The ECS for finishers 🏁
Leading performance in most ECS aspects.
Performance Ratio - see C# ECS Benchmark
| friflo | Flecs.NET | TinyEcs | Arch | fennecs | Leopotam | DefaultEcs | Morpeh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio | 1.00 | 2.55 | 3.42 | 6.96 | 19.02 | 2.57 | 3.81 | 21.09 |
| Notes | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-
features in v3.0.0
Introduced: Index / Search with O(1), Relationships 1:1 and 1:many and Relations. See New features in 3.0.0 -
Published Friflo.Engine.ECS.Boost to enable boosted queries with maximum performance.
-
New GitHub benchmark repository ECS.CSharp.Benchmark - Common use-cases
Get an overview of the feature set or explore various use-cases with examples at friflo ECS · Docs.
- Simple API - no boilerplate, rock-solid 🗿 and bulletproof 🛡️
- High-performance 🔥 compact ECS
- Low memory footprint 👣. Create 100.000.000 entities in 1.5 sec
- Zero ⦰ allocations after buffers are large enough. No struct boxing
- High performant / type-safe queries ⊆
- Efficient multithreaded queries ⇶
- Entity component Search in O(1) ∈
- Fast batch / bulk operations ⏩
- Command buffers / deferred operations ⏭️
- Entity relationships and relations ⌘
- Entity hierarchy / tree ⪪
- Fully reactive / entity events ⚡
- Systems / System groups ⚙️
- JSON Serialization 💿
- SIMD Support 🧮
- Supports .NET Standard 2.1 .NET 5 .NET 6 .NET 7 .NET 8
WASM / WebAssembly, Unity (Mono, AOT/IL2CPP, WebGL), Godot, MonoGame, ... and Native AOT - Debug Tools 🐞: Watch entities, components, tags, relations, query results, systems, ...
- 100% verifiably safe 🔒 C#. No unsafe code, native dll bindings and access violations.
Get package on nuget or use the dotnet CLI.
dotnet add package Friflo.Engine.ECS

Quote from developer: "Just wanted to let you know that Friflo ECS 2.0.0 works like a charm in my little game.
I use it for basically everything (landscape segments, vegetation, players, animations, collisions and even the floating dust particles are entities).
After some optimization there is no object allocation during gameplay - the allocation graph just stays flat - no garbage collection."
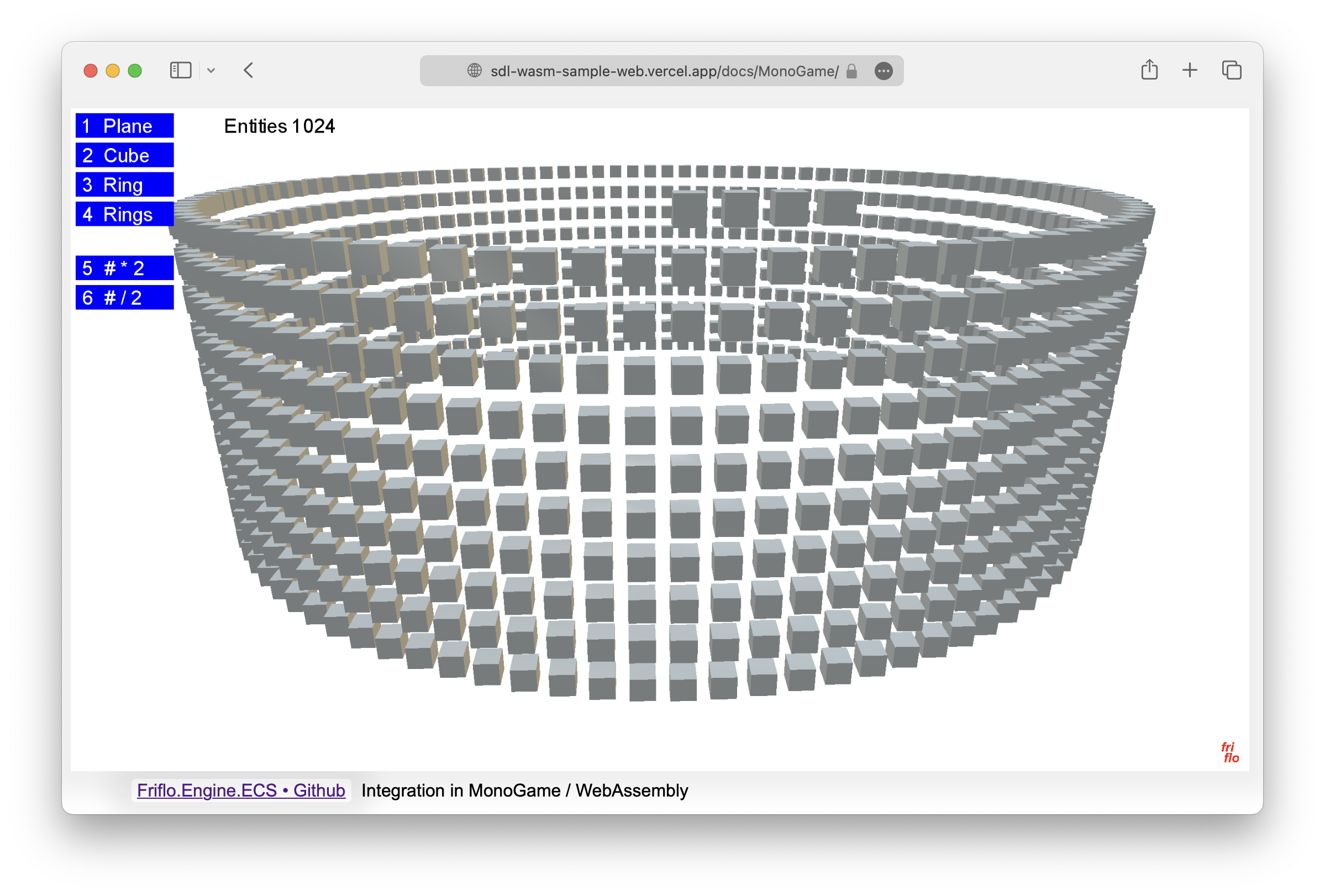
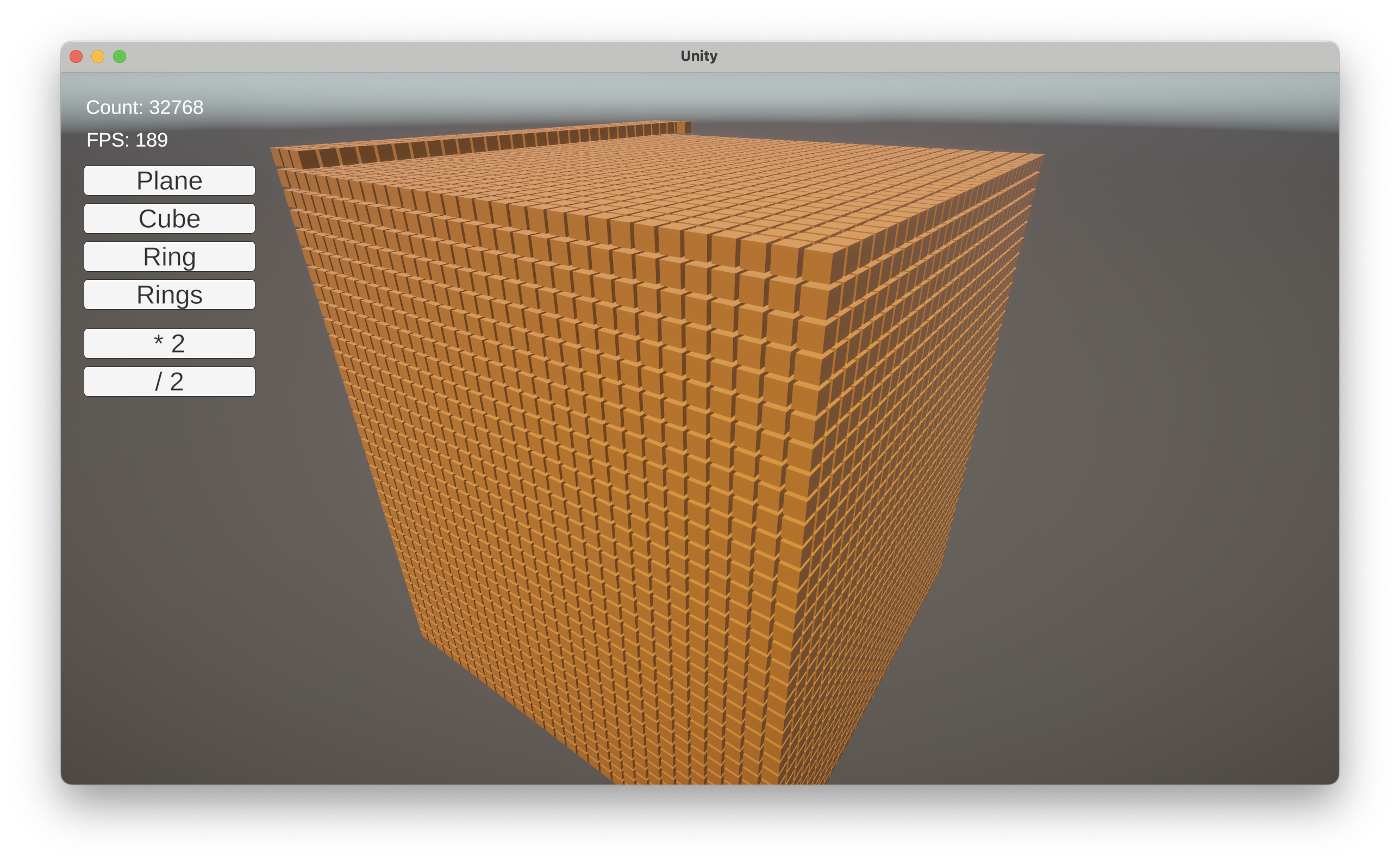
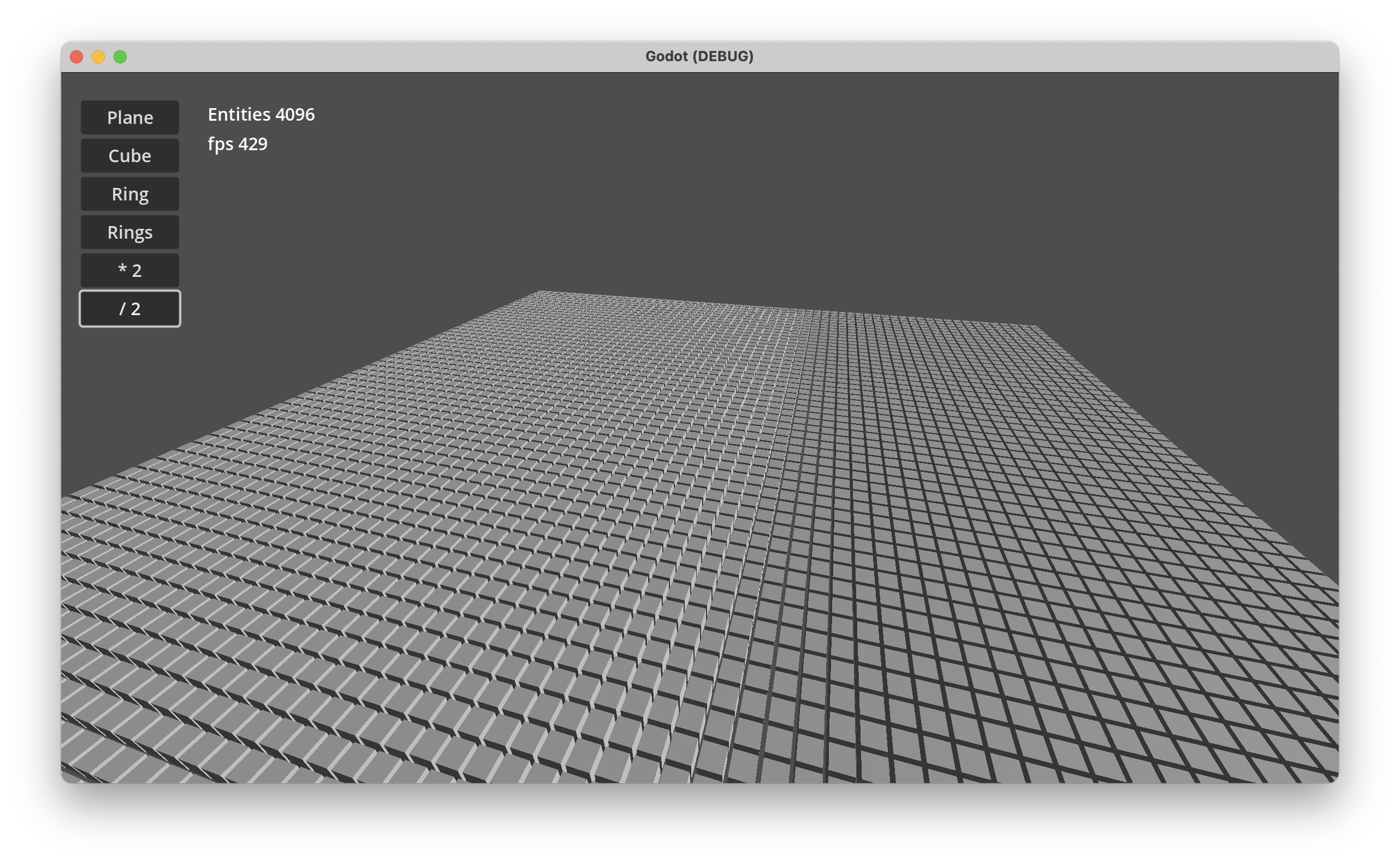
MonoGame Demo is available as WASM / WebAssembly app. Try Demo in your browser.
Demo projects on GitHub below.
 |
 |
 |
| MonoGame | Unity | Godot |
Desktop Demo performance: Godot 202 FPS, Unity 100 FPS at 65536 entities.
All example Demos - Windows, macOS & Linux - available as projects for MonoGame, Unity and Godot.
See Demos · GitHub
An entity-component-system (ECS) is a software architecture pattern. See ECS ⋅ Wikipedia.
It is often used in the Gaming industry - e.g. Minecraft - and used for high performant data processing.
An ECS provide two strengths:
-
It enables writing highly decoupled code. Data is stored in Components which are assigned to objects - aka Entities - at runtime.
Code decoupling is accomplished by dividing implementation in pure data structures (Component types) - and code (Systems) to process them. -
It enables high performant system execution by storing components in continuous memory to leverage CPU caches L1, L2 & L3.
It improves CPU branch prediction by minimizing conditional branches when processing components in tight loops.
-
Index / Search used to search entities with specific component values in O(1). E.g
- To lookup entities having a TileComponent with a specific tile id.
- To lookup network entities with a NetComponent using a custom identifier like a
Guid,longor astring.
-
Relationships to create links / connections between entities. Used for:
- Attack systems
- Path finding / Route tracing
- Model social networks. E.g friendship, alliances or rivalries
- Build any type of a directed graph using entities as nodes and links or relations as edges
-
Relations to add multiple "components" of the same type to a single entity. E.g.
- Inventory systems
- To model one-to-many data structures
Big shout out to fennecs and flecs for the challenge to improve the feature set and performance of this project!
This section contains two typical use cases when using an ECS.
More examples describing use of various features are in the friflo ECS - Documentation.
The hello world examples demonstrates the creation of a world, some entities with components
and their movement using a simple ForEachEntity() call.
public struct Velocity : IComponent { public Vector3 value; }
public static void HelloWorld()
{
var world = new EntityStore();
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++) {
world.CreateEntity(new Position(n, 0, 0), new Velocity{ value = new Vector3(0, n, 0)});
}
var query = world.Query<Position, Velocity>();
query.ForEachEntity((ref Position position, ref Velocity velocity, Entity entity) => {
position.value += velocity.value;
});
}In case of moving (updating) thousands or millions of entities an optimized approach can be used.
See:
Enumerate Query Chunks,
Parallel Query Job and
Query Vectorization - SIMD.
All query optimizations are using the same query but with different enumeration techniques.
Systems are new in Friflo.Engine.ECS v2.0.0
Systems in ECS are typically queries.
So you can still use the world.Query<Position, Velocity>() shown in the "Hello World" example.
Using Systems is optional but they have some significant advantages.
System features
-
Enable chaining multiple decoupled QuerySystem classes in a SystemGroup.
Each group provide a CommandBuffer. -
A system can have state - fields or properties - which can be used as parameters in
OnUpdate().
The system state can be serialized to JSON. -
Systems can be enabled/disabled or removed.
The order of systems in a group can be changed. -
Systems have performance monitoring build-in to measure execution times and memory allocations.
If enabled systems detected as bottleneck can be optimized.
A perf log (see example below) provide a clear overview of all systems their amount of entities and impact on performance. -
Multiple worlds can be added to a single SystemRoot instance.
root.Update()will execute every system on all worlds.
public static void HelloSystem()
{
var world = new EntityStore();
for (int n = 0; n < 10; n++) {
world.CreateEntity(new Position(n, 0, 0), new Velocity(), new Scale3());
}
var root = new SystemRoot(world) {
new MoveSystem(),
// new PulseSystem(),
// new ... multiple systems can be added. The execution order still remains clear.
};
root.Update(default);
}
class MoveSystem : QuerySystem<Position, Velocity>
{
protected override void OnUpdate() {
Query.ForEachEntity((ref Position position, ref Velocity velocity, Entity entity) => {
position.value += velocity.value;
});
}
}A valuable strength of an ECS is establishing a clear and decoupled code structure.
Adding the PulseSystem below to the SystemRoot above is trivial.
This system uses a foreach (var entity in Query.Entities) as an alternative to Query.ForEachEntity((...) => {...})
to iterate the query result.
struct Pulsating : ITag { }
class PulseSystem : QuerySystem<Scale3>
{
float frequency = 4f;
public PulseSystem() => Filter.AnyTags(Tags.Get<Pulsating>());
protected override void OnUpdate() {
foreach (var entity in Query.Entities) {
ref var scale = ref entity.GetComponent<Scale3>().value;
scale = Vector3.One * (1 + 0.2f * MathF.Sin(frequency * Tick.time));
}
}
}System performance monitoring is disabled by default.
To enable monitoring call:
root.SetMonitorPerf(true);When enabled system monitoring captures
- Number of system executions.
- System execution duration in ms.
- Memory heap allocations per system in bytes.
- The number of entities matching a query system.
In a game editor like Unity system monitoring is available in the ECS System Set component.
The performance statistics available at SystemPerf.
To get performance statistics on console use:
root.Update(default);
Console.WriteLine(root.GetPerfLog());The log result will look like:
stores: 1 on last ms sum ms updates last mem sum mem entities
--------------------- -- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
Systems [2] + 0.076 3.322 10 128 1392
| ScaleSystem + 0.038 2.088 10 64 696 10000
| PositionSystem + 0.038 1.222 10 64 696 10000on + enabled - disabled
last ms, sum ms last/sum system execution time in ms
updates number of executions
last mem, sum mem last/sum allocated bytes
entities number of entities matching a QuerySystem
Created a new GitHub repository ECS.CSharp.Benchmark - Common use-cases.
It compares the performance of multiple ECS projects with simple benchmarks.
So they can be used as a guide to migrate form one ECS to another.
See discussion of reddit announcement Post.
Performance comparison using popular ECS C# benchmark on GitHub.
Two benchmarks - subset of GitHub ⋅ Ecs.CSharp.Benchmark + PR #38
running on a Mac Mini M2.
See Benchmark results.
License
This project is licensed under MIT.
Friflo.Engine.ECS
Copyright © 2024 Ullrich Praetz - https://github.com/friflo














