Qodana is a code quality monitoring tool that identifies and suggests fixes for bugs, security vulnerabilities, duplications, and imperfections.
Table of Contents
- Qodana Scan
The Qodana Scan GitHub action allows you to run Qodana on a GitHub repository.
To configure Qodana Scan, save the .github/workflows/code_quality.yml file containing the workflow configuration:
name: Qodana
on:
workflow_dispatch:
pull_request:
push:
branches:
- main
- 'releases/*'
jobs:
qodana:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: 'Qodana Scan'
uses: JetBrains/[email protected]Using this workflow, Qodana will run on the main branch, release branches, and on the pull requests coming to your repository.
Note: fetch-depth: 0 is required for checkout in case Qodana works in pull request mode (reports issues that appeared only in that pull request).
We recommend that you have a separate workflow file for Qodana because different jobs run in parallel .
You can set
up GitHub code scanning
for your project using Qodana. To do it, add these lines to the code_quality.yml workflow file right below
the basic configuration of Qodana Scan:
- uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v2
with:
sarif_file: ${{ runner.temp }}/qodana/results/qodana.sarif.jsonThis sample invokes codeql-action for uploading a SARIF-formatted Qodana report to GitHub and specifies the report
file using the sarif_file key.
GitHub code scanning does not export inspection results to third-party tools, which means you cannot use this data for further processing by Qodana. In this case, you must set up baseline and quality gate processing on the Qodana side before submitting inspection results to GitHub code scanning. See the Quality gate and baseline section for details.
You can enforce GitHub to block the merge of pull requests if the Qodana quality gate has failed. To do it, create a branch protection rule as described below:
- Create a new or open an existing GitHub workflow that invokes the Qodana Scan action.
- Set the workflow to run on
pull_requestevents that target themainbranch.
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- mainInstead of main, you can specify your branch here.
- Set the number of problems (integer) for the Qodana action
fail-thresholdoption. - Under your repository name, click Settings.
- On the left menu, click Branches.
- In the branch protection rules section, click Add rule.
- Add
mainto Branch name pattern. - Select Require status checks to pass before merging.
- Search for the
Qodanastatus check, then check it. - Click Create.
You can combine the quality gate, and baseline features to manage your technical debt, report only new problems, and block pull requests that contain too many issues.
Follow these steps to establish a baseline for your project:
- Run Qodana locally over your project:
cd <source-directory>
qodana scan --show-report-
Open your report at
http://localhost:8080/, add detected problems to the baseline, and download theqodana.sarif.jsonfile. -
Upload the
qodana.sarif.jsonfile to your project root folder on GitHub. -
Append
--baseline,qodana.sarif.jsonargument to the Qodana Scan action configurationargsparameter in thecode_quality.ymlfile:
- name: Qodana Scan
uses: JetBrains/[email protected]
with:
args: --baseline,qodana.sarif.jsonIf you want to update the baseline, you must repeat these steps.
After that, the Qodana Scan GitHub action will generate alerts only for the problems that were not added to the baseline as new.
To establish a quality gate additionally to the baseline, add this line to qodana.yaml in the root of your repository:
failThreshold: <number-of-accepted-problems>Based on this, you will be able to detect only new problems in pull requests that fall beyond the baseline. At the same
time, pull requests with new problems exceeding the fail-threshold limit will be blocked, and the workflow will fail.
If you wish to study Qodana reports directly on GitHub, you can host them on your GitHub Pages repository using this example workflow:
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
uses: peaceiris/actions-gh-pages@v3
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
publish_dir: ${{ runner.temp }}/qodana/results/report
destination_dir: ./Hosting multiple Qodana reports in a single GitHub Pages repository is not supported.
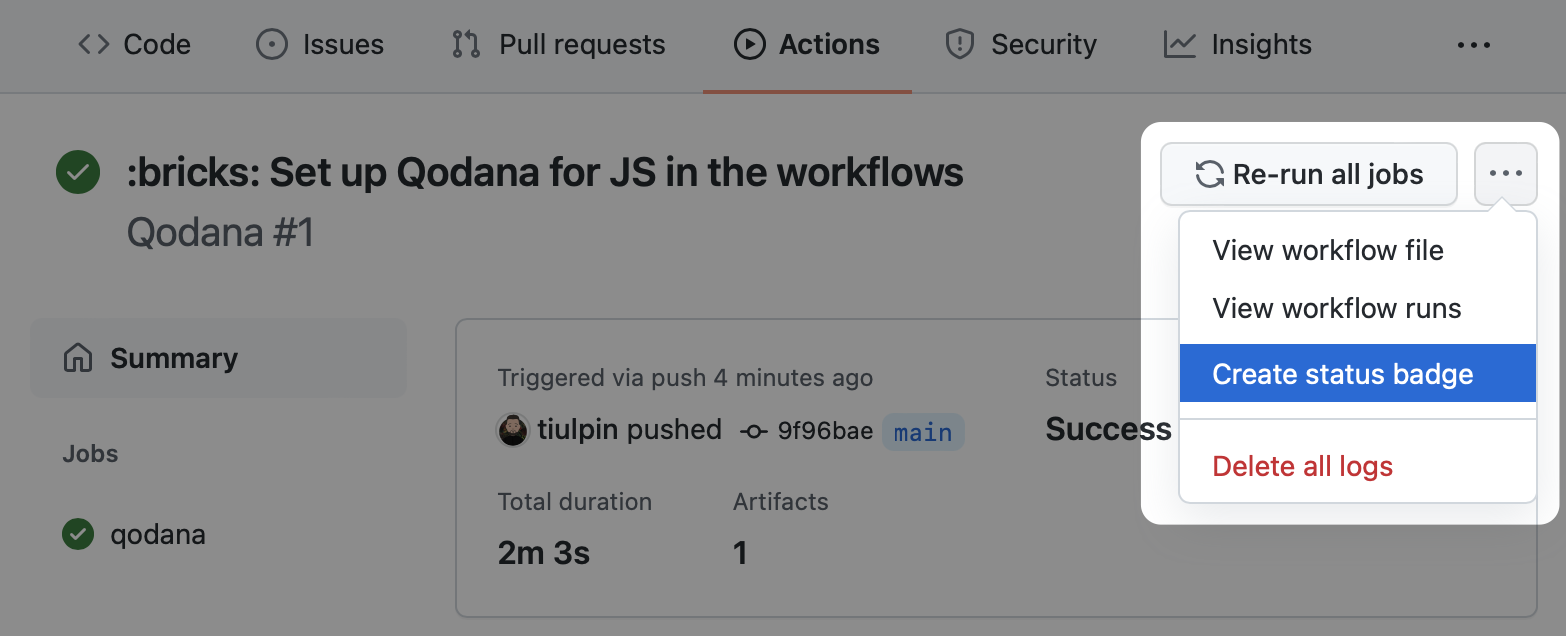
You can set up a Qodana workflow badge in your repository. To do it, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the workflow run that you previously configured.
- On the workflow page, select Create status badge.
- Copy the Markdown text to your repository README file.
Most likely, you won't need other options than args: all other options can be helpful if you are configuring multiple Qodana Scan jobs in one workflow.
Use with to define any action parameters:
with:
args: --baseline,qodana.sarif.json| Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
args |
Additional Qodana CLI scan command arguments, split the arguments with commas (,), for example -i,frontend,--print-problems. Optional. |
- |
results-dir |
Directory to store the analysis results. Optional. | ${{ runner.temp }}/qodana/results |
upload-result |
Upload Qodana results as an artifact to the job. Optional. | true |
artifact-name |
Specify Qodana results artifact name, used for results uploading. Optional. | qodana-report |
cache-dir |
Directory to store Qodana cache. Optional. | ${{ runner.temp }}/qodana/caches |
use-caches |
Utilize GitHub caches for Qodana runs. Optional. | true |
additional-cache-hash |
Allows customizing the generated cache hash. Optional. | ${{ github.sha }} |
use-annotations |
Use annotation to mark the results in the GitHub user interface. Optional. | true |
pr-mode |
Analyze only changed files in a pull request. Optional. | true |
All the issues, feature requests, and support related to the Qodana Azure Pipelines extension are handled on YouTrack.
If you'd like to file a new issue, please use the link YouTrack | New Issue.