This is a Qt GUI for the line_profiler python utility.
It allows to run and display the profiling results using an interactive interface.
It is functionnaly equivalent to the kernprof script, which is used to invoque line_profiler from the command line.
- Command line: Configure and run from the command line, just like
kernprof, - GUI: Configure and run from the GUI, just like
kernprofbut with buttons, - Colors: Highlight lines based on the percentage of time spent on them to easily spot the lines to be optimised,
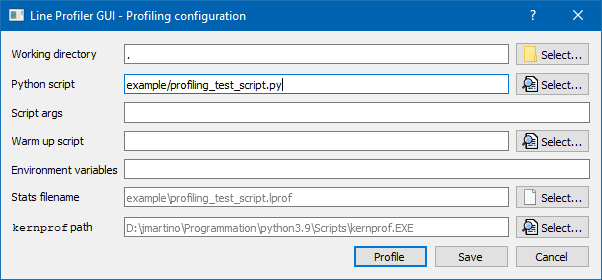
- Configuration: Setup warmup script, environment variables, and more!
- History: Compare timing with previous profiling runs,
- Viewer: Display data from any .lprof file by
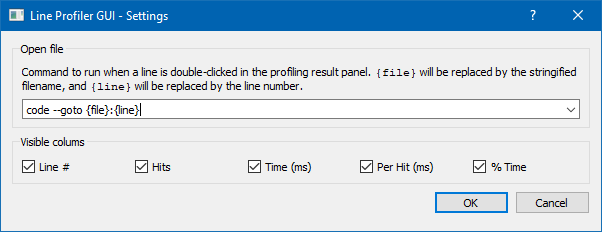
kernprof, - Editor: Double-click on any line to edit it with your favorite editor.
Line Profiler GUI can be installed from pypi using pip:
$ pip install line-profiler-gui
Line Profiler GUI can use anyon of the Qt python bindings by using QtPy: PyQt5, PyQt6, PySide2 or PySide6. You can install the Qt python bindings of your choice in one go by specifying it between square brackets:
$ pip install line-profiler-gui[PySide2] $ pip install line-profiler-gui[PyQt5]
Source releases can be downloaded from PyPI. To check out the development sources, you can use Git:
$ git clone https://github.com/Nodd/lineprofilergui.git
Users should be familiar with the line_profiler line_profiler documentation, but here is a quick reminder.
Since the line by line profiling slown down the execution, not all functions are profiled.
The functions to be profiled have to be marked with a @profile decorator (see the example/ directory for more examples):
@profile
def my_slow_function():
...No import is needed, profile is added to the python builtins for the execution.
Don't forget to remove the added decorators afterwards!
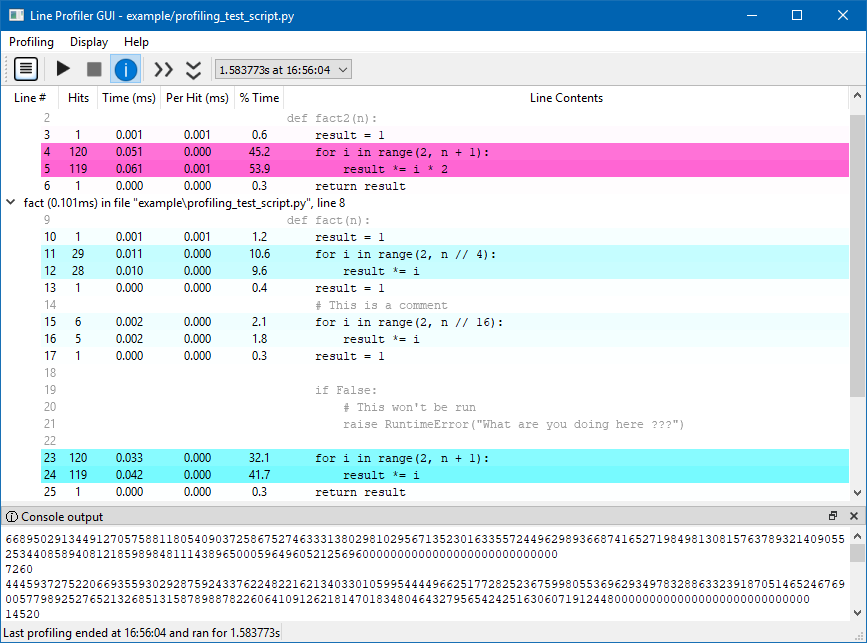
Once the profilng is done, the following data will be disaplyed for each line of the decorated functions:
- Line #: The line number in the file.
- Hits: The number of times that line was executed.
- Time: The total amount of time spent executing the line.
- Per Hit: The average amount of time spent executing the line once.
- % Time: The percentage of time spent on that line relative to the total amount of recorded time spent in the function.
- Line Contents: The actual source code. Note that this is always read from disk when the formatted results are viewed, not when the code was executed. If you have edited the file in the meantime, the lines will not match up, and the formatter may not even be able to locate the function for display.
In the displayed table, the lines are higlighted depending on their % Time. This allows to easily spot the lines to be optimised, and to not be distracted by the rest od the code.
$ lineprofilergui -h
usage: lineprofilergui [-h] [-V] [-l LPROF] [-r] [-o OUTFILE] [-s SETUP]
[script] ...
Run, profile a python script and display results.
positional arguments:
script The python script file to run
args Optional script arguments
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-V, --version show program's version number and exit
-l LPROF, --lprof LPROF
Display data from a .lprof file
-r, --run Profile the python script on launch
-o OUTFILE, --outfile OUTFILE
Save stats to OUTFILE (default: 'scriptname.lprof')
-s SETUP, --setup SETUP
Python script to execute before the code to profile