We provide the code for Neural Manifold ODEs in this repository.
Summary: We introduce Neural Manifold Ordinary Differential Equations, a manifold generalization of Neural ODEs, and construct Manifold Continuous Normalizing Flows (MCNFs). MCNFs require only local geometry (therefore generalizing to arbitrary manifolds) and compute probabilities with continuous change of variables (allowing for a simple and expressive flow construction). We find that leveraging continuous manifold dynamics produces a marked improvement for both density estimation and downstream tasks.
The multi-chart method from our paper (allowing generality) is showcased in the below figure.
Example learned densities, together with baselines, are given below.
| Hyperboloid | Sphere |
|---|---|
 |
 |
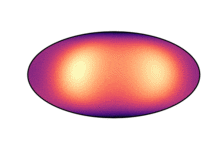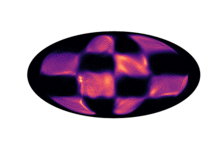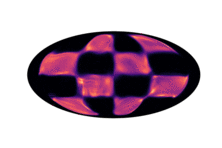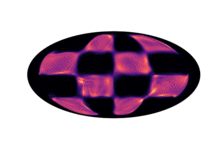
Below we have visualized how our Neural Manifold ODEs learn the 5gaussians and bigcheckerboard densities on the hyperboloid (second and third rows in the hyperboloid figure above), as well as the 4wrapped and bigcheckerboard densities on the sphere (second and third rows in the sphere figure above).
| Hyperboloid Gaussians | Hyperboloid Checkerboard | Sphere Wrapped Normals | Sphere Checkerboard |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
This codebase requires Python 3, PyTorch 1.5+, torchdiffeq (repo here, installed via pip install torchdiffeq), and Cartopy 0.18 (most easily installed via conda conda install -c conda-forge cartopy).
The following command learns a generative flow model for the 5gaussians density on the hyperboloid:
python main_density.py --epochs 300 --dev cuda --lr 1e-2 --dataset 5gaussians --M Hyperboloid --save
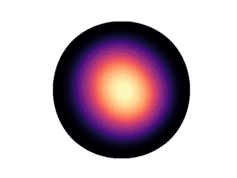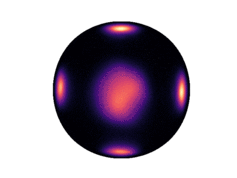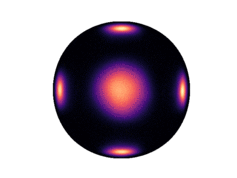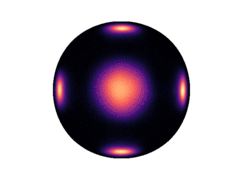
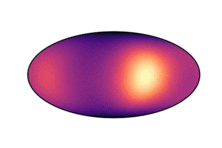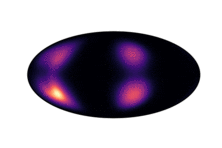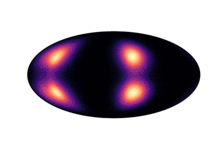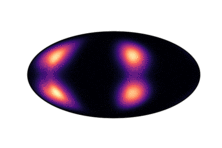
Note that only 200 samples are used per epoch. 5000 epochs were used for the results in the paper. The learned density on the two dimensional hyperboloid is given below (visualized on the Poincaré ball), in comparison with the ground truth density:
| Ground Truth | Ours (100 epochs) | Ours (300 epochs) |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Observe that even after 300 epochs (only 60,000 samples), our model approaches the groundtruth. In general, we found that our method was substantially more sample efficient than the baselines (by nearly an order of magnitude).
All options are given below:
usage: main_density.py [-h] [--lr LR] [--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY]
[--dataset DATASET] [--epochs EPOCHS]
[--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--num_drops NUM_DROPS]
[--flow_hidden_size FLOW_HIDDEN_SIZE] [--save]
[--conc CONC] [--dev DEV] [--M {Hyperboloid,Sphere}]
[--contsave] [--save_freq SAVE_FREQ]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--lr LR
--weight_decay WEIGHT_DECAY
--dataset DATASET for hyperboloid: 1wrapped | 5gaussians |
bigcheckerboard | mult_wrapped, for the sphere:
1wrapped | 4wrapped | bigcheckerboard
--epochs EPOCHS
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
--num_drops NUM_DROPS
number of times to drop the learning rate
--flow_hidden_size FLOW_HIDDEN_SIZE
Hidden layer size for flows.
--save Save a visualization of the learned density
--conc CONC Concentration of vMF
--dev DEV
--M {Hyperboloid,Sphere}
--contsave Continuously save intermediate flow visualization in
contsave/
--save_freq SAVE_FREQ
frequency of continuous saving of intermediate flows
If you use this code or our results in your research, please cite:
@misc{lou2020neural,
title={Neural Manifold Ordinary Differential Equations},
author={Aaron Lou and Derek Lim and Isay Katsman and Leo Huang and Qingxuan Jiang and Ser-Nam Lim and Christopher De Sa},
year={2020},
eprint={2006.10254},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={stat.ML}
}
