A new Flutter project.
I built two application in flutter and one application which I am currently working has started 7 months ago and it still growing. If we want to build a single codebase native performance mobile application for Android and iOS then Flutter is the best choice.
In this article, We will be covering how to structure our large scale application which we have decided to build with Flutter.
When we create the Flutter project then by default only this folder and files are present (see below).
Default flutter app folder and files structure
Almost all the code we need to write inside the lib folder and we can see that by default Flutter doesn’t provide any file structure only the main.dart file with one stateful widget is present to run the sample counter.
Now, we will see what folders and files we need to create so that the application will be scalable.
First, we will create an assets folder in the root of the project which we will use to store images, translation files, custom font files, HTML files.
assets folder contains the following folders:
- fonts: This folder should have all the font files i.e custom fonts which are used in the application (.ttf files)
- html: If our application needs to open some HTML content which we need to add in our mobile app (Generally the licensed content of the application or any .html files which we need to load in the application using the package: webview_flutter or flutter_html)
Note: Generally webview_flutter is used to load the URL of any web content but we can use this plugin for showing the HTML content which is stored locally in the mobile application. I will prepare a separate article explaining how to show local HTML files in flutter and will add the link here when completed. - i18n: If our application supports Internationalization then need to add .json files for all the supporting different languages i.e If we need to support English and French then need to add en.json and fr.json in this folder. we can find more information on this link internationalizing flutter using JSON files
- images: This is the most important folder where we store all our images.
Here is actually how the assets folder looks like:
This is how the assets folder looks
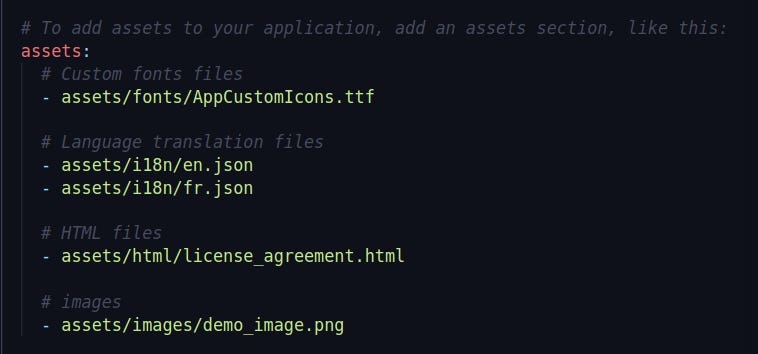
After creating the assets folder we need to add all the assets path in pubspec.yaml file so that flutter recognizes where the assets are present.
Here is how the assets path is added to pubspec.yaml file
This is how application assets path are added in pubspec.yaml
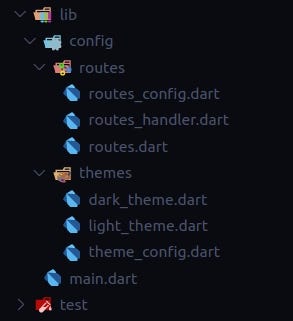
Now, we will be adding the config folder inside the lib folder
config folder contains the following folders:
-
routes: The route folder contains all the files which are based on the application screens navigation code. We will be using the package fluro to separate our route navigation. This folder contains three files: routes.dart, routes_config.dart, routes_handler.dart. we can see the fluro package example code to know about each of these files. Later I will create a separate article for explaining how to use fluro for route navigation in flutter and will add the link for the same here.
-
themes: If our application supports light and dark theme and these themes are custom themes then need to create two files light_theme.dart, dark_theme.dart where we will be adding all the colors which are needed for each widget type. One more file we will be creating theme_config.dart which describes all the constants related to the theme.
flutter theam Doc flutter theam vidNote: As this article is based on folder & files structure we will be describing what actually all the themes files contains and how it works in a separate document which I will prepare soon. For now, you can check this link to build multiple theme support using Bloc
Here is how the config folder looks like:
config folder & file structure
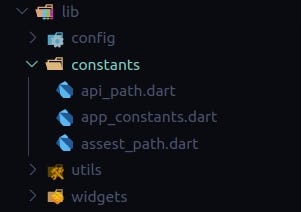
Here are the following constants which are static throughout the applications
- api_path.dart: When using REST API service in dart then we can store all the API endpoints in a separate file api_path.dart
- assest_path.dart: Although we have described the assets path in pubspec.yaml but to use that asset in an application we need to give there relative path in any widgets.
If we add all the assets relative path in one file then it will be easy for us to get all the paths and update the path if required in the future. - app_constants.dart: This is where all our application constants will be present and this is different for each application.
Here is how the constants folder looks like:
App Constant folder & file structure
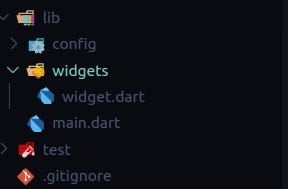
In a large scale application, we need to make more customized widgets rather than flutter default widgets. Suppose we need to make use of our own custom RaisedButton, FlatButton, OutlineButton, Divider, CircularLoader, etc which we can use throughout our application then that kind of customization widgets we can add inside the file widget.dart which will be present inside the folder widgets
Here is how the widgets folder looks like:
widget folder for adding custom widgets
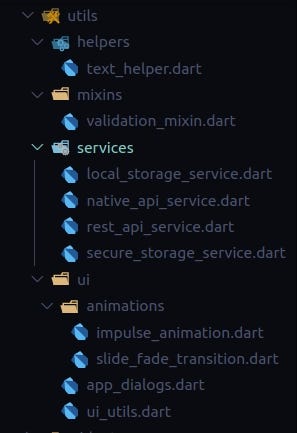
Utils folder contains the helpers, services, UI utils, mixins which are used throughout the application
**Exploring Helpers
**In many scenarios, we need to write code multiple times for the same thing like converting the every word first characters to be uppercase usually used in showing titles for any other widgets, etc. This kind of code can be made common to reduce the redundancy and add that code in helpers files which are present in lib/utils/helpers/text_helper.dart.
text_helper.dart will contain all the code which are required to convert the String to show in a Text widget.
Exploring Services
We will be creating a different kind of service files in the folder _lib/utils/services
_Note: All the services will be singleton classes.
- local_storage_service.dart: In this file, we write all the code needed to store and get data from the local storage using the plugin shared_preferences.
In this file, there will be getters and setters for each and every data to be stored in the local storage. - secure_storage_service.dart: We do not store user credentials, API tokens, secret API keys in local storage, for that we make use of flutter_secure_storage which stores data in the Android Keystore and Apple keychain with platform-specific encryption technique.
In this file, there will be getters and setters for each and every data to be stored in platform secure storage. - rest_api_service.dart: We do call the rest API to get, store data on a remote database for that we need to write the rest API call at a single place and need to return the data if the rest call is a success or need to return custom error exception on the basis of 4xx, 5xx status code. We can make use of http package to make the rest API call in the flutter
- native_api_service.dart: We use multiple packages to access the native services like Camera, Photo Gallery, Location, etc for that we need to write code in a separate file which we can be used from multiple places throughout the application
**Exploring UI Utils
**All the common UI related things should be present inside lib/utils/ui folder
Here is the list of folders and files which will be present in the directory lib/utils/ui
- animations: All the custom animations will be present in this file with separate files like slide_fade_transition.dart, impulse_animation.dart, etc this all custom animations will be used through the application.
- app_dialogs.dart: All the custom app dialogs UI will be present in this file.
- ui_utils.dart: All the custom UI widgets like an input text box with search icon, autocomplete widgets, Error message banners, custom checkbox chips related utils can be present in this file and will be used thoughout the application.
Exploring Mixins
Mixin is a class that contains methods for use by other classes without having to be the parent class of those other classes.” In other words, mixins are normal classes from which we can borrow methods(or variables) from without extending the class.
In the application, we can make different mixins like validation_mixins.dart, orientation_mixins.dart
Here is how the utils folder looks like:
App utils folder & file structure
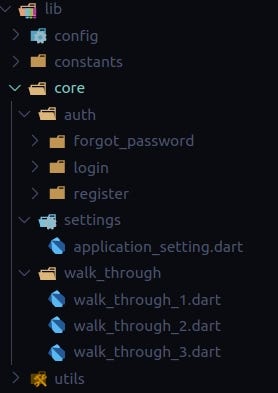
Core features like Login/auth, walkthrough screens (Screens which are only visible at after the install only), application setting features are the core features that should be added in a folder Core.
- auth: Auth folder must contain the features: Register, Login, Forgot password.
- walk_through: Walkthrough screens must contain all the screens which will be visible only when the application starts for the first time after the fresh install.
- settings: This will be the application setting feature
Here is how the core folders and files look like:
Core features folder and file structure
Before proceeding with modules, I would like to show how each and every module is implemented. i.e each and every module and core features which we discussed above are based on the Bloc pattern which we can find more in this package flutter_bloc.
Bloc design pattern helps to separate presentation from business logic. Following the Bloc pattern facilitates testability and reusability. This package abstracts reactive aspects of the pattern allowing developers to focus on writing the business logic.
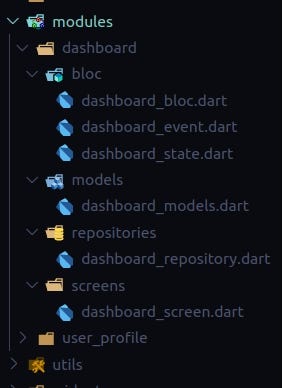
Let's take the example with module dashboard in the application which contains the following folders:
- bloc: This folder contains the three files dashboard_bloc.dart, dashboard_events.dart, dashboard_states.dart. I will create a separate document describing the bloc pattern and how to incorporate it into the flutter application. For now, you can understand the bloc pattern from flutter_bloc.
- models: This folder contains the data models which need to be shown on the dashboard screen.
- repositories: This folder contains the repository files which is used to write code for services call and for computation works.
- screens: This folder consists of all the screens UI widgets that will be visible to the user.
Note: All the modules and core features should contain these four folders to separate out the business logic from the UI.
Here is how the module dashboard looks like:
Modules folders and files structure
Complete Folder and File structure for a scalable application
Hope! you get how to make use of this folder & file architecture for large scale applications.
I will be continually adding more articles regarding managing different custom themes, Bloc Design pattern following the DDD approach, Internationalization in Flutter.
Thank you