This example illustrates how to use RocketMQ Binder implement pub/sub messages for Spring Cloud applications.
RocketMQ is a distributed messaging and streaming platform with low latency, high performance and reliability, trillion-level capacity and flexible scalability.
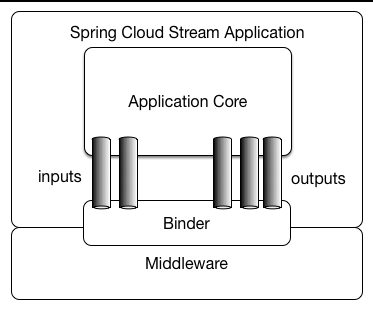
Before we start the demo, let's look at Spring Cloud Stream.
Spring Cloud Stream is a framework for building message-driven microservice applications. Spring Cloud Stream builds upon Spring Boot to create standalone, production-grade Spring applications and uses Spring Integration to provide connectivity to message brokers. It provides opinionated configuration of middleware from several vendors, introducing the concepts of persistent publish-subscribe semantics, consumer groups, and partitions.
There are two concepts in Spring Cloud Stream: Binder 和 Binding.
- Binder: A strategy interface used to bind an app interface to a logical name.
Binder Implementations includes KafkaMessageChannelBinder of kafka, RabbitMessageChannelBinder of RabbitMQ and RocketMQMessageChannelBinder of RocketMQ.
- Binding: Including Input Binding and Output Binding.
Binding is Bridge between the external messaging systems and application provided Producers and Consumers of messages.
This is an overview of Spring Cloud Stream.
You should startup Name Server and Broker before using RocketMQ Binder.
-
Download RocketMQ and unzip it.
-
Startup Name Server
sh bin/mqnamesrv- Startup Broker
sh bin/mqbroker -n localhost:9876Add dependency spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq to the pom.xml file in your Spring Cloud project.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq</artifactId>
</dependency>sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t test-topicConfigure Input and Output Binding and cooperate with @EnableBinding annotation
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableBinding({ Source.class, Sink.class })
public class RocketMQApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQApplication.class, args);
}
}Configure Binding:
# configure the nameserver of rocketmq
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.binder.name-server=127.0.0.1:9876
# configure the output binding named output
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.destination=test-topic
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.content-type=application/json
# configure the input binding named input
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.destination=test-topic
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.content-type=application/json
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.group=test-group
- Add necessary configurations to file
/src/main/resources/application.properties.
spring.application.name=rocketmq-example
server.port=28081-
Start the application in IDE or by building a fatjar.
- Start in IDE: Find main class
RocketMQApplication, and execute the main method. - Build a fatjar: Execute command
mvn clean packageto build a fatjar, and run commandjava -jar rocketmq-example.jarto start the application.
- Start in IDE: Find main class
Using the binding named output and sent messages to test-topic topic.
And using two input bindings to subscribe messages.
-
input1: subscribe the message of
test-topictopic and consume ordered messages(all messages should in the same MessageQueue if you want to consume ordered messages). -
input2: subscribe the message of
test-topictopic and consume concurrent messages which tags aretagStr, the thread number in pool is 20 in Consumer side.
see the configuration below:
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.binder.name-server=127.0.0.1:9876
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.destination=test-topic
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.content-type=application/json
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.destination=test-topic
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.content-type=text/plain
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.group=test-group1
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input1.consumer.orderly=true
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.destination=test-topic
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.content-type=text/plain
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.group=test-group2
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input2.consumer.orderly=false
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input2.consumer.tags=tagStr
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.consumer.concurrency=20
Using MessageChannel to send messages:
public class ProducerRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private MessageChannel output;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS, "tagStr");
Message message = MessageBuilder.createMessage(msg, new MessageHeaders(headers));
output.send(message);
}
}Or you can use the native API of RocketMQ to send messages:
public class RocketMQProducer {
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("producer_group");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
producer.start();
Message msg = new Message("test-topic", "tagStr", "message from rocketmq producer".getBytes());
producer.send(msg);
}Using @StreamListener to receive messages:
@Service
public class ReceiveService {
@StreamListener("input1")
public void receiveInput1(String receiveMsg) {
System.out.println("input1 receive: " + receiveMsg);
}
@StreamListener("input2")
public void receiveInput2(String receiveMsg) {
System.out.println("input2 receive: " + receiveMsg);
}
}sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t broadcastapplication.yml
server:
port: 28085
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-broadcast-producer-example
cloud:
stream:
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: broadcast
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugcode
Use ApplicationRunner and StreamBridge to send messages.
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
return args -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String key = "KEY" + i;
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage<SimpleMsg>(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
}
};
}
}Startup two consumers.
application.yml
server:
port: 28084
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-broadcast-consumer1-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
consumer-in-0:
consumer:
messageModel: BROADCASTING
bindings:
consumer-in-0:
destination: broadcast
group: broadcast-consumer
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugcode
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer1 Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
};
}
}application.yml
server:
port: 28083
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-broadcast-consumer2-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
consumer-in-0:
consumer:
messageModel: BROADCASTING
bindings:
consumer-in-0:
destination: broadcast
group: broadcast-consumer
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugcode
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer2 Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
};
}
} RocketMQ provides ordered messages using FIFO order.
There are two types of ordered messages.
- Global: For a specified topic, all messages are published and consumed in strict FIFO (First In First Out) order.
- Partition: For a specified topic, all messages are partitioned according to the
Sharding Key. Messages within the same partition are published and consumed in strict FIFO order.Sharding Keyis a key field used to distinguish different partitions in sequential messages, and it is a completely different concept from the Key of ordinary messages.
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t orderlyapplication.yml
server:
port: 28082
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-orderly-consume-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
# 定义messageSelector
messageQueueSelector: orderlyMessageQueueSelector
consumer-in-0:
consumer:
# tag: {@code tag1||tag2||tag3 }; sql: {@code 'color'='blue' AND 'price'>100 } .
subscription: 'TagA || TagC || TagD'
push:
orderly: true
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: orderly
consumer-in-0:
destination: orderly
group: orderly-consumer
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugMessageQueueSelector
Choose a partition selection algorithm for you, and ensure that the same parameters get the same results.
@Component
public class OrderlyMessageQueueSelector implements MessageQueueSelector {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(OrderlyMessageQueueSelector.class);
@Override
public MessageQueue select(List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) {
Integer id = (Integer) ((MessageHeaders) arg).get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID);
String tag = (String) ((MessageHeaders) arg).get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS);
int index = id % RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.tags.length % mqs.size();
return mqs.get(index);
}
}Producer&Consumer
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
/***
* tag array.
*/
public static final String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC", "TagD", "TagE"};
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
return args -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String key = "KEY" + i;
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS, tags[i % tags.length]);
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
}
};
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
String tagHeaderKey = RocketMQMessageConverterSupport.toRocketHeaderKey(
MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS).toString();
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " TAG:" +
msg.getHeaders().get(tagHeaderKey).toString());
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
};
}
}Scheduled messages differ from normal messages in that they won’t be delivered until a provided time later.
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t delayapplication.yml
server:
port: 28086
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-delay-consume-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: delay
consumer-in-0:
destination: delay
group: delay-group
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugcode
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producerDelay() {
return args -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String key = "KEY" + i;
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
// Set the delay level 1~10
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_DELAY_TIME_LEVEL, 2);
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Delay RocketMQ " + i), headers);
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
}
};
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
};
}
}sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t sqlapplication.yml
RocketMQ stream binder supports filter by tag or sql, just setting spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.<channelName>.consumer.subscription.
Tag example: tag:red || blue
Sql example: sql:(color in ('red1', 'red2', 'red4') and price>3)
More: Filter
server:
port: 28087
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-sql-consume-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
consumer-in-0:
consumer:
# tag: {@code tag1||tag2||tag3 }; sql: {@code 'color'='blue' AND 'price'>100 } .
subscription: sql:(color in ('red1', 'red2', 'red4') and price>3)
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: sql
consumer-in-0:
destination: sql
group: sql-group
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugcode
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication.class, args);
}
/**
* color array.
*/
public static final String[] color = new String[] {"red1", "red2", "red3", "red4", "red5"};
/**
* price array.
*/
public static final Integer[] price = new Integer[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
return args -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String key = "KEY" + i;
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
headers.put("color", color[i % color.length]);
headers.put("price", price[i % price.length]);
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
}
};
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
String colorHeaderKey = "color";
String priceHeaderKey = "price";
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " COLOR:" +
msg.getHeaders().get(colorHeaderKey).toString() + " " +
"PRICE: " + msg.getHeaders().get(priceHeaderKey).toString());
};
}
}Refer to Transaction Example.
It can be thought of as a two-phase commit message implementation to ensure eventual consistency in distributed system. Transactional message ensures that the execution of local transaction and the sending of message can be performed atomically.
Refer to https://rocketmq.apache.org/
1、 Transactional status
There are three states for transactional message: (1) TransactionStatus.CommitTransaction: commit transaction,it means that allow consumers to consume this message. (2) TransactionStatus.RollbackTransaction: rollback transaction,it means that the message will be deleted and not allowed to consume. (3) TransactionStatus.Unknown: intermediate state,it means that MQ is needed to check back to determine the status.
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t txapplication.yml
server:
port: 28088
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-tx-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
transactionListener: myTransactionListener
producerType: Trans
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: tx
consumer-in-0:
destination: tx
group: tx-group
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debugTransactionListenerImpl
To execute local transaction.
@Component("myTransactionListener")
public class TransactionListenerImpl implements TransactionListener {
@Override
public LocalTransactionState executeLocalTransaction(Message msg, Object arg) {
Object num = msg.getProperty("test");
if ("1".equals(num)) {
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " unknown");
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
}
else if ("2".equals(num)) {
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " rollback");
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
}
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " commit");
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
}
@Override
public LocalTransactionState checkLocalTransaction(MessageExt msg) {
System.out.println("check: " + new String(msg.getBody()));
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
}
}producer and consumer
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQTxApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQTxApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQTxApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
return args -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
MessageBuilder builder = MessageBuilder.withPayload(new SimpleMsg("Hello Tx msg " + i));
builder.setHeader("test", String.valueOf(i))
.setHeader(MessageHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, MimeTypeUtils.APPLICATION_JSON);
builder.setHeader(RocketMQConst.USER_TRANSACTIONAL_ARGS, "binder");
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = builder.build();
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
System.out.println("send Msg:" + msg.toString());
}
};
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
Object arg = msg.getHeaders();
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " ARG:"
+ arg.toString());
};
}
}- Retry consumption message: According to the configured number of re-consumption, the server will re-push the message according to whether the client's consumption is successful or not.
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t retrieableapplication.yml
server:
port: 28089
spring:
application:
name: rocketmq-retrieable-consume-example
cloud:
stream:
function:
definition: consumer;
rocketmq:
binder:
name-server: localhost:9876
bindings:
producer-out-0:
producer:
group: output_1
consumer-in-0:
consumer:
## According to the configured number of `max-reconsume-times`,
## the server will re-push the message according to whether the client's consumption is successful or not
push:
max-reconsume-times: 3
bindings:
producer-out-0:
destination: retrieable
consumer-in-0:
destination: retrieable
group: retrieable-consumer
logging:
level:
org.springframework.context.support: debug
code
@SpringBootApplication
public class RocketMQRetrieableConsumeApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(RocketMQRetrieableConsumeApplication.class);
@Autowired
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQRetrieableConsumeApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
return args -> {
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(
new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ For Retrieable ."), headers);
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
};
}
@Bean
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
return msg -> {
// Mock Exception in consumer function.
throw new RuntimeException("mock exception.");
};
}
}Add dependency spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq to your pom.xml file, and configure your endpoint security strategy.
- Spring Boot1.x: Add configuration
management.security.enabled=false - Spring Boot2.x: Add configuration
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
To view the endpoint information, visit the following URLS:
- Spring Boot1.x: Sentinel Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/rocketmq_binder.
- Spring Boot2.x: Sentinel Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/actuator/rocketmq-binder.
Endpoint will metrics some data like last send timestamp, sending or receive message successfully times or unsuccessfully times.
{
"runtime": {
"lastSend.timestamp": 1542786623915
},
"metrics": {
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.totalConsumed": {
"count": 11
},
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.totalConsumedFailures": {
"count": 0
},
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.totalSentFailures": {
"count": 0
},
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.consumedPerSecond": {
"count": 11,
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.012163847780107841,
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.03614605351360527,
"meanRate": 0.3493213353657594,
"oneMinuteRate": 0.17099243039490175
},
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.totalSent": {
"count": 5
},
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.sentPerSecond": {
"count": 5,
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.005540151995103271,
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.01652854617838251,
"meanRate": 0.10697493212602836,
"oneMinuteRate": 0.07995558537067671
},
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.sentFailuresPerSecond": {
"count": 0,
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.0,
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.0,
"meanRate": 0.0,
"oneMinuteRate": 0.0
},
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.consumedFailuresPerSecond": {
"count": 0,
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.0,
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.0,
"meanRate": 0.0,
"oneMinuteRate": 0.0
}
}
}Note: You should add metrics-core dependency if you want to see metrics data. endpoint will show warning information if you don't add that dependency:
{
"warning": "please add metrics-core dependency, we use it for metrics"
}For more information about RocketMQ, see RocketMQ Project.
If you have any ideas or suggestions for Spring Cloud RocketMQ Binder, please don't hesitate to tell us by submitting GitHub issues.