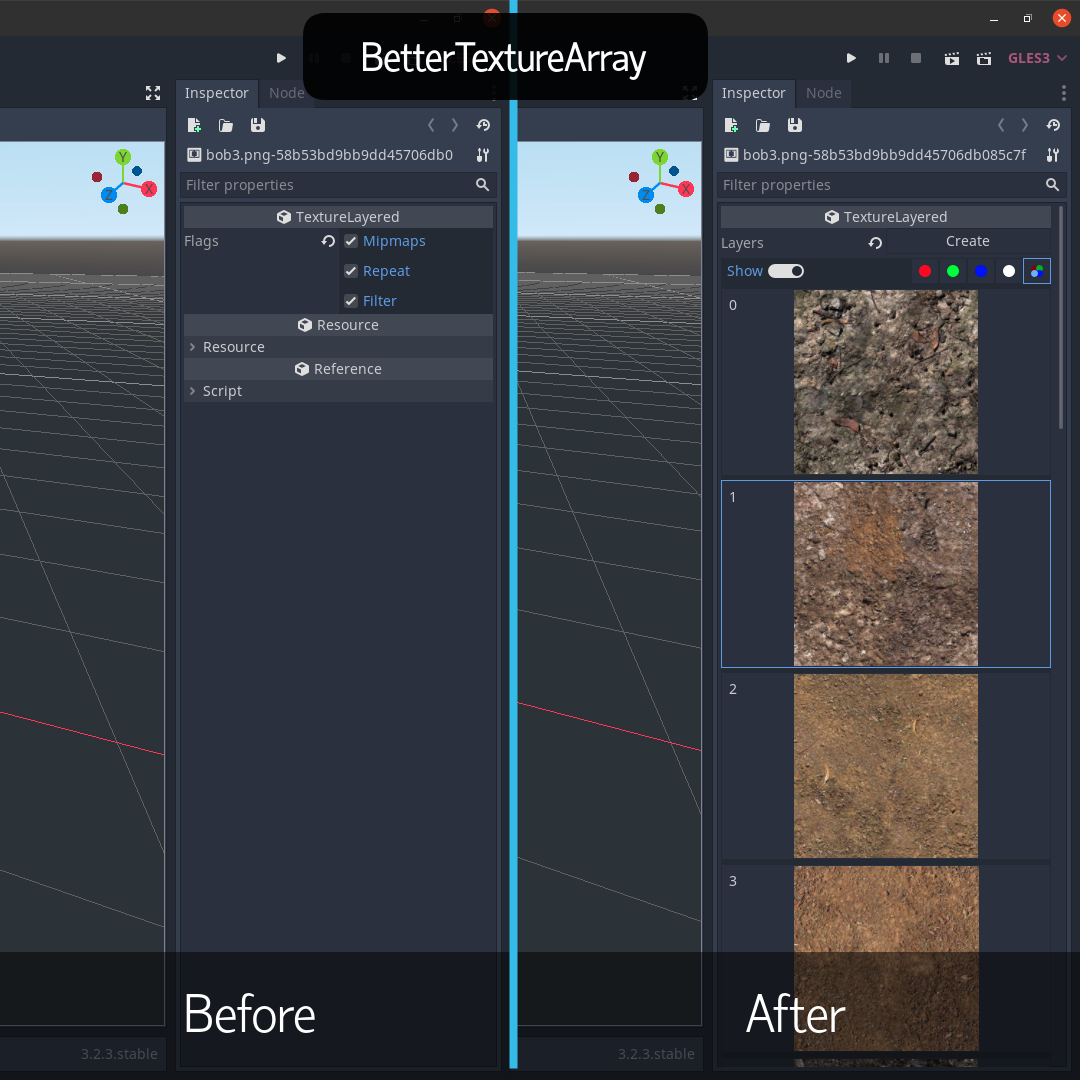
Adds support for saving, viewing and editing TextureArray and Texture3D in Godot 3.
Godot 3.x has very buggy behaviour when attempting to save a TextureLayered (TextureArray and Texture3D), it also has poor support for TextureLayered (TextureArray and Texture3D) in the editor.
Attempting to save TextureArray and Texture3D inside the scene or as .res or .tres, produces errors.
This plugin adds support for saving TextureArray and Texture3D as .texarr and .tex3d files both in the editor and from code.
These are the native Godot importer formats for TextureArray and Texture3D.
This plugin also adds UI so that you can create, view, edit and, save TextureArray and Texture3D in the editor. The editor UI allows you to edit individual layers, and each RGBA channel on a layer as well. This is very useful when trying to merge multiple PBR material textures into one file.
The plugin also provides a custom importer for TextureArray and Texture3D.
The builtin importer requires a large single image with each of the layers as a tile in a grid.
With the BetterTextureArray importer, you can use a simple JSON build format to create TextureArray and Texture3D from a list of other image files.
- To install copy the
better-texture-arrayfrom theaddonsfolder to your project'saddonsfolder. - Open your project in the edtior and choose Project Settings... -> Plugins from the Project menu and enable BetterTextureArray.
- To create a new TextureArray or Texture3D click the create new resource icon in the inspector.
- Then click the create button in the new resource to set the width, height and depth (the number of layers), and choose the image format.
- Click the show toggle to show or hide the layers.
- You should have several new white layers.
- Double click a layer to set an image for that layer.
- Select a channel from the channel buttons to view only that channel for the layers.
- With a channel selected, double click a layer to set data for that channel only. The file chooser in channel mode will include a drop down to choose the source channel from your selected file.
- You can select a layer by clicking on it. The index of the selected layer will be set in the metadata of the TextureArray or Texture3D as
layer_selectedand thechangedsignal will be emitted. This is useful if you want to interact with this UI in another editor plugin. - When saving the TextureArray or Texture3D from the Editor, you must choose to save as either a
.texarror.tex3dfile, DO NOT save as.resor.tres, these will error. Also DO NOT save the TextureArray or Texture3D in your scene, this will error and bloat your scene file.
Create a JSON file with a .ta-builder file extension for TextureArray and .t3d-builder extension for Texture3D.
Select the file from the importer in the editor to customize import properties.
The JSON object must contain a size array property, and a layers array property.
The size property must have two values for the width and height the layers.
The layers will contain URLs to each image file or resource to use for each layer. You can use a res:// or a file:// reference.
A simple example file:
{
"size": [1024, 1024],
"layers": [
"res://assets/textures/rock1.jpg",
"res://assets/textures/rock2.jpg",
"res://assets/textures/rock3.jpg",
"file://home/user/assets/snow1.jpg",
],
}The layers property can also contain a more complex blending object instead of a simple URL if you want to mix channels from multiple sources into one layer.
A more complex channel mixing example:
{
"size": [1024, 1024],
"layers": [
{
"rgb": ["res://assets/textures/albedo.jpg", "rgb"],
"a": ["res://assets/textures/bump.jpg", "r"],
},
],
}The blending object property keys are the target channels, represented by r, g, b, and a, on their own or in combination.
The blending object property value is an array of two values, the first is the source file or resource, the second is string with the source channels or channel, again represented by r, g, b, and a.