###分析webpack中的Compiler/Compilation/Stats对象及构建顺序
- Compiler instance of watch method
Compiler.prototype.watch = function(watchOptions, handler) {
this.fileTimestamps = {};
this.contextTimestamps = {};
var watching = new Watching(this, watchOptions, handler);
return watching;
};注意:watch的时候,我们会给我们的Compiler实例对象添加一个fileTimestamps和contextTimestamps对象。而且可以清楚的知道这里返回的是我们通过watchOptions实例化的一个Watching实例对象 我们可以使用下面这种方式调用,例如在atool-build中调用:
if (args.watch) {
compiler.watch(args.watch || 200, doneHandler);
} else {
compiler.run(doneHandler);
}2.compiler实例化的时候同时实例化一个Parser对象
function Compiler() {
Tapable.call(this);
this.parser = {
plugin: function(hook, fn) {
this.plugin("compilation", function(compilation, data) {
data.normalModuleFactory.plugin("parser", function(parser) {
parser.plugin(hook, fn);
});
});
}.bind(this),
apply: function() {
this.plugin("compilation", function(compilation, data) {
data.normalModuleFactory.plugin("parser", function(parser) {
parser.apply.apply(parser, args);
});
});
}.bind(this)
};
this.options = {};
}我们的Compiler会先继承了Tapable;在parser.plugin中注入的回调函数。具体parser的使用,请见文末参考文献。
compiler.parser.plugin("var rewire", function (expr) {
//if you original module has 'var rewire'
//you now have a handle on the expresssion object
return true;
});3.调用compiler.run方法会分别执行'before-run','run',继而调用compiler的compile方法
Compiler.prototype.run = function(callback) {
var self = this;
var startTime = new Date().getTime();
//before run
self.applyPluginsAsync("before-run", self, function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
//run
self.applyPluginsAsync("run", self, function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
self.readRecords(function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
//compile函数被调用,我们传入run函数的回调函数会在compile回调函数中调用
//也就是在compiler的'done'之后回调
self.compile(function onCompiled(err, compilation) {
if(err) return callback(err);
if(self.applyPluginsBailResult("should-emit", compilation) === false) {
var stats = compilation.getStats();
stats.startTime = startTime;
stats.endTime = new Date().getTime();
self.applyPlugins("done", stats);
return callback(null, stats);
}
self.emitAssets(compilation, function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
if(compilation.applyPluginsBailResult("need-additional-pass")) {
compilation.needAdditionalPass = true;
var stats = compilation.getStats();
stats.startTime = startTime;
stats.endTime = new Date().getTime();
self.applyPlugins("done", stats);
self.applyPluginsAsync("additional-pass", function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
self.compile(onCompiled);
});
return;
}
self.emitRecords(function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
var stats = compilation.getStats();
stats.startTime = startTime;
stats.endTime = new Date().getTime();
self.applyPlugins("done", stats);
return callback(null, stats);//调用'done'
});
});
});
});
});
});
};注意: (1)我们compiler.compile方法运行结束后会进行相应的回调,其中回调函数就是我们通过compile.run调用时候传入的函数
(2)其中我们要注意我们传入的callback会被传入一个参数,这个参数是通过如下方式来获取到的:
var stats = compilation.getStats();
stats.startTime = startTime;
stats.endTime = new Date().getTime();那么getStats到底得到的是什么呢?
getStats() {
return new Stats(this);
}也就是说我们得到的是一个Stats对象,具体用法看参考文献。那么我们给出一个例子:
function doneHandler(err, stats) {
if (args.json) {
const filename = typeof args.json === 'boolean' ? 'build-bundle.json' : args.json;
const jsonPath = join(fileOutputPath, filename);
writeFileSync(jsonPath, JSON.stringify(stats.toJson()), 'utf-8');
console.log(`Generate Json File: ${jsonPath}`);
}
//如果出错,那么退出码是1
const { errors } = stats.toJson();
if (errors && errors.length) {
process.on('exit', () => {
process.exit(1);
});
}
// if watch enabled only stats.hasErrors would log info
// otherwise would always log info
if (!args.watch || stats.hasErrors()) {
const buildInfo = stats.toString({
colors: true,
children: true,
chunks: !!args.verbose,
modules: !!args.verbose,
chunkModules: !!args.verbose,
hash: !!args.verbose,
version: !!args.verbose,
});
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
console.error(buildInfo);
} else {
console.log(buildInfo);
}
}
if (err) {
process.on('exit', () => {
process.exit(1);
});
console.error(err);
}
if (callback) {
callback(err);
}
}主要的代码就是调用stats.toJson方法,内容就是获取本次编译的主要信息。同时参考文献中也给出了一个输出的例子,可以自己查看。
(3)我们自己的回调函数是在compiler的'done'回调以后触发的,而且和compiler的'done'回调一样,我们也是也是给我们的函数传入err和Stats对象!
然后我们看看compile中的内容:
Compiler.prototype.compile = function(callback) {
self.applyPluginsAsync("before-compile", params, function(err) {
self.applyPlugins("compile", params);
var compilation = self.newCompilation(params);
//调用compiler的compile方法,我们才会构建出一个Compilation实例对象,在
//'make'钩子里面我们就可以获取到compilation对象了
self.applyPluginsParallel("make", compilation, function(err) {
compilation.finish();
compilation.seal(function(err) {
self.applyPluginsAsync("after-compile", compilation, function(err) {
//在compilation.seal方法调用以后我们才会执行'after-compile'
});
});
});
});
};我们再来看看compilation的finish方法:
finish() {
this.applyPlugins1("finish-modules", this.modules);
this.modules.forEach(m => this.reportDependencyErrorsAndWarnings(m, [m]));
}我们再来看看compilation.seal方法:
seal(callback) {
self.applyPlugins0("seal");
self.applyPlugins0("optimize");
while(self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-modules-basic", self.modules) ||
self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-modules", self.modules) ||
self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-modules-advanced", self.modules));
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-modules", self.modules);
//这里是optimize module
while(self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-chunks-basic", self.chunks) ||
self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-chunks", self.chunks) ||
self.applyPluginsBailResult1("optimize-chunks-advanced", self.chunks));
//这里是optimize chunk
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-chunks", self.chunks);
//这里是optimize tree
self.applyPluginsAsyncSeries("optimize-tree", self.chunks, self.modules, function sealPart2(err) {
self.applyPlugins2("after-optimize-tree", self.chunks, self.modules);
const shouldRecord = self.applyPluginsBailResult("should-record") !== false;
self.applyPlugins2("revive-modules", self.modules, self.records);
self.applyPlugins1("optimize-module-order", self.modules);
self.applyPlugins1("advanced-optimize-module-order", self.modules);
self.applyPlugins1("before-module-ids", self.modules);
self.applyPlugins1("module-ids", self.modules);
self.applyModuleIds();
self.applyPlugins1("optimize-module-ids", self.modules);
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-module-ids", self.modules);
self.sortItemsWithModuleIds();
self.applyPlugins2("revive-chunks", self.chunks, self.records);
self.applyPlugins1("optimize-chunk-order", self.chunks);
self.applyPlugins1("before-chunk-ids", self.chunks);
self.applyChunkIds();
self.applyPlugins1("optimize-chunk-ids", self.chunks);
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-chunk-ids", self.chunks);
self.sortItemsWithChunkIds();
if(shouldRecord)
self.applyPlugins2("record-modules", self.modules, self.records);
if(shouldRecord)
self.applyPlugins2("record-chunks", self.chunks, self.records);
self.applyPlugins0("before-hash");
self.createHash();
self.applyPlugins0("after-hash");
if(shouldRecord)
self.applyPlugins1("record-hash", self.records);
self.applyPlugins0("before-module-assets");
self.createModuleAssets();
if(self.applyPluginsBailResult("should-generate-chunk-assets") !== false) {
self.applyPlugins0("before-chunk-assets");
self.createChunkAssets();
}
self.applyPlugins1("additional-chunk-assets", self.chunks);
self.summarizeDependencies();
if(shouldRecord)
self.applyPlugins2("record", self, self.records);
self.applyPluginsAsync("additional-assets", err => {
if(err) {
return callback(err);
}
self.applyPluginsAsync("optimize-chunk-assets", self.chunks, err => {
if(err) {
return callback(err);
}
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-chunk-assets", self.chunks);
self.applyPluginsAsync("optimize-assets", self.assets, err => {
if(err) {
return callback(err);
}
self.applyPlugins1("after-optimize-assets", self.assets);
if(self.applyPluginsBailResult("need-additional-seal")) {
self.unseal();
return self.seal(callback);
}
return self.applyPluginsAsync("after-seal", callback);
});
});
});
});
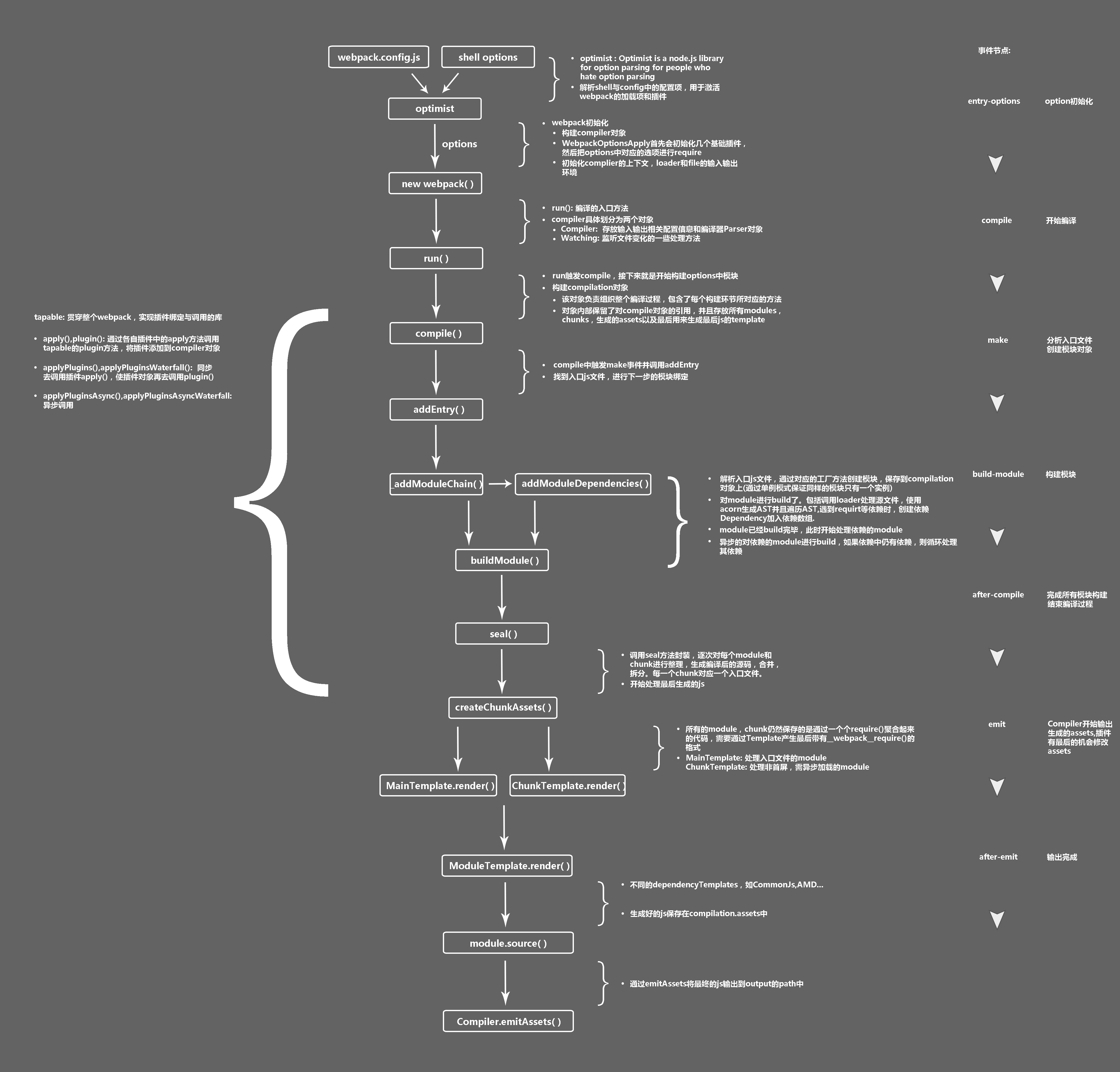
}从上面提到的第3点,我们可以知道webpack的编译过程大致如下:
'before run'
'run'
compile:func//调用compile函数
'before compile'
'compile'//(1)compiler对象的第一阶段
newCompilation:object//创建compilation对象
'make' //(2)compiler对象的第二阶段
compilation.finish:func
"finish-modules"
compilation.seal
"seal"
"optimize"
"optimize-modules-basic"
"optimize-modules-advanced"
"optimize-modules"
"after-optimize-modules"//首先是优化模块
"optimize-chunks-basic"
"optimize-chunks"//然后是优化chunk
"optimize-chunks-advanced"
"after-optimize-chunks"
"optimize-tree"
"after-optimize-tree"
"should-record"
"revive-modules"
"optimize-module-order"
"advanced-optimize-module-order"
"before-module-ids"
"module-ids"//首先优化module-order,然后优化module-id
"optimize-module-ids"
"after-optimize-module-ids"
"revive-chunks"
"optimize-chunk-order"
"before-chunk-ids"//首先优化chunk-order,然后chunk-id
"optimize-chunk-ids"
"after-optimize-chunk-ids"
"record-modules"//record module然后record chunk
"record-chunks"
"before-hash"
compilation.createHash//func
"chunk-hash"//webpack-md5-hash
"after-hash"
"record-hash"//before-hash/after-hash/record-hash
"before-module-assets"
"should-generate-chunk-assets"
"before-chunk-assets"
"additional-chunk-assets"
"record"
"additional-assets"
"optimize-chunk-assets"
"after-optimize-chunk-assets"
"optimize-assets"
"after-optimize-assets"
"need-additional-seal"
unseal:func
"unseal"
"after-seal"
"after-compile"//(4)完成模块构建和编译过程(seal函数回调)
"emit"//(5)compile函数的回调,compiler开始输出assets,是改变assets最后机会
"after-emit"//(6)文件产生完成
注意:上面没有标出第三个阶段,也就是compiler的'build-module'阶段,在这个阶段,我们调用了addEntry等方法通过入口文件_addModuleChain,processModuleDependencies等方法分析模块的依赖关系!
详细内容可以参考下面这种图:
4.上面的第二段代码有compiler.watch方法的调用 其本质是使用了相关的配置生成了Watching对象:
var watching = new Watching(this, watchOptions, handler);我们看看Watching对象是如何处理的:
Watching.prototype.watch = function(files, dirs, missing) {
this.watcher = this.compiler.watchFileSystem.watch(files, dirs, missing, this.startTime, this.watchOptions, function(err, filesModified, contextModified, missingModified, fileTimestamps, contextTimestamps) {
this.watcher = null;
if(err) return this.handler(err);
this.compiler.fileTimestamps = fileTimestamps;
this.compiler.contextTimestamps = contextTimestamps;
this.invalidate();
}.bind(this), function(fileName, changeTime) {
this.compiler.applyPlugins("invalid", fileName, changeTime);
}.bind(this));
};这个很容易看出来,如果我们的文件发生了变化,那么我们直接调用Watching实例的invalidate方法,并通知compiler重新开始编译过程!这也是我们最重要的watch逻辑!这也是我们为什么有上面这样的代码:
if (args.watch) {
compiler.watch(args.watch || 200, doneHandler);
} else {
compiler.run(doneHandler);
}而且我们知道compiler的watch方法返回的是一个watching,那么我们看看Watching对象的内部结构:
function Watching(compiler, watchOptions, handler) {
this.startTime = null;
this.invalid = false;//是否已经文件变化
this.error = null;
this.stats = null;
this.handler = handler;
this.compiler = compiler;//compiler句柄
this.running = true;
}
Watching.prototype._go = function() {
};
Watching.prototype._done = function(err, compilation) {
};
Watching.prototype.watch = function(files, dirs, missing) {
};
Watching.prototype.invalidate = function() {
if(this.watcher) {
this.watcher.pause();
this.watcher = null;
}
if(this.running) {
this.invalid = true;
return false;
} else {
this._go();
}
};
Watching.prototype.close = function(callback) {
if(callback === undefined) callback = function() {};
if(this.watcher) {
this.watcher.close();
this.watcher = null;
}
if(this.running) {
this.invalid = true;
this._done = function() {
callback();
};
} else {
callback();
}
};通过上面的结果你应该可以知道invalidate和close方法的具体作用了,这里就不在赘述
5.我们看看如何获取到我们最重要的compiler对象
// Run compiler.
const compiler = webpack(webpackConfig);
// Hack: remove extract-text-webpack-plugin log
if (!args.verbose) {
compiler.plugin('done', (stats) => {
stats.stats.forEach((stat) => {
stat.compilation.children = stat.compilation.children.filter((child) => {
return child.name !== 'extract-text-webpack-plugin';
});
});
});
}(1)我们的'done'回调是当'emit,after-emit'都调用结束了以后才会触发的,所以这时候我们所有的文件assets都已经生成结束了。
(2)当我们调用webpack方法的时候,返回的就是compiler对象!
(3)我们的stats对象有一个compilation属性,从构造函数就可以看到:
class Stats {
constructor(compilation) {
this.compilation = compilation;
this.hash = compilation.hash;
}
}同时我们的compilation.children也是一个数组
this.children.forEach(child => {
this.fileDependencies = this.fileDependencies.concat(child.fileDependencies);
this.contextDependencies = this.contextDependencies.concat(child.contextDependencies);
this.missingDependencies = this.missingDependencies.concat(child.missingDependencies);
});不过我们的compilation对象的fileDependencies,contextDependencies等会包含所有的子模块的内容!至于上面的'done'回调处理,我们就是为了防止我们的extract-text-webpack-plugin输出太多的log而设置的!请看下面的参考文献
参考资料: http://webpack.github.io/docs/node.js-api.html#stats
http://taobaofed.org/blog/2016/09/09/webpack-flow/
webpack-contrib/extract-text-webpack-plugin#35
http://webpack.github.io/docs/plugins.html#the-parser-instance