The Automobile industry's supply chain is massive logistical arrangment that is an integral part of any automobile manufacturing company. It mediates between multiple parties, and optimizes the creation of distribution of resources, but the presence of numerous interacting parties, differential pricing, and quality & complicance issues create a logistical nightmare which wastes both time and resources. The failure of Boeing's supply chain for 787 led to a disastrous 3 year delay of their product. Using that as a case-study, we show blockchains are currently the best-suited solution to the problems in current supply chain infrastructure.
- Differential Pricing: Companies prefer keeping their pricings a secret, since this allows them to pay lower prices when outsourcing to developing countries.
- Numerous Parties Invovled: Mediating between so many parties can be a big problem for logistics-providers, slowing down the delivery of services and creating a large overhead for logistics. Furthermore, a centralized mediator of these parties can misuse power to perfer some parties over others.
- Quality & Compliance issues: Procuring a replacement for defective parts is a long-drawn and uncomfortable process.
- Inevitable disruptions: LEAN "on-demand" manufacturing falls flat in a situations where natural disasters and socio-economic problems are common. For example, Japan (frequently affected by earthquakes) has outsourced most of it's supply chain logistics to other countries.
- Centralization: A central mediator for parties is required, which centralizes power in the hands of a few and is a gateway to misuse of resources.
- Fraud by Middlemen: As number of interacting parties increase, there is a proportional increase in middlemen. They lead to fraud and slow down the supply without adding anything to the network.
- Tracking history of any product: Validating identity vendor and checking for tampering by middlemen is not possible.
| Problems | How our solution solves them |
|---|---|
| Differential Pricing | Permissioned ledger for confidential transactions between parties |
| Numerous parties invovled | Consensus between multiple parties is maintained through Smart Contracts |
| Quality & Compliance issues | Smart contract stores money while all solutions are checked and tested |
| Inevitable disruptions | Digital ledger is free of geographical constraints like natural disasters, socio-economic issues |
| Procuring replacements for defective pieces | Smart contract only lets out payments once both parties satisified |
| Centralization | Risk of fraud is mitigated by using decentralized nodes for checking delivery status |
| Fraud by Middlemen | Because of using doubly-signed smart contracts, no financial fraud by middlemen can occur in the system |
| Tracking supply-chain history of each part | Using our network's merkle trees we can verify vendor identity and validity of product |
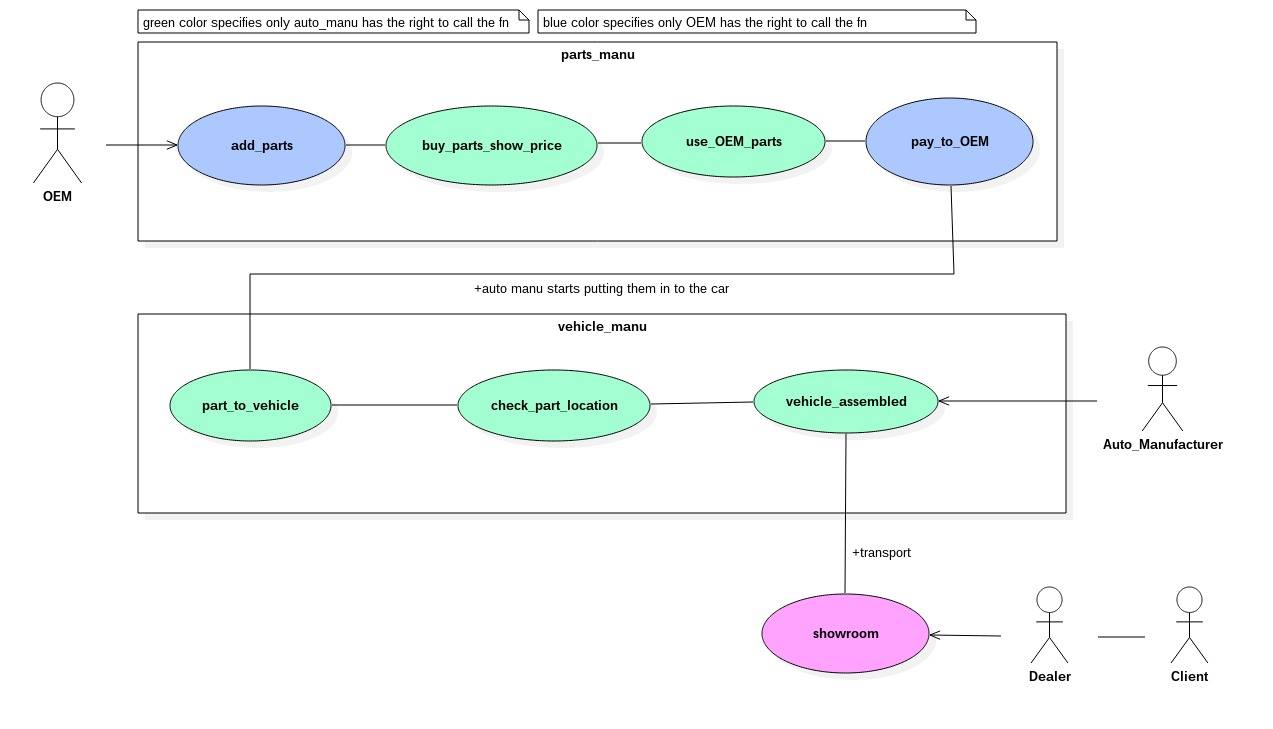
- Manufacture requests parts from OEM.
- OEM lists down all the parts and their details in the contract.
- If parts are genuine and non defective the OEM gets paid.
- Now Manufacturer starts assembling the car.
This protocol has been implemented as a smart contract, and has been optimized for the use-case of automobile supply chains. It has been deployed and tested on the Ropsten network. The link to that deployed contract can be found here.
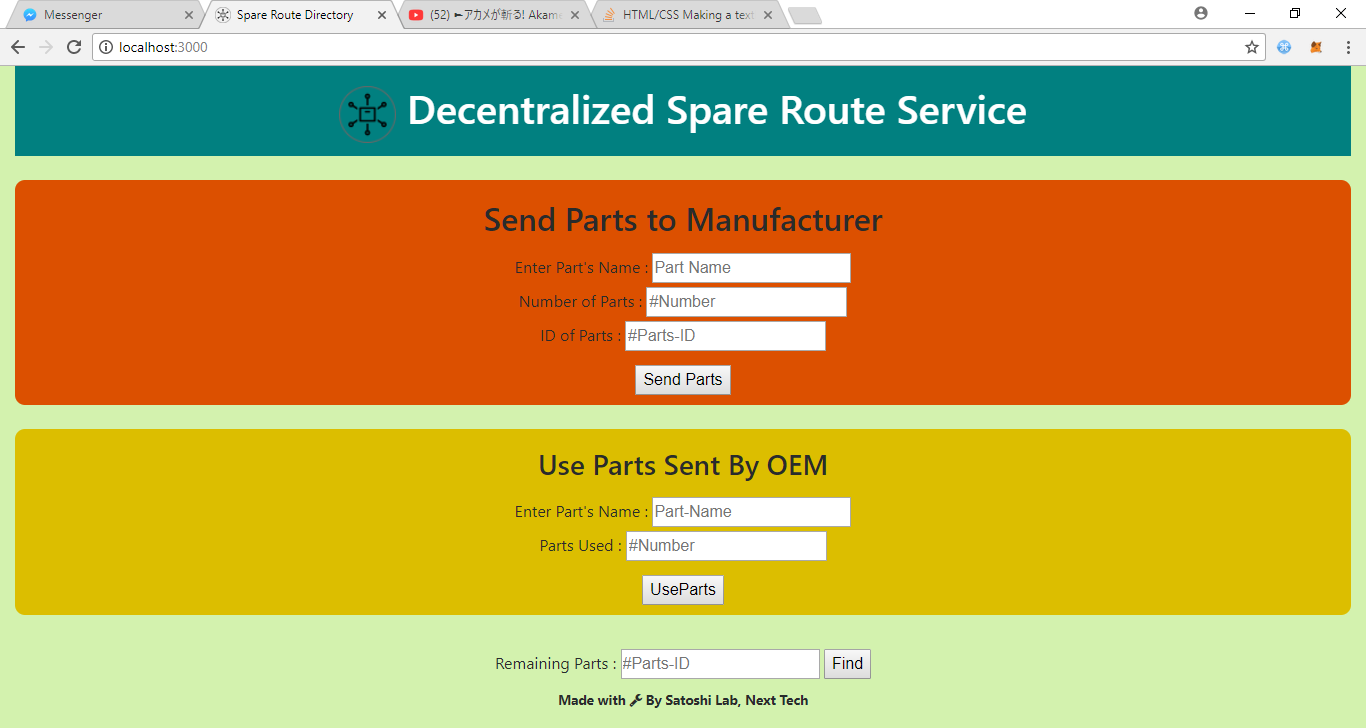
- Add parts - The OEM uses the function Add parts for adding the produced spare part with its name,quantity,ID and price per unit.
- Buy parts show price - The Automobile Manufacturer finds the price he has to pay by calling this function with the name and number of part he needs.
- Use OEM parts - The Automobile Manufacturer pays money temporarily for the parts only if the parts are found to be genuine.
- Pay to OEM - The OEM can call this function to claim the money for the parts only after 10 hours from the time the Manufacturer pays(if defective products are found the Manufacturer refunds the part).
- Part to vehicle - This function is used to assign the part to the Vehicle in which the part is to be installed.
- Check part location - This function is used to check the vehicle in which the part is installed.
- Vehicle assembled - This function is used to set the vehicle as manufactured completely and ready to be sent to the dealer.
- Showroom - The Dealer and client can get the final vehicle from here.
- Ethereum smart constracts (in solidity)
- Ropsten testnet
- Truffle framework
- Remix IDE
- Web3.js
- Geth
- git clone https://github.com/SatoshiNextTechLab/BlockSCM.git
- truffle compile
- truffle migrate
- truffle console
- Interact using Web3.js
- clone repo https://github.com/SatoshiNextTechLab/BlockSCM.git
- cd into TheSpareRoute-master/GUI
- npm install .
- npm install lite-server --save-dev
- npm run dev