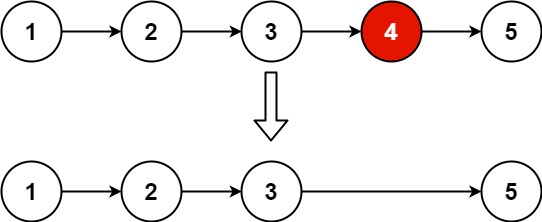
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
思路:增加头节点
过程简单,leetcode一遍过
/**
*看一下链表的定义
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode N = new ListNode();
N.next = head;
ListNode Left = N;
ListNode L = head;
while(L != null){
if(L.val == val){
Left.next = L.next;
L = Left.next;
}
else{
Left = Left.next;
L = L.next;
}
}
return N.next;
}
}★★★★707. 设计链表
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。 addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。 addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。 addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。 deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addAtHead(1);
linkedList.addAtTail(3);
linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回2
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回3
思路:
将MyLinkedList对象看成一个链表,这个链表中需要知道size、头结点head以及各种链表的点结构,
因此还需要再定义链表的点结构对象,点结构对象需要存储值和next指针。
但链表实现
class LinkNode{
int val;
LinkNode next;
public LinkNode(int val){this.val = val;}
}
class MyLinkedList {
public int size = 0;
LinkNode head;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyLinkedList() {
LinkNode L = new LinkNode(-1);
head = L;
}
/** Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. */
public int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) return -1;
LinkNode L = head;
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) { //这里必须使用等号,不然L是当前节点的前序节点
L = L.next;
}
return L.val;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. */
public void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkNode nowNode = new LinkNode(val);
if(head.next!=null){ //如果头结点不为空
LinkNode right = head.next;
nowNode.next = right;
head.next = nowNode;
}
else{
head.next = nowNode;
}
size++;
}
/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */
public void addAtTail(int val) {
//遍历到最后一个
LinkNode L = head;
while(L.next != null){
L = L.next;
}
LinkNode tail = new LinkNode(val);
L.next = tail;
size++;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. */
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index == size){
this.addAtTail(val);
return; //这里必须加return,不然和下面的size++重合导致空指针错误
}
else if (index > size){
return;
}
else if (index <= 0){
this.addAtHead(val);
return;
}
else{
LinkNode left = head;
LinkNode right = head.next;
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){
left = left.next;
//疑问:此时需不需要判断right的next为空 疑问解决,可以为空
right = right.next;
}
LinkNode nowNode = new LinkNode(val);
nowNode.next = right;
left.next = nowNode;
// nowNode.next = left.next;
// left.next = nowNode;
}
size ++;
}
/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) return;
LinkNode L = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
L = L.next;
}
L.next = L.next.next;
size --;
}
}
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj.get(index);
* obj.addAtHead(val);
* obj.addAtTail(val);
* obj.addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj.deleteAtIndex(index);
*/
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
思路:两个指针代表前后 temp表示后指针的next 并不断后移。 ( 一遍过 )
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//边界条件
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode L = head; //代表当前结点
ListNode R = L.next; //代表后续结点
L.next = null; //让头节点的next为空
while (R!=null){
ListNode temp = R.next;
R.next = L;
L = R;
R = temp;
}
return L;
}
}给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode L = head;
ListNode R = head.next;
if (R == null) return head; //边界条件,R为空就无法进行后续操作
//先进行一次交换从而找到头结点在哪里
ListNode temp = R.next;
R.next = L;
L.next = temp;
ListNode res = R; // 表示最终结果的头结点
ListNode pre = L; // 表示该组交换之后的结束
L = temp;
if (temp!=null){
R = temp.next;
}
while (L != null && R != null){
ListNode temp2 = R.next;
pre.next = R; //与上一组交换结果相连
//交换
R.next = L;
L.next = temp2;
pre = L; //更新pre
//到下一组
L = temp2;
if (temp2!=null){
R = temp2.next;
}
}
return res;
}
}给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
**进阶:**你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
思路:要用一趟完成,就需要找到距离结尾为n+1的结点,然后将倒数第n个删除
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
//边界 1 表为空 2 n如果比链表长 3 表的长度为1
if(head == null) return head;
ListNode L = new ListNode();
L.next = head; //空表头 保证能删除第一个节点
ListNode res = L; //最终结果
ListNode R = head;
int count = 1; //计数器 找到相聚为n+1的结点
while(R.next != null){
R = R.next;
if(count == n ){
L = L.next;
}
else{
count++;
}
}
if(count < n) return head; //解决边界2问题
L.next = L.next.next;
return res.next;
}给定两个(单向)链表,判定它们是否相交并返回交点。请注意相交的定义基于节点的引用,而不是基于节点的值。换句话说,如果一个链表的第k个节点与另一个链表的第j个节点是同一节点(引用完全相同),则这两个链表相交。
示例 1:
输入:listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5]
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
思路:遍历找到两个链表的长度,然后让长的链表先走长度差的距离,因为后面相交之后就是完全相同的尾部了,所以走过一段距离之后再同时向后移动,直到最终找到相同的
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//边界条件 空
if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode L1 = headA;
ListNode L2 = headB;
int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;
while(L1 != null){
len1++;
L1 = L1.next;
}
while(L2 != null){
len2++;
L2 = L2.next;
}
ListNode LL1 = len1 > len2 ? headA : headB;
ListNode LL2 = len1 <= len2 ? headA : headB; //LL1代表长的,LL2代表短的
int interval = Math.abs(len1 - len2); //记录长度差
while(LL1 != null && interval-- > 0){
LL1 = LL1.next;//长的先走一个长度差的位置
}
while(LL1 != null && LL2 != null && LL1!= LL2 ){
LL1 = LL1.next;
LL2 = LL2.next;
}
if(LL1==null) return null;
return LL1;
}
}★★★★142. 环形链表 II
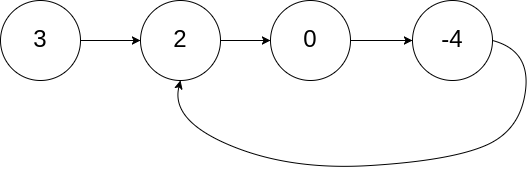
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
思路: 背诵这个思路,因为推导太麻烦。
首先,一个指针走两步,另一个走一步,找到交点。
其次,找到交点之后,一个指针回开头,一个指针不动,同时往前走,就找到了链表入口。
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode low = head;
//边界 是否是环
while(fast != null && fast.next != null && low != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
low = low.next;
if(fast == low){
ListNode L = head;
ListNode R = low;
while(L!=R){
L = L.next;
R = R.next;
}
return L;
}
}
return null;
}
}1、之前困扰的问题一直在于能否让指针为null,如果会用到该指针的next和val的属性,那么不能为空,如果没有用到可以为空
2、链表的虚拟头结点很管用