-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 127
Test_strategy
William French edited this page Aug 7, 2014
·
1 revision
- TestLead: Roman Snytsar [email protected]
- Project at Trello: https://trello.com/chronozoom
- Requirements(User Stories): https://trello.com/chronozoom
- Documents: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/ai0ln6eg7h16xv6/Yc2ZRUugYu
- CI: http://tfs.cs.msu.ru:8080/
- SDET Alexey Chumagin ([email protected])
- SDET Vladimir Avdeev ([email protected])
Automation testing:
- Rapid regression testing to allow systems/applications to continue to change and improve over time without long "testing" phases at the end of each development cycle
- Finding defects and problems earlier and faster especially when tests can be run on developer machines, and as part of a build on a CI server
- Ensure the user can interact with the system as expected
Overall, with automated testing we are aiming for increased project delivery speed with built in quality.
Manual Testing:
- Cover areas where automation testing unavailable
- Main functionality is covered by tests
- Customers don't find a critical bugs
- Avoid fake test fails
- Decrease test execution time
- Cover "canvas" elements by automated tests
Testing start:
- New build is deployed
- Smoke tests (all tasks from status Deployed)
- Every night or weekend
- Regression test
- By request
- All tests are put through
- A tester does not find the bug for a long time
- A build is not suitable for testing
- A new build is deployed
Test approach for manual testing:
- Script testing
- Exploratory testing
- Student role
- Lecturer role
- Researcher
- Author
Test approach automation testing
- UI (Acceptance layer)
- Integration testing (API layer)
- Unit testing (by developers)
Related links
| Priority | Test that checks | The order of the test |
|---|---|---|
| High | 1. All have to work, work | Run first |
| 2. And working properly | ||
| 3. And everything is available, that is necessary for the rights | ||
| 4. Use the correct input (with permission). | ||
| Normal | 1. All have to work, work | If possible |
| And working properly | ||
| Use the correct input (with permission) | ||
| Tests to "break the program": | ||
| search for conditions under which does not work. | ||
| Or malfunctioning. | ||
| Or works that rights are not supposed to. | ||
| Used incorrect input (negative tests) | ||
| Low | Tests that test rarely used functionality and interface features | Performed by the presence of time |
GitHub Workflow
Short:
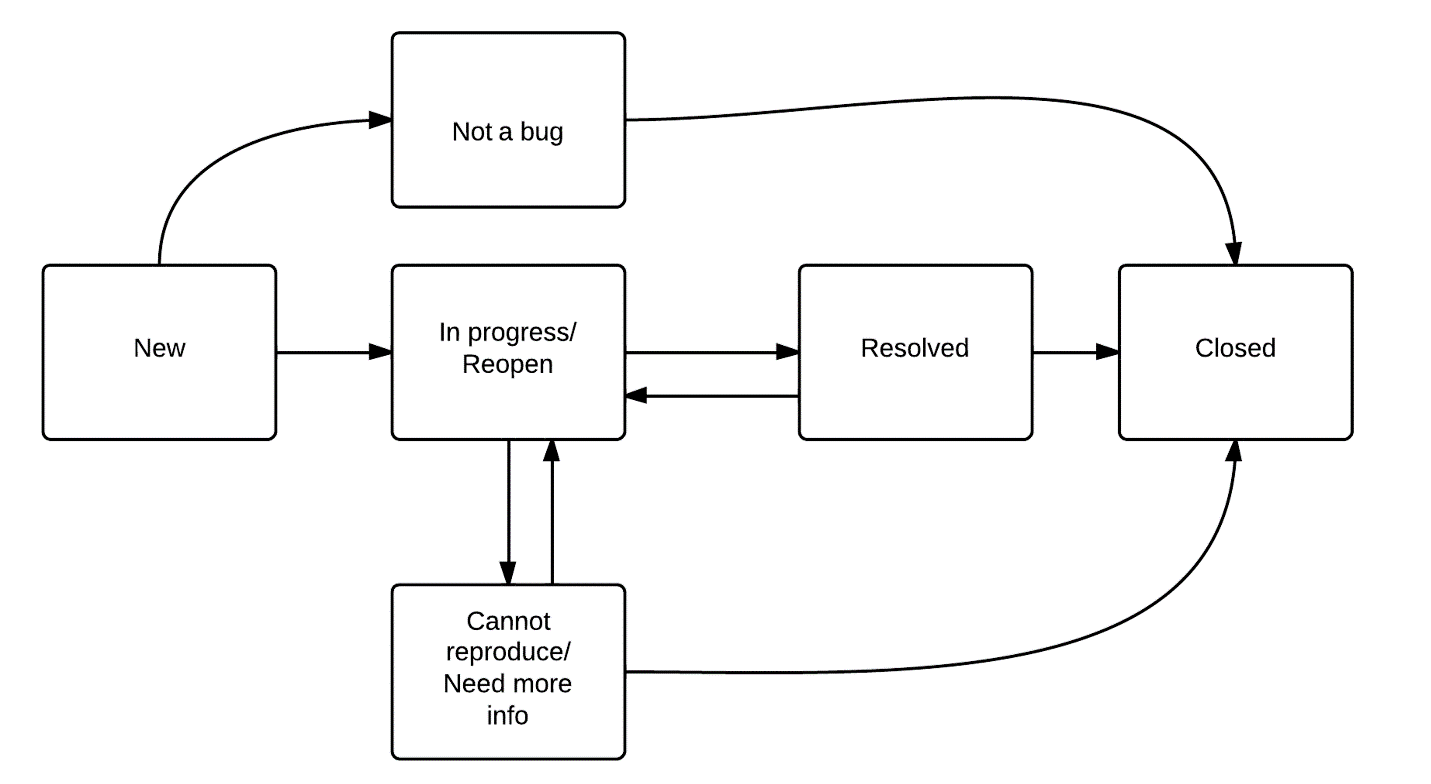
Full:
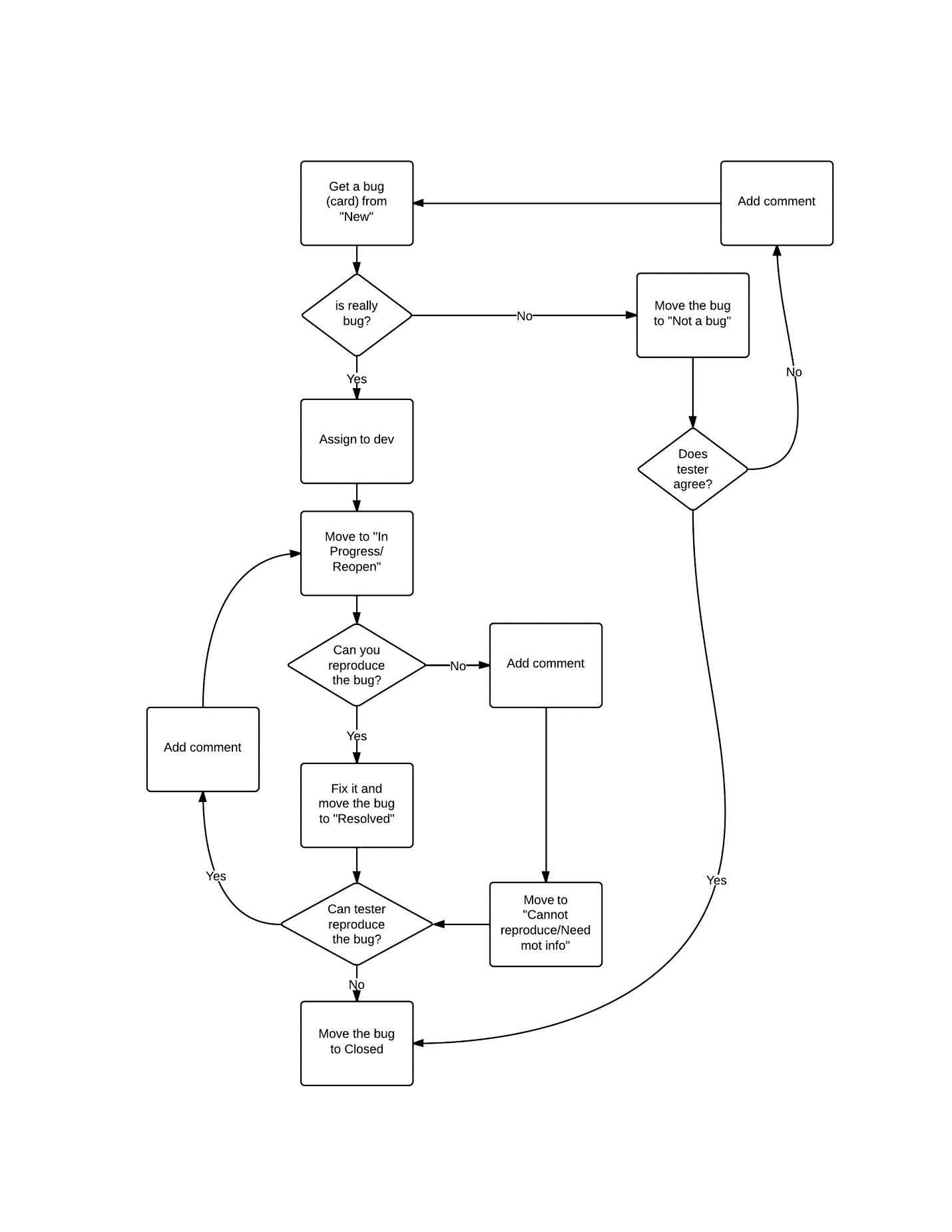
- Blocker: The defect affects critical functionality or critical data. It does not have a workaround. Example: Cannot login, cannot upload data,
- Critical: The defect affects major functionality or major data. It has a workaround but is not obvious and is difficult. Example: All exceptions, security bugs
- Minor: The defect affects minor functionality or non-critical data. It has an easy workaround. Example: Open unexpected page
- Trivial: The defect does not affect functionality or data. It does not even need a workaround. It does not impact productivity or efficiency. It is merely an inconvenience. Example: Petty layout discrepancies, spelling/grammatical errors.
- Open chronozoom
- Magnify to any leap year and to February mounth. // Or simply open [Url]
- Try to find 29 February
Observed result: Text
Expected result: Text