentation. Or, get started quickly with JupyterLab and STDIO transport here below.
pip install jupyterlab==4.4.1 jupyter-collaboration==4.0.2 jupyter-mcp-tools>=0.1.4 ipykernel
pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt
pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17Tip
To confirm your environment is correctly configured:
- Open a notebook in JupyterLab
- Type some content in any cell (code or markdown)
- Observe the tab indicator: you should see an "×" appear next to the notebook name, indicating unsaved changes
- Wait a few seconds—the "×" should automatically change to a "●" without manually saving
This automatic saving behavior confirms that the real-time collaboration features are working properly, which is essential for MCP server integration.
# Start JupyterLab on port 8888, allowing access from any IP and setting a token
jupyter lab --port 8888 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKEN --ip 0.0.0.0Note
If you are running notebooks through JupyterHub instead of JupyterLab as above, you should:
- Set the environment variable
JUPYTERHUB_ALLOW_TOKEN_IN_URL=1in the single-user environment. - Ensure your API token (
MY_TOKEN) is created withaccess:serversscope in the Hub.
Next, configure your MCP client to connect to the server. We offer two primary methods—choose the one that best fits your needs:
- 📦 Using
uvx(Recommended for Quick Start): A lightweight and fast method usinguv. Ideal for local development and first-time users. - 🐳 Using
Docker(Recommended for Production): A containerized approach that ensures a consistent and isolated environment, perfect for production or complex setups.
📦 Using uvx (Quick Start)
First, install uv:
pip install uv
uv --version
# should be 0.6.14 or higherSee more details on uv installation.
Then, configure your client:
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["jupyter-mcp-server@latest"],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}🐳 Using Docker (Production)
On macOS and Windows:
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "JUPYTER_URL",
"-e", "JUPYTER_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://host.docker.internal:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}On Linux:
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "JUPYTER_URL",
"-e", "JUPYTER_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"--network=host",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"JUPYTER_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"JUPYTER_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}Tip
- Port Configuration: Ensure the
portin your Jupyter URLs matches the one used in thejupyter labcommand. For simplified config, set this inJUPYTER_URL. - Server Separation: Use
JUPYTER_URLwhen both services are on the same server, or set individual variables for advanced deployments. The different URL variables exist because some deployments separate notebook storage (DOCUMENT_URL) from kernel execution (RUNTIME_URL). - Authentication: In most cases, document and runtime services use the same authentication token. Use
JUPYTER_TOKENfor simplified config or setDOCUMENT_TOKENandRUNTIME_TOKENindividually for different credentials. - Notebook Path: The
DOCUMENT_IDparameter specifies the path to the notebook the MCP client default to connect. It should be relative to the directory where JupyterLab was started. If you omitDOCUMENT_ID, the MCP client can automatically list all available notebooks on the Jupyter server, allowing you to select one interactively via your prompts. - Image Output: Set
ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUTtofalseif your LLM does not support mutimodel understanding.
For detailed instructions on configuring various MCP clients—including Claude Desktop, VS Code, Cursor, Cline, and Windsurf — see the Clients documentation.
- Interact with LLMs that supports multimodal input (like Gemini 2.5 Pro) to fully utilize advanced multimodal understanding capabilities.
- Use a MCP client that supports returning image data and can parse it (like Cursor, Gemini CLI, etc.), as some clients may not support this feature.
- Break down complex task (like the whole data science workflow) into multiple sub-tasks (like data cleaning, feature engineering, model training, model evaluation, etc.) and execute them step-by-step.
- Provide clearly structured prompts and rules (👉 Visit our Prompt Templates to get started)
- Provide as much context as possible (like already installed packages, field explanations for existing datasets, current working directory, detailed task requirements, etc.).
We welcome contributions of all kinds! Here are some examples:
- 🐛 Bug fixes
- 📝 Improvements to existing features
- ✨ New feature development
- 📚 Documentation improvements and prompt templates
For detailed instructions on how to get started with development and submit your contributions, please see our Contributing Guide.
Looking for blog posts, videos, or other materials about Jupyter MCP Server?
👉 Visit the Resources section in our documentation for more!
If this project is helpful to you, please give us a ⭐️
Made with ❤️ by Datalayer