Given the edges of a directed graph where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates there is an edge between nodes ai and bi, and two nodes source and destination of this graph, determine whether or not all paths starting from source eventually, end at destination, that is:
- At least one path exists from the
sourcenode to thedestinationnode - If a path exists from the
sourcenode to a node with no outgoing edges, then that node is equal todestination. - The number of possible paths from
sourcetodestinationis a finite number.
Return true if and only if all roads from source lead to destination.
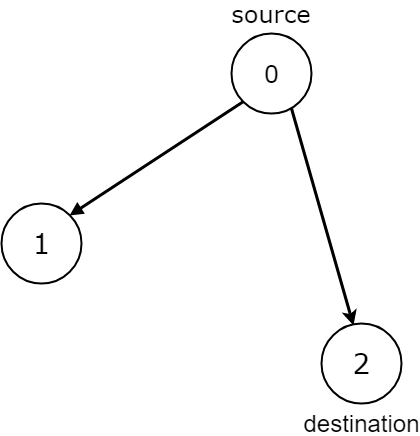
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], source = 0, destination = 2 Output: false Explanation: It is possible to reach and get stuck on both node 1 and node 2.
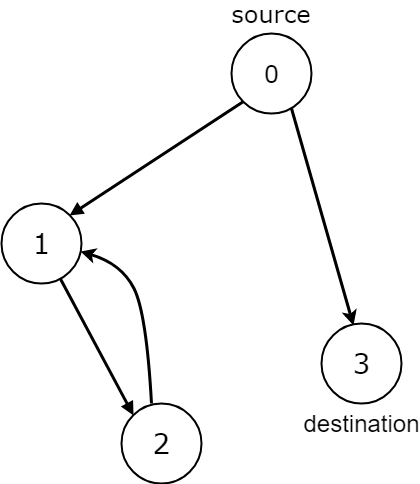
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,3],[1,2],[2,1]], source = 0, destination = 3 Output: false Explanation: We have two possibilities: to end at node 3, or to loop over node 1 and node 2 indefinitely.
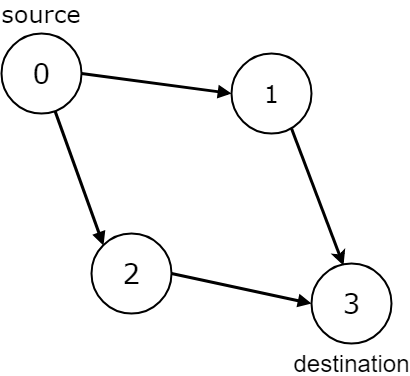
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[2,3]], source = 0, destination = 3 Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1040 <= edges.length <= 104edges.length == 20 <= ai, bi <= n - 10 <= source <= n - 10 <= destination <= n - 1- The given graph may have self-loops and parallel edges.
class Solution:
def leadsToDestination(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
@cache
def dfs(i):
if i == destination:
return not g[i]
if i in vis or not g[i]:
return False
vis.add(i)
for j in g[i]:
if not dfs(j):
return False
return True
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
vis = set()
return dfs(source)class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] f;
private boolean[] vis;
private int k;
public boolean leadsToDestination(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
vis = new boolean[n];
g = new List[n];
k = destination;
f = new int[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, key -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
}
return dfs(source);
}
private boolean dfs(int i) {
if (i == k) {
return g[i].isEmpty();
}
if (f[i] != 0) {
return f[i] == 1;
}
if (vis[i] || g[i].isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
f[i] = -1;
return false;
}
}
f[i] = 1;
return true;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool leadsToDestination(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
vector<bool> vis(n);
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
vector<int> f(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
}
function<bool(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i == destination) {
return g[i].empty();
}
if (f[i]) {
return f[i] == 1;
}
if (vis[i] || g[i].empty()) {
return false;
}
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
f[i] = -1;
return false;
}
}
f[i] = 1;
return true;
};
return dfs(source);
}
};func leadsToDestination(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool {
vis := make([]bool, n)
g := make([][]int, n)
f := make([]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
}
var dfs func(int) bool
dfs = func(i int) bool {
if i == destination {
return len(g[i]) == 0
}
if f[i] != 0 {
return f[i] == 1
}
if vis[i] || len(g[i]) == 0 {
return false
}
vis[i] = true
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !dfs(j) {
f[i] = -1
return false
}
}
f[i] = 1
return true
}
return dfs(source)
}