This fork of KaRadio implements both internet radio and bluetotth speaker with minimalistic user interface. This means that once uploaded, you're able to switch between net radio and bluetooth speaker on the run, with a push of a button.
Bluetooth portion of the code has been directly copied from repository https://github.com/MrBuddyCasino/ESP32_MP3_Decoder
- ESP32 lolin pro
*(16MB Flash, 8MB PSRAM) - ESP32 toolchain
- Rotary encoder
* You will need at least 8MB of flash to fit the program, and probably more RAM than standard model offers. My initial tests with ESP32 (4MB, 512k RAM) were unsuccessful
-
Clone this repo to your PC
git clone https://github.com/vedranMv/Ka-Radio32 -
Compile the code in repository
cd Ka-Radio32
make -j12 -
Make partition table. In case you move the partitions around (they can be placed wherever as long as they fit in your memory and are after 0x1000), make sure to change the offsets later on in the ESP32 download tool
make partition_table
ESP32 pinout for I2S, encoder, LED etc can be found in board/lolin32dpro.cvs file. You can change the pinout in the file and run ./nvs_partition_generator.sh [fileName.csv] in order to generate new .bin file in board/build directory. For more info, refer to the original Ka-Radio32 repository documentation.
Radio mode is default after flashing the chip. Once the ship starts, it will create a hotspot to which you can connect in order to enter AP details. After confirming the details, ESP32 automatically resets and connects to your AP. Now you can navigate to the new IP, open web UI and add some stations to your playlist.
- Play/stop radio station by pressing the encoder button
- Adjust volume by turning the rotary encoder
- Move between the stations by pressing the encoder for about a second, then rotating it. Rotating counter-clockwise goes to the next station on the list, while counter-clockwise goes to the previous station
- Double click the encoder quickly in order to change to bluetooth speaker mode
Once in bluetooth mode, ESP32 becomes visible under name Speaker (creative, I know). Use any capable device to connect to it and start playing.
- Adjust volume by turning the rotary encoder
- Double click the encoder quickly in order to change to radio mode
- When playing radio streams, web UI becomes unresponsive. Pause the stream to gain access to the UI
- AAC streams fail to play, resulting in constant cuts and unnatural sound. Potential fix (not tested) might be to increase buffer size from 40k to 512k (for devices with 8MB PSRAM)
- When in bluetooth speaker mode, there will be no sound until the volume has been adjusted for the first time
I have installed my ESP32 inside a 3D printed case and equipped with UDA1334A I2S DAC followed by HXJ8002 audio amplifer. Internally, a 3.3V buck-boost powers ESP32 and DAC, while a 5V boost converter suplies amplifier and speaker. All powered by a single cell 1500mAh Li-Ion gives about 5-6h of listening time.
- UDA1334 DAC: https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32914177542.html
- HJX8002 amplifier: www.aliexpress.com/item/32805837141.html
- Speaker: https://www.visaton.de/en/products/fullrange-systems/frs-8-m-8-ohm
The case was 3D printed from two parts, one of which I decided to cover in red fabric. User interface is simple, consisting of one latching power button with white LED and a rotary encoder with push button.

LED is connected to pin 5, displaying status of the ESP32.
- In radio mode it will be constantly on, with occasional interruptions
- In bluetooth speaker mode, it will blink with 5Hz frequency until you start playing, then it will remain mostly off for as long as the music plays. Pausing the music (even though it's still connected to the phone/PC/TV), LED will start blinking again.
Release 1.9 Stable
Works on any esp32 board.
See the boards directory for a list of pre-configured boards.
See : Hardware configuration partition
- The esp32 adds the output on the internal dac or with i2s to an external dac but only mp3 stations can be played.
Adding a vs1053 board, all stations can be played.
On a wrover cpu with external psram, every AAC streams can be played without the vs1053 board. - Compatible with esp8266 KaRadio addons.
- Serial or telnet commands : Interfaces description
A new android application is born:
- KaRadio Remote Control by Vassilis Serasidis on google Play.
It is an easy and fast WiFi remote control for your KaRadio or KaRadio32 hardware.
With this android app you can select the WebRadio station you want to play, set the volume and get the station information such as Station name, Genre, Bit rate, Meta data and more.
Found it at
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.serasidis.karadio.rc
Thanks Vassilis.
Work with i2s, internal DAC or a vs1053.
Output mode set in Setting panel on web page of KaraDio32 :
- I2S for connection to an external DAC
- I2SMERUS to connect a merus amplifier
- DAC to use the built in DAC of the esp32
- PDM to output a PDM (Pulse Density Modulation) stream
- VS1053 to connect to a vs1053 board, I2S output of the vs1053 enabled.
- all VS1053 tones control
- AAC decoding on I2S with a wrover cpu (4mB of external psram). Mp3 only on I2S with a wroom cpu.
- Interfaces available on serial, telnet and html
- up to 255 editable stations.
- Handles bitrates up to 320 kbps.
- Stations can be saved and restored from html in and from a file.
- Hardware configuration file to adapt the standard delivery to all boards and addons you need.
- all configurable parameters automatically saved.
- mDNS support.
- wrover esp32 support. About 10 seconds of buffering, and soon A2DP support (sink and source)
- Time Zone Offset support.
- Latin, Cyrillic and Greek support on screen.
- 28 types of lcd or oled B/W or Color supported.
- Programmable lcd backlight off timer.
- Touch screen if the hardware supports it.
- Two joysticks (set of two adc buttons), one for volume, one for stations.
- Two max rotary encoders. One for volume priority, one for station change priority.
- Two max set of 3 buttons. One for volume priority, one for station change priority.
- Rotary encoder and set of buttons support included. Common functions : play/stop, volume, station change, date time display.
- ADC keyboard with 6 buttons.
- Date format DD:MM:YYYY or MM:DD:YYYY .
- Remote IR support integrated. Nec protocol only.
- Two configurable access points .
- OTA (Over The Air) update of the software.
- Uses a 40 kB (I2S), 50 kB (vs1053) or 420 Kb (wrover) queue to provide smooth playback.
- many more configurable parameters. See Interfaces document
If the default configuration doesn't fit your needs, you can externally configure the software to fit your hardware and peripherals to suit your needs.
The configuration file is to be flashed only one time. After, the standard delivery will become compatible with your hardware gpio use and peripherals configuration. A future standard OTA will automatically works for your configuration.
See : Hardware configuration partition
For a wrover cpu you need a csv file with psram in the name. Without it, the default configuration will fail.
To build your own release if you want to do some improvments, you must install the idf https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf and the toolchain.
To flash all build output, run 'make flash' or :
python /home/yourhome/esp/esp-idf/components/esptool_py/esptool/esptool.py \
--chip esp32 --port com5 --baud 460800 --before default_reset \
--after hard_reset write_flash -u --flash_mode dio \
--flash_freq 40m --flash_size detect \
0x1000 /home/yourhome/esp/Ka-Radio32/build/bootloader/bootloader.bin \
0x10000 /home/yourhome/esp/Ka-Radio32/build/KaRadio32.bin \
0x8000 /home/yourhome/esp/Ka-Radio32/build/partitions.bin
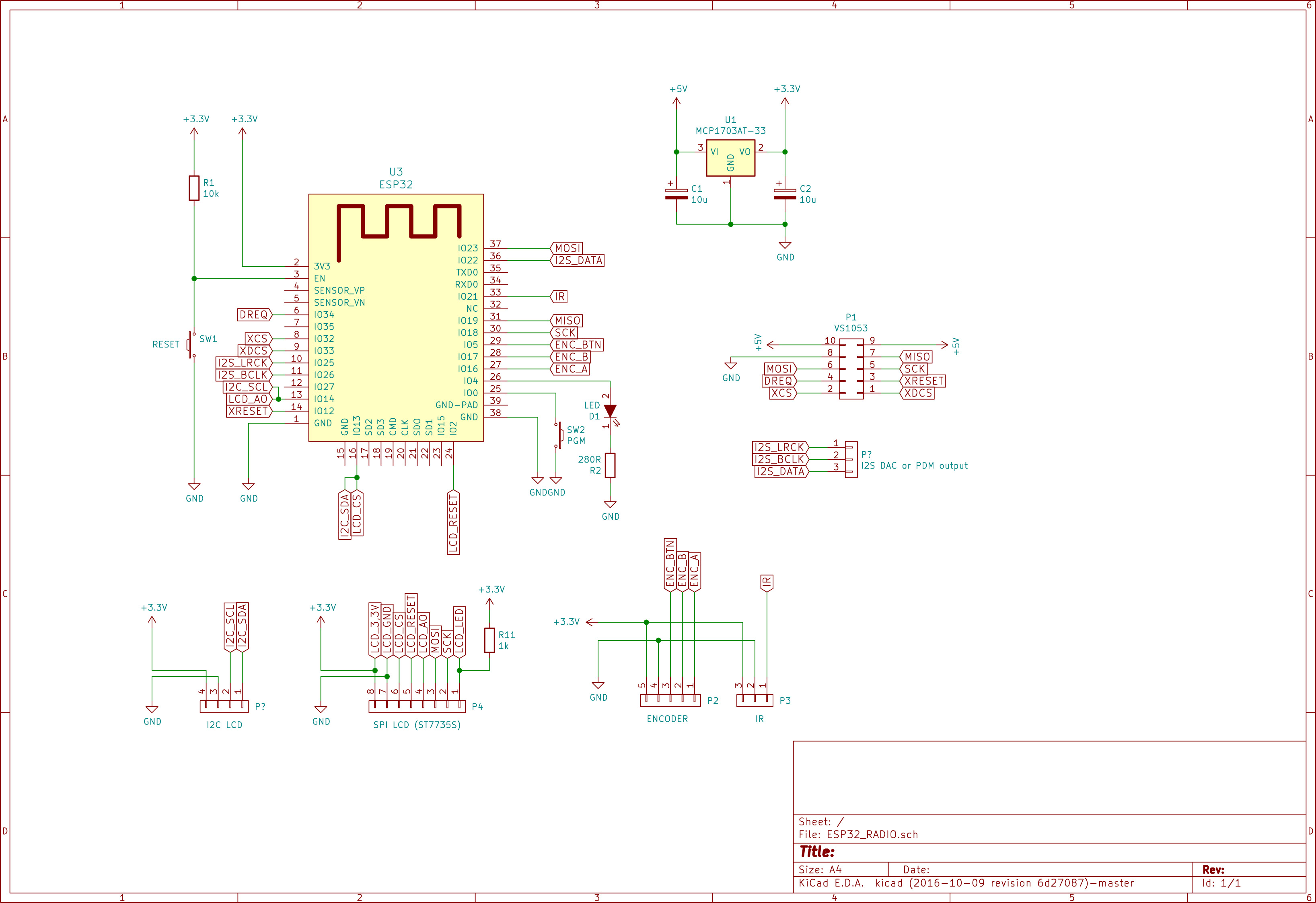
The default configuration is given below. It includes an encoder, an IR remote and a LCD or OLED.
To add or edit GPIO definitions and add or remove some devices, you may need a hardware configuration file. Some examples are in the boards directory.
See the file main/include/gpio.h and main/include/addon.h
WARNING: this configuration will not work for a wrover processor.
You need an adapted csv configuration.
//--------------------------------------//
// Define GPIO used in KaRadio32 //
// if no external configuration is used //
//--------------------------------------//
// Compatible ESP32 ADB
// https://www.tindie.com/products/microwavemont/esp32-audio-developing-board-esp32-adb/
// Default value, can be superseeded by the hardware partition.
// Must be HSPI or VSPI
#define KSPI VSPI_HOST
// KSPI pins of the SPI bus
//-------------------------
#define PIN_NUM_MISO GPIO_NUM_19 // Master Input, Slave Output
#define PIN_NUM_MOSI GPIO_NUM_23 // Master Output, Slave Input Named Data or SDA or D1 for oled
#define PIN_NUM_CLK GPIO_NUM_18 // Master clock Named SCL or SCK or D0 for oled
// status led if any.
//-------------------
// Set the right one with command sys.led
// GPIO can be changed with command sys.ledgpio("x")
#define GPIO_LED GPIO_NUM_4 // Flashing led or Playing led
// gpio of the vs1053
//-------------------
#define PIN_NUM_XCS GPIO_NUM_32
#define PIN_NUM_RST GPIO_NUM_12
#define PIN_NUM_XDCS GPIO_NUM_33
#define PIN_NUM_DREQ GPIO_NUM_34
// + KSPI pins
// Encoder knob
//-------------
#define PIN_ENC0_A GPIO_NUM_16 //16 // 255 if encoder not used
#define PIN_ENC0_B GPIO_NUM_17 //17 // DT
#define PIN_ENC0_BTN GPIO_NUM_5 //5// SW
#define PIN_ENC1_A GPIO_NONE // 255 if encoder not used
#define PIN_ENC1_B GPIO_NONE // DT
#define PIN_ENC1_BTN GPIO_NONE // SW
// 3 Buttons
//-------------
#define PIN_BTN0_A GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_BTN0_B GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_BTN0_C GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_BTN1_A GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_BTN1_B GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_BTN1_C GPIO_NONE
// Joystick (2 buttons emulation on ADC)
//--------------------------------------
#define PIN_JOY_0 GPIO_NONE
#define PIN_JOY_1 GPIO_NONE
// I2C lcd (and rda5807 if lcd is i2c or LCD_NONE)
//------------------------------------------------
#define PIN_I2C_SCL GPIO_NUM_14
#define PIN_I2C_SDA GPIO_NUM_13
#define PIN_I2C_RST GPIO_NUM_2 // or not used
// SPI lcd
//---------
#define PIN_LCD_CS GPIO_NUM_13 //CS
#define PIN_LCD_A0 GPIO_NUM_14 //A0 or D/C
#define PIN_LCD_RST GPIO_NUM_2 //Reset RES RST or not used
// KSPI pins +
// IR Signal
//-----------
#define PIN_IR_SIGNAL GPIO_NUM_21 // Remote IR source
// I2S DAC or PDM output
//-----------------------
#define PIN_I2S_LRCK GPIO_NUM_25 // or Channel1
#define PIN_I2S_BCLK GPIO_NUM_26 // or channel2
#define PIN_I2S_DATA GPIO_NUM_22 //
// ADC for keyboard buttons
#define PIN_ADC GPIO_NONE //GPIO_NUM_32 TO GPIO_NUM_39 or GPIO_NONE if not used.
// LCD backlight control
#define PIN_LCD_BACKLIGHT GPIO_NONE // the gpio to be used in custom.c
// touch screen T_DO is MISO, T_DIN is MOSI, T_CLK is CLk of the spi bus
#define PIN_TOUCH_CS GPIO_NONE //Chip select T_CS
You can configure the kind of display used in your configuration with the command
'sys.lcd("x")' with x:
#define LCD_NONE 255
// Black&White
//I2C
#define LCD_I2C_SH1106 0 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1306 1 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1309 2 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1325 3 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1306NN 4 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1309NN 5 //128X64
#define LCD_I2C_SSD1306UN 6 //128x32
#define LCD_I2C_ST7567 7 //64x32
//SPI
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1306 64 //128X32 (LCD_SPI =0x40)
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1309 65 //128X64
#define LCD_SPI_ST7565_ZOLEN 66 //128X64
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1322_NHD 67 //256X64
#define LCD_SPI_IL3820_V2 68 //296X128
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1607 69 //200X200
#define LCD_SPI_LS013B7DH03 70 //128X128
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1306NN 71 //128X64
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1309NN 72 //128X64
#define LCD_SPI_ST7920 73 //128X64
#define LCD_SPI_ST7567_pi 74 //132X64
#define LCD_SPI_ST7567 75 //64X32
#define LCD_SPI_ST7565_NHD_C12864 76 //128X64
// Colors
#define LCD_SPI_ST7735 192 // 128x160 (LCD_COLOR|LCD_SPI =0xC0)
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1351 193 // 128x128
#define LCD_SPI_ILI9341 194 // 240x320
#define LCD_SPI_ILI9163 195 // 128x128
#define LCD_SPI_PCF8833 196 // 132x132
#define LCD_SPI_SSD1331 197 // 96x64
#define LCD_SPI_SEPS225 198 // 96x64
#define LCD_SPI_ST7789V 199 // 240x320
#define LCD_SPI_ST7735S 200 // 128x128
#define LCD_SPI_ST7735L 201 // 80x160
#define LCD_SPI_ST7735W 202 // 128x160 shifted 2+1
- If the access point of your router is not known, the webradio initialize itself as an AP. Connect the wifi of your computer to the ssid "WifiKaRadio",
- Browse to 192.168.4.1 to display the page, got to "setting" "Wifi" and configure your ssid ap, the password if any, the wanted IP or use dhcp if you know how to retrieve the dhcp given ip (terminal or scan of the network).
- In the gateway field, enter the ip address of your router.
- Validate. The equipment restart to the new configuration. Connect your wifi to your AP and browse to the ip given in configuration.
- Congratulation, you can edit your own station list. Don't forget to save your stations list in case of problem or for new equipments.
- if the AP is already know by the esp32, the default ip is given by dhcp.
- a sample of stations list is on http://karadio.karawin.fr/WebStations.txt . Can be uploaded via the web page.
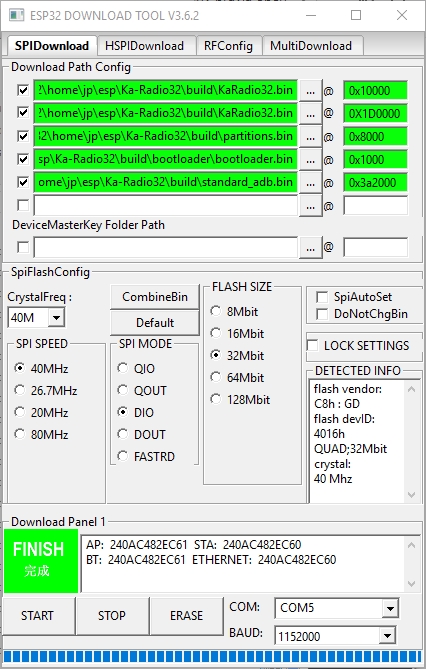
To flash your KaRadio32 without generating it, you will need the files in the binaries directory.
The tool to use is here :
http://espressif.com/en/support/download/other-tools
(change the security of the installation directory to permit all)
See the image at :
http://karadio.karawin.fr/karawin32Flash.jpg
WARNING: the standard_adb.bin must be changed for a wrover processor or another configuration.
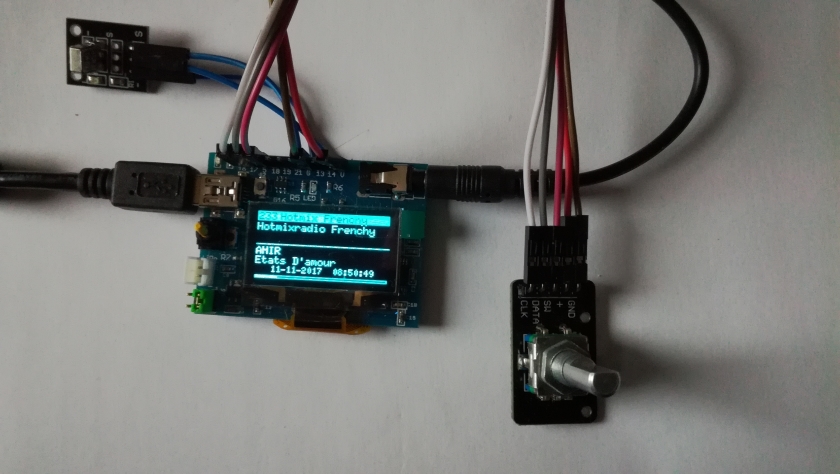
Just an example of a realization.
In the Setting panel on the webpage of KaraDio32 you can set the desired output method for audio.
For output on a simple speaker or a general analog amplifier :
- DAC to use the built in DAC of the esp32
- PDM to output a PDM (Pulse Density Modulation) stream. Wiki on PDM : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulse-density_modulation
For output via addional I2S or VS1053 hardware :
- I2S for connection to ac external DAC
- I2SMERUS to connect a merus amplifier
- VS1053 to connect to a vs1053 board.
You can connect the GPIO25 (left audio channel), GPIO26 (right audio channel) and Ground directly to a small loudspeaker, a simple earphone (like from an mp3 player) or the input of an analog amplifier. The quality is less perfect than using an I2S or VS1053 board, bit it is very simple hardware-wise.
Connect like this :
+------------------------------------+
ESP32-GPIO25 (left) -----+speaker/earphone/analog-amp (left) +-----+
+------------------------------------+ |
|
+------------------------------------+ |
ESP32-GPIO26 (right) ----+speaker/earphone/analog-amp (right +------+
+------------------------------------+ |
|
ESP32-GROUND --------------------------------------------------------+
If the audio signal level is too high for your speaker, earphone or amplifier you can add a potentiometer to decrease the level. Connect the potentiometer like this (only pictured for 1 audio channel, for stereo you need 2 potentiometers or a stereo-potmeter.
+--------------------------------------+
ESP32-GPIO25 (left) -------+ +-----+speaker/earphone/analog-amp (left) +------+
+-+ | +--------------------------------------+ |
+P+ | |
+o+--+ |
+t+ |
+++ |
| |
ESP32-GROUND --------------+-------------------------------------------------------+
An analog DAC signal always has some noise that may cause some distortion on the audio output, especially on low volume passages in the sound. This noise can be decreased with a low-pass filter. The digital PDM signal needs allways low pass filter to convert the digital signal to an analog signal. Fortunately the speaker and earphone acts as a low pass filter, although not in a perfect way.
You can improve the analog signal with an external low-pass filter. A simple low-pass RC filter can be find on the internet, f.i. here :
http://www.pavouk.org/hw/usbdac/en_index.html.
If Karadio32 is configured to use ADC, PDM or I2S output (to an external dac) it can play audio streams in mp3 format. Other formats like AAC and WMV require too much dynamic memories and can not be played this way.
When you want to play other formats you add an external VS1053 decoder to Karadio. Details on the features of this decoder can be found here : http://www.vlsi.fi/en/products/vs1053.html
Many boards can be found at :
https://www.aliexpress.com/wholesale?catId=0&initiative_id=SB_20180113141636&SearchText=vs1053b
Normally a radio station is played without interruption.
But when a connection to the server of the radio station is (temporarily) disrupted (due to internet problems or server problems) Karadio behaves as follows:
- Playing of the radio stream stops, after a short while Karadio retries to relaunch the connection to the radio stream.
- If the relaunch of the connection fails again, the webpage of Karadio then shows “invalid address” and goes into the stop state. If you have a display connected to Karadio it will then show the Date, Time and IP address.
- You can try to relaunch the connection manually by pressing “play” on the Karadio webpage, or resetting the ESP32.
- If the wifi is disconnected, the esp is rebooted.
- The Espressif IDF : https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf
- The Esp8266 KaRadio : https://hackaday.io/project/11570-wifi-webradio-with-esp8266-and-vs1053
- The KaRadio addons : https://github.com/karawin/karadio-addons
- Webradio for ESP-ADB module : https://github.com/kodera2t/ESP32_OLED_webradio
- Webradio with the MP3 decoder software : https://github.com/MrBuddyCasino/ESP32_MP3_Decoder
- Black/White oled lcd library : https://github.com/olikraus/u8g2
- Color LCD library : https://github.com/olikraus/ucglib
- u8g2 Hal for esp32 : https://github.com/nkolban/esp32-snippets/tree/master/hardware/displays/U8G2
- Encoder : https://github.com/soligen2010/encoder