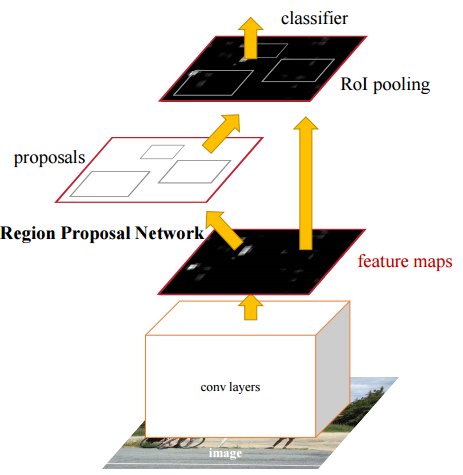
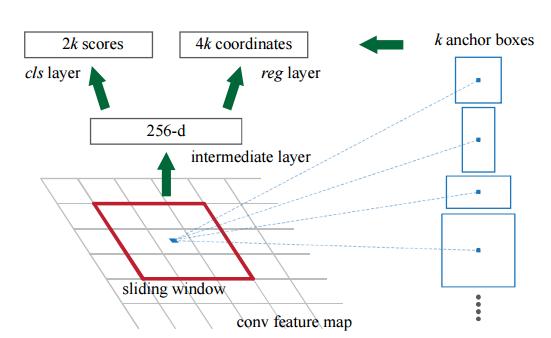
Two key ideas are proposed in Faster R-CNN:
- Proposes RPN (Region Proposal Network) to generate region proposals, which is faster and more accurate than Selective Search.
- Use an iterative joint training method to train RPN and Fast R-CNN jointly.
- Higher detection mAP due to integrated structure and "anchor boxes";
- More efficiency and accurate region proposal method -- RPN.
- Definition of "anchor box": anchor boxes can be regarded as a bunch of prior boxes, they have different scales and aspect ratios, for a W*H feature map, there's a total of W*H*k anchor boxes, k anchor boxes for each grid cell. A predicted bounding box is obtained by fine-tuning on existing anchor boxes. The adoption of anchor boxes introduces translation invariance to the network, enabling tranlastion invariance when single-sized images are taken as inputs.
- RPN: A region proposal network takes an image as its inputs, and a set of regions proposals along with their objectness scores as outputs. To generate these regions proposals, RPN slides a small network over the convolutional feature map output by the last convolutional layer. At each window, this small network predicts an objectness score and four regression coordinates scores.
- The last part of the model is the Fast R-CNN detector. To merge RPN and Fast R-CNN, the authors propose a 4-stage training method: The first stage trains a RPN initialized with weights from ImageNet models; The second stage trains a Fast R-CNN also initialized with weights from ImageNet models and feeding the Fast R-CNN with region proposals from RPN; The third stage uses Fast R-CNN weights to initialize a RPN but only fine-tune the layers unique to RPN; The fourth stage fine-tunes Fast R-CNN unique layers.
- Convolutional feature maps can be used for generating region proposals.
- When training RPN, they have more negative samples than positive samples, a way to balance the data is to sample the positive and negative anchors so that they have a ratio up to 1:1.
- Anchors which cross image boundries should be dealt with care, if the boundary-crossing outliers are not ignored in training, they introduce large, difficult to correct error terms in the objective, and training does not converge.
- An interesting experiment is that RPN can still performs well when using less region proposals while selective search will performs much worse with fewer proposals. This is because that the cls layer which predicts objectness is accurate in RPN, it gives high score for anchors that are more likely to contain objects, so with fewer high ranked regions, RPN can still perform well.
- The author also mentions comparison bewteen two-stage object detection algorithm v.s. one-stage detection algorithms. He claims that two-stage detection algorithms perform better due to region-wise features that more faithfully cover objects
The training process is 4-staged, which is somewhat cubersome and not elegant.
Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun, Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks, arXiv:1506.01497.