-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Description
spark执行的大致流程
To summarize, the following phases occur during Spark execution:
- User code defines a DAG (directed acyclic graph) of RDDs
Operations on RDDs create new RDDs that refer back to their parents, thereby
creating a graph.- Actions force translation of the DAG to an execution plan
When you call an action on an RDD it must be computed. This requires computing
its parent RDDs as well. Spark’s scheduler submits a job to compute all needed
RDDs. That job will have one or more stages, which are parallel waves of
computation composed of tasks. Each stage will correspond to one or more RDDs in
the DAG. A single stage can correspond to multiple RDDs due to pipelining.
Tasks are scheduled and executed on a cluster- Stages are processed in order, with individual tasks launching to compute segments
of the RDD. Once the final stage is finished in a job, the action is complete.
task、partition关系
- stage里面的task = 当前RDD其依赖或上一次的RDD partition,若是从file生成的RDD依赖指定的partition数量
- task由scheduler 指定partition所在的node去执行, 等于说哪个节点保存这个partition, 由这个节点去计算task.
The number of tasks in a stage is the same as the number of partitions in the last RDD in the stage. The number of partitions in an RDD is the same as the number of partitions in the RDD on which it depends, with a couple exceptions: the coalesce transformation allows creating an RDD with fewer partitions than its parent RDD, the union transformation creates an RDD with the sum of its parents’ number of partitions, and cartesian(笛卡尔) creates an RDD with their product.
RDDs produced by textFile or hadoopFile have their partitions determined by the underlying MapReduce InputFormat that's used. Typically there will be a partition for each HDFS block being read. Partitions for RDDs produced by parallelize come from the parameter given by the user, or spark.default.parallelism if none is given.
- To determine the number of partitions in an RDD
rdd.partitions().size().
lineage(血统)
each RDD has a set of partitions, which
are atomic pieces of the dataset; a set of dependencies on
parent RDDs, which capture its lineage; a function for
computing the RDD based on its parents; and metadata
about its partitioning scheme and data placement.
-
dependencies between RDDs
- narrow dependencies, where
each partition of the child RDD depends on a constant
number of partitions of the parent (not proportional(比例) to its
size) - wide dependencies, where each partition of the
child can depend on data from all partitions of the parent.
For example, map leads to a narrow dependency, while
join leads to to wide dependencies (unless the parents are
hash-partitioned)
- narrow dependencies, where
-
stage
- 从narrow到wide dependency的时候需要产生新的stage
- 产生action动作的时候会产生新的stage
Each stage contains as many pipelined transformations
with narrow dependencies as possible. The
boundaries of the stages are the shuffle operations required
for wide dependencies wide dependency or any cached partitions
that can short-circuit the computation of a parent RDD.
-
fault-tolerant
- narrow dependency
lost partition can be recomputed in parallel on other nodes
- wide dependency
node failure in the cluster may result in the loss
of some slice of data from each parent RDD, requiring
a full recomputation- checkpoint
可以使用persist() 保存一个checkpoint, 不需要从血统的起点开始计算
-
lineage与DAG的区别
lineage 描述的是RDD的依赖关系, 依赖链, 如图1; 而DAG 是有向无环图, 节点是rdd, 边是rdd的转化关系, 并能区分stage, 如图2
Above figure depicts an RDD graph, which is the result of the following series of transformations:
val r00 = sc.parallelize(0 to 9)
val r01 = sc.parallelize(0 to 90 by 10)
val r10 = r00 cartesian df01
val r11 = r00.map(n => (n, n))
val r12 = r00 zip df01
val r13 = r01.keyBy(_ / 20)
val r20 = Seq(r11, r12, r13).foldLeft(r10)(_ union _)
RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset)
- 在内存中计算, 内存中放不下遵循LRU(最近最少使用算法)将其余置换到disk
- 懒计算, 直到执行action 操作, 才会去计算RDD
- 容错性
使用lineage (血统) 可以在其他节点并行计算failed partition of RDD, 如果有备份则可以直接计算,更快; 否则要根据上次计算的结果重新计算.
若driver故障, 则所有executor的计算结果都会丢失
设置replication, 参考 RDD Persistence , 使用这个配置: MEMORY_ONLY_2, MEMORY_AND_DISK_2, etc.
- 不可变性(Immutability)
一旦创建了rdd, 就是不能修改的, 除非生成新的 rdd, 避免了并发计算的问题, 而且每次 rdd transformation是确定的
rdd.toDebugString() 可以打印出rdd 的生成链
- rdd, dataframe, dataset的区别
参考 infoQ
rdd属于最底层的抽象, 提供最复杂的操作; dataFrame, dataSet提供某些场景下定制化的api, 使代码更加明确和易用, 也提供了性能上的优化, 适用于半结构化的数据, 例如json; 而dataSet 可以作为有类型的抽象, 将数据映射到java对象上, 对语法错误和解析错误提供编译时检查(说白了可以在编译时检查数据类型), dataFrame可以当做是dataSet 是无类型的
spark persist
- checkPoint
分为reliable 和local 两种.
- reliable
SparkContext.setCheckpointDir(directory: String) to set the checkpoint directory, 目录必须是hdfs路径, 因为 checkPoint file实际上是保存在executor 机器上的.
用法: RDD.checkpoint() , 当前rdd被保存, 对 parent rdd的引用都会被移除; 每个job执行完之后, 会往前回溯所有的RDD, 若需要checkpoint, 则标记为 CheckpointingInProgress, 最后启动一个新的job 完成Checkpoint.
job完成 checkpoint之后, 会将rdd的所有 dependency释放掉, 设置该rdd的状态为 checkpoint, 并为该rdd 设置一个强依赖, 设置该rdd的 parent rdd为 CheckpointRDD, 该 CheckpointRDD 负责读取文件系统的 Checkpoint文件, 生成对应rdd 的 partition.
checkpoint 也是lazy的, 触发了action之后, 才会往前回溯到需要checkpoint的RDD 进行checkpoint.
checkpoint的时候, 会重新起一个新的job 去计算需要checkpoint 的rdd, 所以一般在checkpoint 之前先执行 cache, 则后续的checkpoint 的过程就直接把内存中的数据持久化到硬盘中了, 省去了重复计算.
- cache
将中间数据存储在内存中, 以便其他job使用. 当task计算某个rdd的partition, 如果该partition需要cache, 则计算后存到内存.
- cache和checkpoint的区别
cache之后, 整个lineage 还会保留, 但是cache的数据不能在多个driver program之间共享; 但是 checkpoint 之后,会把 lineage全部删除, 因为是持久化到 hdfs的, 可以供其他job使用;
- 与mr的checkpoint的区别
Hadoop MapReduce 在执行 job 的时候,不停地做持久化,每个 task 运行结束做一次,每个 job 运行结束做一次(写到 HDFS)。在 task 运行过程中也不停地在内存和磁盘间 swap 来 swap 去。 可是讽刺的是,Hadoop 中的 task 太傻,中途出错需要完全重新运行,比如 shuffle 了一半的数据存放到了磁盘,下次重新运行时仍然要重新 shuffle。Spark 好的一点在于尽量不去持久化,所以使用 pipeline,cache 等机制。用户如果感觉 job 可能会出错可以手动去 checkpoint 一些 critical 的 RDD,job 如果出错,下次运行时直接从 checkpoint 中读取数据。唯一不足的是,checkpoint 需要两次运行 job
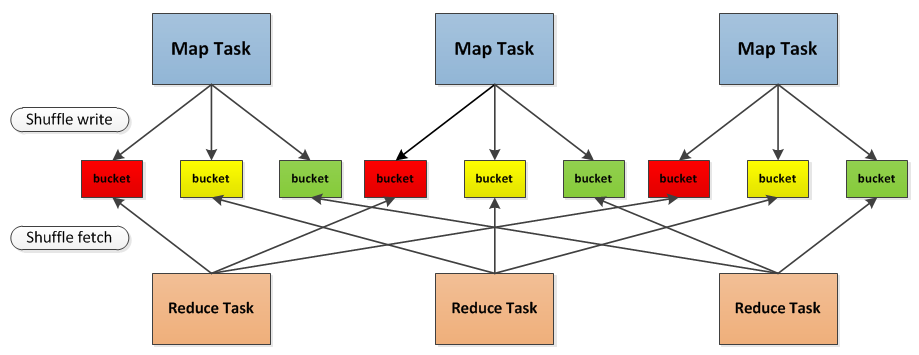
spark shuffle
参考自 SparkInternals-shuffleDetails
shuffle会产生两个stage, 分别对应 shuffle write和shuffle read
shuffle write: 可以当做mapper阶段, 第一个stage 中每个task中的记录, 通过 partitioner.partition(record.getKey())) (默认是HashPartitioner), 会被分散到 bucket上, 每个task 对应的bucket的数量 == reducer的数量 == 下一个stage的task的数量
shuffle read: 可以当做reducer阶段, 第二个stage 中的task, 根据task的id 和mapper的id从远端或者本地的 bucket上面 fetch 记录进行reduce.
- reducer端如何进行fetch
若是reduceByKey, 则只需要持有一个hashMap, key为record的key, val则按照 record的次数进行更新; 但若是groupByKey, 需要
-
性能调优
- 提升shuffle的内存占比, 尽量避免shuffle的时候数据因为内存不够被刷写到磁盘中.
spark.shuffle.memoryFraction , shuffle可以使用executor的内存占比, 默认0.2 , 可适当提高该比例
- 提高shuffle操作的并行度
- spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 提高sparkSql中shuffle类操作的并行度, 默认是200, 对应200个shuffle read tasks
-
这篇博文还需再看 link
spark 资源分配
- executor core
--executor-cores in shell(or in conf spark.executor.cores) 5 means that each executor can run a maximum of five tasks at the same time。A rough guess is that at most five tasks per executor can achieve full write throughput, so it’s good to keep the number of cores per executor below that number
- executor memory
the heap size can be controlled with the --executor-memory flag or the spark.executor.memory property - spark.yarn.executor.memoryOverhead
指的是 off-heap memory per executor, 用来存储 VM overheads, interned strings, other native overheads, 默认值是 Max(384MB, 10% of spark.executor-memory), 所以每个executor的实际物理内存需要囊括spark.yarn.executor.memoryOverhead 和executor memory两部分. - spark memory model
link - num of executor
--num-executors command-line flag or spark.executor.instances configuration property control the number of executors requestedStarting in CDH 5.4/Spark 1.3, you will be able to avoid setting this property by turning on dynamic allocation with the spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled property. Dynamic allocation enables a Spark application to request executors when there is a backlog of pending tasks and free up executors when idle.
- yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb
controls the maximum sum of memory used by the containers on each node. - yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores
controls the maximum sum of cores used by the containers on each node.
YARN may round the requested memory up a little. YARN’s yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb and yarn.scheduler.increment-allocation-mb properties control the minimum and increment request values respectively.
- 跑批任务中(hive on spark, hive on mr)的资源分配
spark.executor.instance(实例数), spark. executor.memory(单个实例内存), 这两个参数可以根据实际情况进行相应调整。当处理数据量较大逻辑较为简单时可以增大实例数减小内存,提高批处理的并行数;当处理数据量不大但是逻辑较为复杂的任务时可以提高单个实例的内存,减小实例数,提升每个实例的处理能力。
- spark 的并行程度
推荐 executor instances * core per executor 的两到三倍 = num of task , 避免cpu浪费(某些task 已经跑完了, 可以跑剩下的task)
- 如何设置并行度
- spark sql
spark.sql.shuffle.partitions=[num_tasks]
- spark.defalut.parallelism , 只在shuffle的时候才生效,
val rdd2 = rdd1.reduceByKey() //若设置 spark.defalut.parallelism=10, rdd2的分区数就是10
- 源数据在hdfs上面,
sparkContext.textFile(String filePath,int minPartition)
// minPartition 决定了这个文件被分成几片,
split size = 总文件大小/ minPartition,
actual split size = Math.max(mapred.min.split.size,Math.min(split size,file block size(默认128MB)))
再为每个split 创建一个task
- 可以repartition
- val rdd3 = rdd1.join(rdd2)
rdd3里面partiiton的数量是由父RDD中最多的partition数量来决定,因此使用join算子的时候,增加父RDD中partition的数量
spark 性能调优
- 避免创建重复RDD
2.尽量重复使用RDD
3.对多次使用的RDD持久化
4.尽量避免shuffle类算子
5.使用map端预聚合的算子, 类似于MR的combiner
6.使用高性能算子
数据倾斜
某个parttion的大小远大于其他parttion,stage执行的时间取决于task(parttion)中最慢的那个,导致某个stage执行过慢
- 情形暂定为两种
- 相同的key的数据量太大
- 不同的key在同一个parttion的数据量太大
由于同一个Stage内的所有Task执行相同的计算,在排除不同计算节点计算能力差异的前提下,不同Task之间耗时的差异主要由该Task所处理的数据量决定。
- 提升并行程度,
- 在hive端就去除倾斜的现象, 保证spark端使用的时效
- 过滤少数导致数据倾斜的key
- 将key添加随机前缀, 进行局部聚合,然后去掉随机前缀, 再进行全局聚合
- 改变parttion的数量
- 自定义parttion
- 避免shuffle
driver的作用
- 生成lineage, 将用户提交的程序划分成多个task去执行,
- 作为调度的角色, 提交请求到executor
spark sql和presto的区别
- spark sql更方便进行数据的分析, 适合做OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing)
- presto更适合做实时的响应, 更适合做交互式查询, 在数据量和内存差不多的时候性能较好, 因为完全基于内存做计算,适合做OLTP(on-line transaction processing)
- presto的社区人数相比spark而言比较少, 出现问题不容易解决
hive on spark, hive on MR 和spark sql的区别
- hive on spark 和spark sql 计算引擎都是spark, 只是从sql翻译成执行计划不一样
hive on spark, sql的优化都是通过hive的, 这方便hive的经验比较丰富, 最后启动的还是一个spark job
spark sql 默认使用hive metastore去管理metadata, 使用spark 自身的sql 优化器: catalyst.
-
若要讨论spark和MR的区别
- spark 容易编程, 不需要过多的抽象;MR需要较为复杂的抽象; spark支持多种算子, 而MR只支持map和reduce, 功能没有spark 丰富和易用.
- spark支持内存和硬盘以及混合存储三种方式, 而mr只支持hdfs一种, 这个是spark比较快的一个重要原因.
- spark的任务分配是更细粒度的, 例如划分了多个rdd, 中间有任务失败不需要从头开始计算; 而mr需要从头
- spark默认是lazy compution, 可以对中间过程进行很多优化
- 性能对比, hive on spark , hive on mr, spark sql ,hive on tez
2014-benchmark,
总而言之, hive on spark在large join时性能突出, spark sql在map join时性能突出, hive on mr比较慢
spark-submit
- shell 脚本
#!/bin/sh
set -o nounset
# 第一个错误, shell终止执行
set -o errexit
export SPARK_HOME=
lib_path=
tempView=mblTempView
outputDir=/user/wutong/mblOutput
mblFile=mbl.txt
hdfs dfs -rm -r -f ${outputDir}
${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-submit" \
--class com.mucfc.cms.spark.job.mainClass.PushMblToMerchantShellMain \
--master yarn \
--deloy-mode client \
--queue root \
--diver-class-path ${lib_path}"*" \
--jars ${lib_path}"" \
--conf spark.default.parallelism=200 \
--conf spark.sql.shuffle.partitions=400 \
--conf spark.executor.cores=3 \
--conf spark.executor.memory=450m \
--conf spark.executor.instances=4 \
${lib_path}"cms-sparkintegration.jar" "$@" \
-file_name
-insertSql "insert overwrite table crm_appl.mbl_filter select * ${tempView}" \
-tempView ${tempView} \
-outputSql "select * from crm_app.mbl_filter" \
-showSql "select * from ${tempView}" \
-outputDir ${outputDir} \
-inputPartitionNum 200 \
-outputPartitionNum 200 \
-inputFlag true \
-appNme PushMblToMerchantShellMain \
-local_file_path ${lib_path}${mblFile}
-remote_file_path /user/wutong/mblFile \
-countForShortMbl 3000
-encrypt_type md5
spark sql 执行的大致流程
参考自
- sparksql-catalyst
- mit.edu-sigmod_spark_sql.pdf , 百度云网盘/book
首先将sql 语句通过parser模块解析成语法树, 称作 unresoloved logical plan, 这个plan再通过 Analyzer借助元数据解析为 logical plan, 再通过基于规则的优化, 得到 optimized logical plan, 此时执行计划依然是逻辑的, 并不能被spark 理解, 还需要转化为 physical plan.
- parser
将一长串sql 解析为一个语法树, 相当于是划分成一个个token, 并指定了token执行的先后顺序, 该模块基本都使用第三方类库 antlr实现.
- analyzer
遍历第一步提到的语法树, 将一个个token替换为具体的函数, 例如token为sum(), 则替换为具体的聚合函数; 并做数据类型的绑定, 定位到那个表的哪个列.
- optimzer
分为基于规则优化和基于代价优化(目前支持还不好, 具体说来是比较多种规则优化下哪个的时间代价越小, 就采用哪些规则进行优化), 规则优化例如谓词下推(Predicate Pushdown), 例如是filter下推到join之前, 先进行过滤再join, 减少大量数据; 常量累加(Constant Folding), 将中间值事先计算, 得出一个中间结果; 和列值裁剪(Column Pruning), 例如只要一列数据的, 就只传递该列数据, 减少大量的io和带宽.
- 将逻辑执行计划转化为物理执行计划, 转化为特定的算子进行计算.
- 查看spark sql执行计划
- 使用queryExecution方法查看逻辑执行计划,使用explain方法查看物理执行计划, 在spark-sql 命令行, 执行
spark.sql("xxxsql").queryExecution()
spark.sql("xxxsql").explain()
- 使用Spark WebUI进行查看
spark join
分为 shuffle hash join、broadcast hash join以及sort merge join
- hash join
将小表作为Build Table,大表作为Probe Table; 先将小表的join key, hash到bucket中, 构建hashtable, hashtable如果太大, 会放到磁盘上; 再讲大表的join key进行hash到同一个bucket中, 再判断两者的key是否相同. > 时间复杂度: O(a+b), 传统的笛卡尔积是 O(a*b)
选择小表作为build table, 生成的hashTable比较小, 能够完全放到内存中.
- hash join的分布式改造
- broadcast hash join
将小表广播到大表的所有节点上, 适用于小表很小的情况
SparkSQL规定broadcast hash join执行的基本条件为被广播小表必须小于参数spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold,默认为10M。
- Shuffle Hash Join
将两个表按照join key进行重分区(HashPartition) , 再在各个节点上进行hash join, 适用于一个大表,一个小表的情况.
- Sort-Merge Join
可以看下 spark-join-pull过程
将两个表先进行shuffle, 再在各个分区节点的数据进行sort, 最后再根据join key 进行merge. 适用两个大表的情况, 因为spark的shuffle是 sort-based shuffle,shuffle之前就排序好了.
spark log
分为三部分: driver log, executor log, spark history server log
- driver log
使用 yarn logs -applicationId xxxId > tmp.log
- executor log
- spark history server log
配置的路径
也可以去spark history server直接看, 但是可能会找不到, 需要看配置. 包含了spark application执行的整个流程和rdd的细节.
疑问
- 还是要把本地windows环境起起来, spark如何指定 scala, hadoop
- spark 序列化
- 基准测试 benchmark
- spark集群容错, 如果没有保留中间结果, 则如何重新计算, 从哪里开始 ?
工作踩坑指南
spark 任务提交
-
spark和scala的包都指定为provided,在客户端上指定SPARK_HOME和SCALA_HOME就可依赖到,避免版本问题
- 如果SPARK_HOME有问题则,会出现
ClassNotFound: sparkSession
- 出现 xx.scala.xx error, 一般是scala 包有冲突
-
环境变量配置好后,用source生效,然后打开一个新的终端去重启应用才可以取到新的环境变量
-
需要配置分离,不用打包就可以改配置
-
hive元数据库(mysql),hive存储文件的位置(hdfs)在切换集群时都需要更换
-
指定hadoop版本
- 启动脚本
在spark-class2.cmd 有一个 LAUNCHER_OUTPUT, 默认启动完会删除, 可以保留看下启动的脚本, 帮助排查问题
- windows环境下启动spark, 有可能脚本报错, 然后报错信息是乱码, 可以把spark的输出指定 GBK解码, 可能是因为中文环境下windows cmd的编码是中文编码, 所以用utf-8解码是乱码, 看到报错信息之后就很好排查问题了.
待看
- http://www.cnblogs.com/jcchoiling/p/6440102.html
- book: sigmod_spark_sql.pdf , 百度云网盘
经典资料