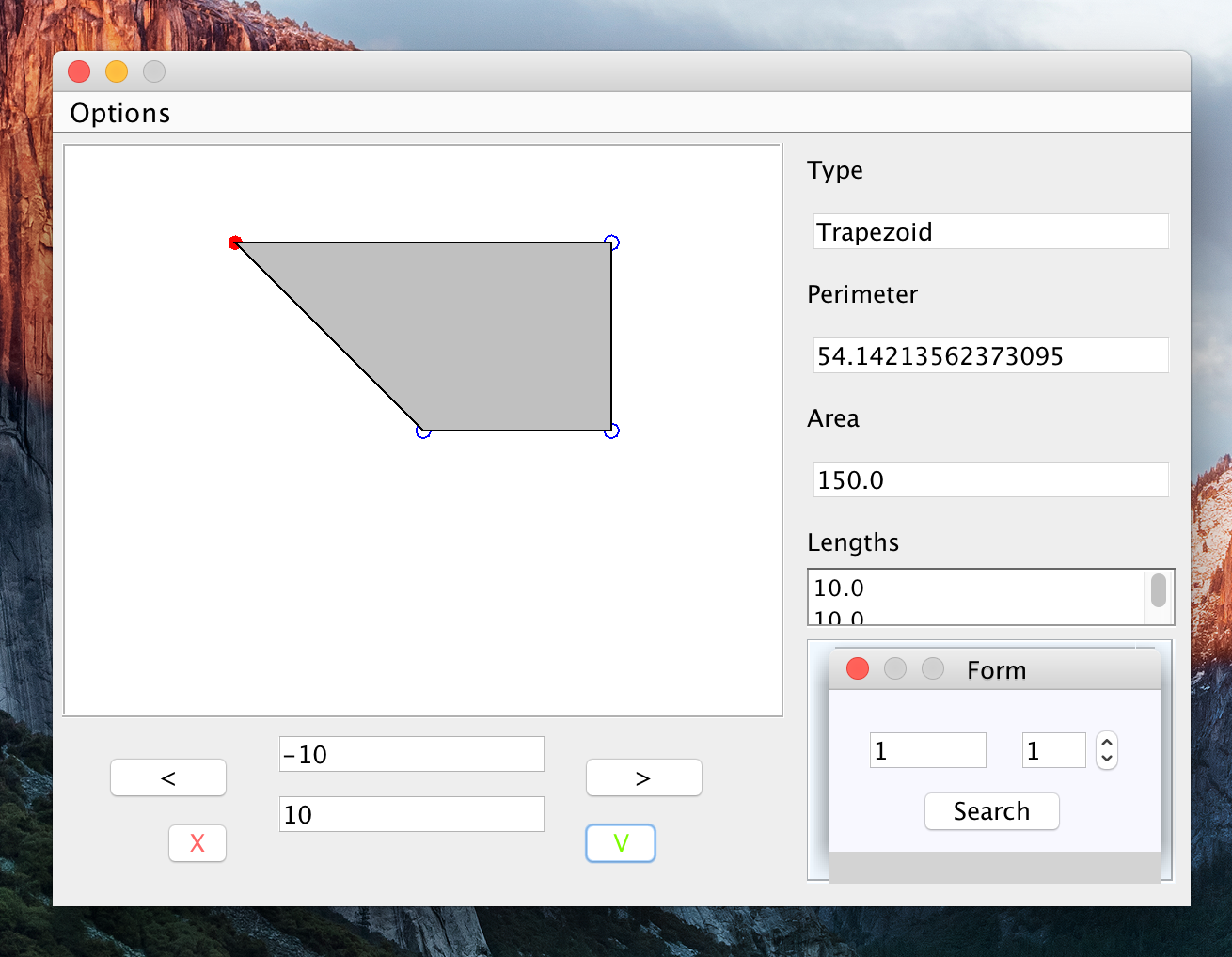
A Java application to draw basic geometric shapes. Using an interface, the user is able to precise points coordinates and the app will get the distance, area and type of figure.
It implements some design patterns very widely used such as MVC, DAO, Observer, Singleton, Factory patterns...
This tiny project was coded using IntelliJ IDEA for an academic purpose: there is no better way to learn programming than getting his own hands dirty. While learning a programming language, I'd recommend building a GeomApp, a game, or other simple app in that programming language of choice to test yourself.
In order to run the source code, open it with IntelliJ and run src/Main.java. You might have to configure the build path for external libraries to be used, especially if you are using Eclipse which might require some configurations.
No framework was used to build this project. However the MVC architecture was implemented along with several design patterns.
There are four main layers corresponding to :
- Persistence
- Business
- Presentation
- Database
Perform create, read, update and delete CRUD.
One package implements this layer :
- database : implements the basic layer to interact with the database
This layer relies heavily on the DAO design pattern. The GeomAppConnection class only instantiates the connection one time throughout the Application Lifecycle with regard to the Singleton pattern.
All logic which is tied to the GeomApp is located in this layer. Basically, the rules to distinguish figures, compute lengths and aeras are implemented here.
The packages to refer to are :
- model package which implements basic types of geometric shapes (Rectangular, Trapezoid, Square, Rhombus ,etc)
In a few words, each family of figure relies on a single factory that takes as input the number of points and their coordinates then knows which sub-type of figure to produce.
The presentation layer is responsible of the user interface.
- MVCModel contains the models used by the views, and links to the business layer
- MVCViews implements the User Interface. It relies on the Swing Library
- MVCController links the interface to the models
MVCModel and MVCViews are wired together through an Observer pattern managed by the MVCController package. Simply put, the model is the observable object, and the view is an observer, updated each time the model is changed.
This apps runs on a SQLite database. But it can also be use a MySQL database, as in the previous versions. You can set the connection in GeomAppConnection.java by providing url, username, and password if ever you decide to switch to a MySQL database. Otherwise, you can leave the code as it is. Here the name of the database is FiguresGeometriques and you can seed is using the .sql file The Relational model is described here :
- Figure : A figure is a geometric shape defined by
- id : Primary key
- type : Type of the figure (e.g Trapezoid)
- perimeter : value of the perimeter
- area : value of the area area
- Length : A length or a distance between two points
- id : Primary key
- value : Value of the length
- id_figure : id of the figure to with the corresponding segment belongs to
- num_length : Number of the segment
- Point
- id : Primary key
- x : abscissa of the point (int)
- y : ordinate of the point (int)
- id_figure : id of the figure to which the figure belongs too (int)
- num_point : Number of the point (int)